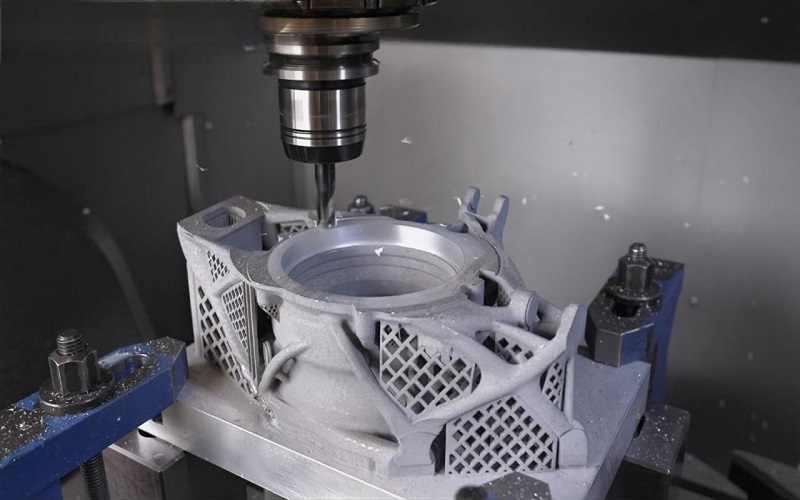
Why choose aluminum for 3D printing? This guide covers the benefits, uses, and costs of 3D printer aluminum. Learn how automotive and aerospace industries use its lightweight and strong properties.
Understanding Aluminum for 3D Printing
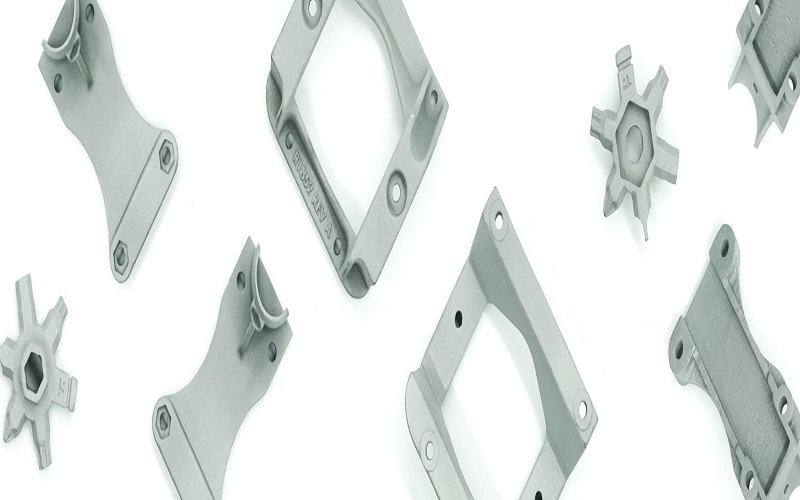

Aluminum is renowned for its excellent aluminum strength-to-weight ratio, making both aluminum alloys and pure forms a go-to material in the realm of 3D printing. This unique property allows for the production of lightweight yet robust components, which are crucial in industries where weight and superior strength are paramount, such as automotive and aerospace.
This high strength-to-weight ratio not only reduces weight but also enhances performance and efficiency, demonstrating impressive tensile strength and ultimate strength, further improved through heat treatment processes that optimize durability and structural integrity.
One of aluminum’s standout qualities is its exceptional corrosion resistance. This property ensures that 3D-printed aluminum parts have a prolonged operational life, even in harsh environments.
Additionally, aluminum exhibits high thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for applications that require efficient heat dissipation and electrical performance, such as heat sinks and wiring.
Together, these material properties make both aluminum forms a versatile and valuable material for 3D printing, enhanced by heat treatment for superior performance.
Dimensions and Build Volume for Aluminum 3D Prints
When it comes to 3D printing aluminum, the available resolutions and build volumes cater to a wide range of needs. High-resolution printing (20 μm) allows for maximum dimensions of approximately 3.8 in. x 3.8 in. x 3.7 in., with a minimum feature size of 0.015 in. This level of precision is ideal for intricate parts requiring fine details and density.
On the other hand, normal resolution (30 μm) can handle larger parts up to 9.6 in. x 9.6 in. x 13.0 in., making it suitable for more substantial components. For even larger projects, the build volume for large aluminum 3D-printed parts extends to 31.5 in. x 15.7 in. x 19.7 in.
