Want to know the 5 key prototyping phases that turn ideas into successful products? This article covers each phase, from ideation to final launch, explaining their importance in product development.
Ideation and Concept Modeling
The ideation and concept modeling stage is the birthplace of innovative ideas and creative solutions. This phase is crucial because it:
- Generates numerous ideas and potential solutions, providing a strong foundation for the entire product development process.
- Employs diverse brainstorming techniques to foster creativity and lead to a wide array of concepts that can be explored.
- Involves an iterative process, which is the essence of the design thinking process, encouraging as many ideas as possible to address the design challenge at hand.
Low-fidelity prototypes help explore the solutions identified in the ideation phase. These early models are crucial for understanding product limitations and user interactions within the problem space. A solution based approach to quick concept testing enables teams to assess feasibility and gather valuable user feedback for subsequent problem solving stages, especially when addressing complex problems.
Prototyping in the ideation phase aims to test concepts swiftly to gauge feasibility and user response. These initial models highlight critical product aspects that guide further refinement during the prototyping phases. This phase is rich with potential, transforming numerous ideas into tangible concepts for further exploration.
Rapid Prototyping Techniques
Rapid prototyping techniques are the lifeblood of the ideation phase, allowing teams to quickly and efficiently iterate on designs. The goal here is to identify the best possible innovative solutions and various solutions for each identified problem.
Inexpensive prototypes allow teams to explore key solutions from the ideation phase without significant resource commitment. Techniques like 3D CAD modeling help designers visualize and iterate on concepts, blending technological and aesthetic elements before physical creation.
Additionally, employing ideation techniques can enhance the creative process during this phase to create solutions, often guided by frameworks like the design thinking model (a human-centered approach emphasizing empathy, ideation, and iterative testing to solve problems creatively).
3D printed or machined materials are commonly used for plastic parts, enabling the creation of multiple prototypes to test various design aspects. This iterative process, often structured as a linear process (a sequential approach where each stage, from ideation to prototyping to testing, builds on the previous one), refines the initial prototype and deepens the understanding of product limitations and user interactions.
Customer feedback gathered during this third stage can drive future iterations and lead to the development of a successful final prototype.