These varying capacities highlight the versatility of aluminum 3D printing, allowing for both intricate small-scale parts and large structural components. This diverse range of flexibility is crucial for addressing different industry needs, from detailed prototypes to significant functional parts.
Applications of 3D-Printed Aluminum in Various Industries
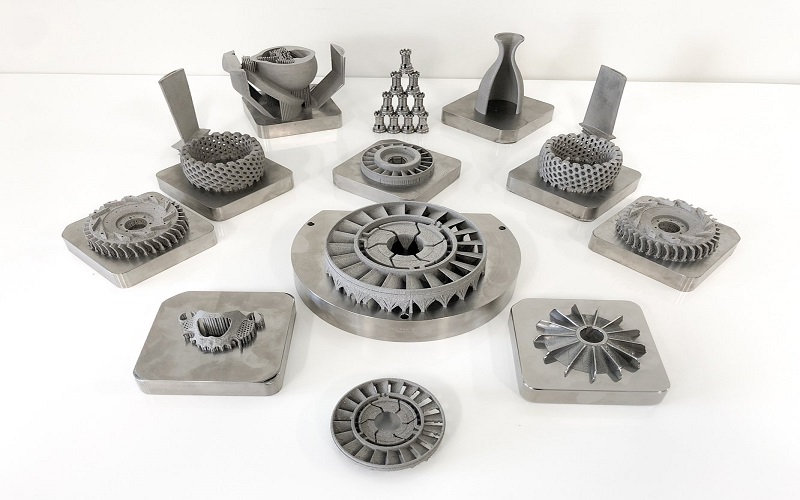

The automotive and aerospace industries have been at the forefront of adopting 3D-printed aluminum, leveraging its low density for enhanced performance. In the automotive sector, companies like Bugatti have showcased the technology’s potential by using it to manufacture brake calipers for high-performance vehicles like the Chiron.
Another automotive manufacturer managed to reduce the weight of their vehicle components by 30% using 3D-printed aluminum parts, demonstrating significant improvements in efficiency and performance due to aluminum’s low density and heat tolerance.
In aerospace, the benefits of aluminum’s strength-to-weight ratio are even more pronounced. Aerospace companies have successfully produced complex components such as turbine blades and brackets using 3D printing, significantly reducing assembly times and enhancing fuel efficiency. Giants like Airbus and Boeing have adopted lightweight aluminum components, capitalizing on their heat tolerance to withstand high-temperature environments and lower melting point for easier processing, to improve overall performance and reduce emissions.
Beyond automotive and aerospace, aluminum 3D printing is making waves in various other industries. From marine applications to consumer goods, the material’s low density and durable nature are being leveraged to create innovative products.
For instance, corrosion-resistant aluminum, with its lower melting point, is ideal for marine environments, while its strength, heat tolerance, and lightweight properties are perfect for manufacturing bike frames and drone bodies.
Comparing Aluminum Alloys for 3D Printing
Aluminum alloys play a critical role in 3D printing, providing a balance of strength, weight, and corrosion resistance that makes them suitable for diverse applications. The comparison of these alloys often involves analyzing:
- Elemental composition
- Thermal and electrical conductivity
- Weight
- Corrosion resistance
- Alloying elements
- Machinability.
Let’s delve into some of the most commonly used aluminum alloys in 3D printing.
AlSi10Mg Alloying elements
AlSi10Mg is a standout aluminum alloy in the 3D printing world, known for:
- Excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and lightweight characteristics
- High fluidity, which ensures enhanced print quality and reduces the likelihood of defects during the printing process
- Good ductility, improving the toughness of the final 3D-printed components
Moreover, AlSi10Mg can withstand high thermal cycles, making it suitable for applications in high-temperature environments. Its properties make it a favorite in the automotive and aerospace industries, where lightweight yet durable magnesium parts are crucial.
Other Popular Aluminum Alloys
Other notable aluminum alloys used in 3D printing include:
- A20X: Designed specifically for additive manufacturing, offers impressive tensile and yield strength.
- AlSi7Mg: Recognized for its versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- 6061
- 7075.
Alloys like 6061 and 7075 are also popular due to their excellent mechanical properties. Alloy 6061 is known for its machinability and weldability, making it ideal for structural applications.
Meanwhile, 7075 aluminum alloy is renowned for its high strength and is commonly used in aerospace applications, providing robust performance in demanding environments.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity of 3D-Printed Aluminum
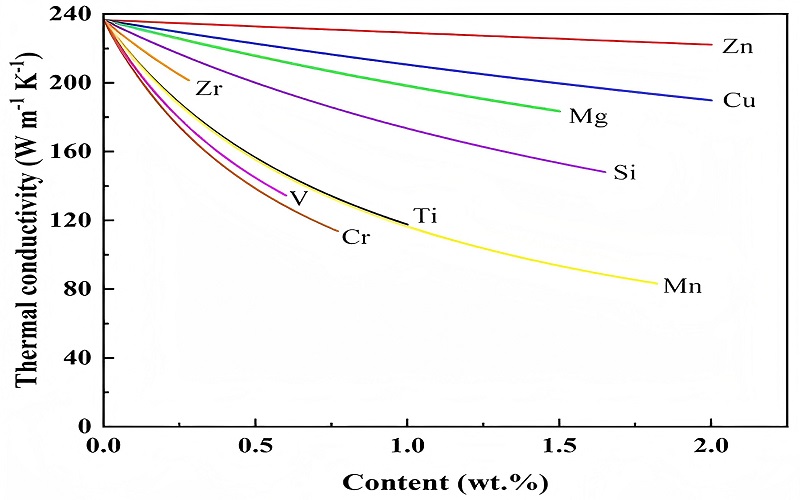
Aluminum’s thermal conductivity, approximately 210 W/m-K, enables it to effectively dissipate heat, which is essential in applications like heat sinks and heat exchangers. This high thermal conductivity makes aluminum an ideal material for components that need to withstand high temperatures and manage heat efficiently.
In terms of electrical conductivity, aluminum performs admirably, surpassing titanium but offering only 64% of copper’s conductivity. This makes aluminum and titanium the preferred choice for electrical wiring and components, combining decent conductivity with the benefits of low weight and good conductivity.
Corrosion Resistance of 3D-Printed Aluminum
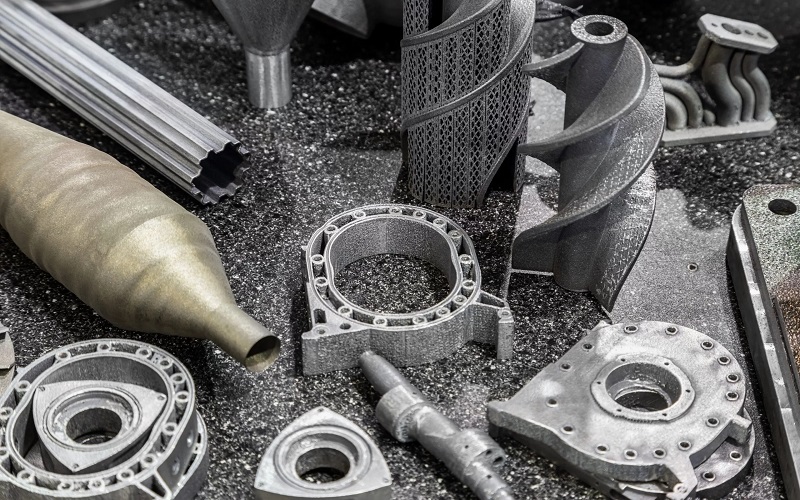

One of the remarkable properties of aluminum is its natural ability to resist corrosion. This is achieved through the formation of a protective oxide layer when exposed to air, which shields the material from corrosive elements. This inherent corrosion resistance aluminum is a significant advantage in extending the durability and longevity of 3D-printed aluminum parts that may also benefit from zinc, primarily composed of aluminum with trace elements to enhance its properties.
AlSi10Mg alloy, in particular, is widely used in 3D printing for its high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, as well as its higher hardness and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for applications like surgical instruments where precision and durability are critical.
Post-processing techniques like anodizing can further enhance the surface properties and corrosion resistance of machined aluminum, ensuring that components, such as those used in surgical instruments, remain durable and reliable in various environments.
Machinability and Post-Processing Options
The machinability of aluminum is one of its key advantages in 3D printing. Processes such as:
- Milling
- Turning
- Drilling allow for achieving precise shapes and dimensions. The efficiency of these machining processes depends on factors like:
- Cutting speed
- Tool material
- Effectiveness of coolant applications.
Post-processing is equally critical in achieving high-quality finishes and precise dimensions in 3D-printed aluminum. Using carbide tools can enhance wear resistance when machining aluminum, though proper selection is crucial to avoid brittleness. These post-processing steps ensure that the final product meets the required specifications and performs optimally in its intended application.
Cost Considerations for 3D Printing with Aluminum
Cost is a critical factor when choosing materials for 3D printing and material selection plays a vital role. Aluminum alloys are increasingly favored in additive manufacturing due to their balance of low cost and excellent mechanical properties.
Compared to titanium, aluminum is significantly more affordable, making it accessible for budget-conscious projects, despite the higher cost of some alternatives.
The affordability of aluminum impacts manufacturing decisions, especially for large-scale applications. Aluminum’s cost-effectiveness is further enhanced by its excellent machinability, which facilitates easier post-processing compared to titanium.
This makes aluminum a suitable material for both prototyping and production, ensuring cost-effectiveness without compromising quality.
Environmental Impact of Aluminum 3D Printing
The environmental impact of aluminum 3D printing is a growing concern. Key factors include:
- The sourcing and disposal of materials, which play a significant role in environmental sustainability.
- Implementing sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials.
- Employing efficient production methods to minimize waste.
Advancements in aluminum 3D printing technology aim to improve sustainability, including the development of biodegradable materials. By focusing on recycling and reducing waste, the industry can mitigate its environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Case Studies of Aluminum 3D Printing

Real-world case studies highlight the practical advantages of aluminum 3D printing. For instance, a startup used aluminum 3D printing to develop custom tooling, leading to a 40% cost reduction in production processes. This showcases the potential for significant cost savings and efficiency improvements in manufacturing.
Consumer goods also benefit from aluminum’s lightweight and durable nature. Aluminum applications such as bicycle frames and carbon drone bodies demonstrate the versatility and practicality of aluminum 3D printing in creating innovative products.
These case studies underscore the transformative impact of aluminum 3D printing across various industries.
Future Trends in Aluminum 3D Printing
Looking ahead, the future of aluminum 3D printing is bright. Developments will focus on creating specialized metal alloys that enhance the strength and lightweight characteristics of components. The integration of artificial intelligence in the design process is expected to facilitate more intricate and optimized geometries in aluminum parts.
Hybrid manufacturing methods that combine 3D printing with traditional subtractive techniques are emerging as a trend to improve the manufacturing process efficiency. Additionally, the accessibility of aluminum 3D printing services is increasing through the expansion of online quoting and service platforms.
These advancements point to a future where aluminum 3D printing plays an even more significant role in manufacturing.

Summary
In summary, aluminum 3D printing offers a multitude of advantages, from its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance to its thermal and electrical conductivity. The material’s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, marine, and consumer goods.
As we look to the future, advancements in aluminum 3D printing technology and sustainable practices will continue to drive innovation and efficiency.
Embracing these developments will ensure that 3D printing with aluminum remains at the forefront of manufacturing, offering endless possibilities for creating high-performance components.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes aluminum a popular choice for 3D printing?
Aluminum’s excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and high thermal and electrical conductivity make it a highly versatile choice for 3D printing applications. These properties enhance the performance and durability of printed components.
How does aluminum 3D printing benefit the automotive and aerospace industries?
Aluminum 3D printing significantly benefits the automotive and aerospace industries by enabling the creation of lightweight yet durable components, which enhances performance and efficiency. This technological advancement contributes to the overall advancement of these critical sectors.
What are the cost considerations when 3D printing with aluminum?
Cost considerations when 3D printing with aluminum include its affordability compared to titanium, which makes it suitable for budget-conscious projects, and its excellent machinability that further enhances cost-effectiveness.
How does aluminum 3D printing impact the environment?
Aluminum 3D printing can significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing recycled materials and minimizing waste. Implementing sustainable practices is essential for maximizing these benefits.
What future trends can we expect in aluminum 3D printing?
You can expect future trends in aluminum 3D printing to include the development of specialized alloys, the integration of AI in design processes, and the adoption of hybrid manufacturing methods to improve production efficiency. These advancements will likely lead to more innovative applications and enhanced performance in various industries.

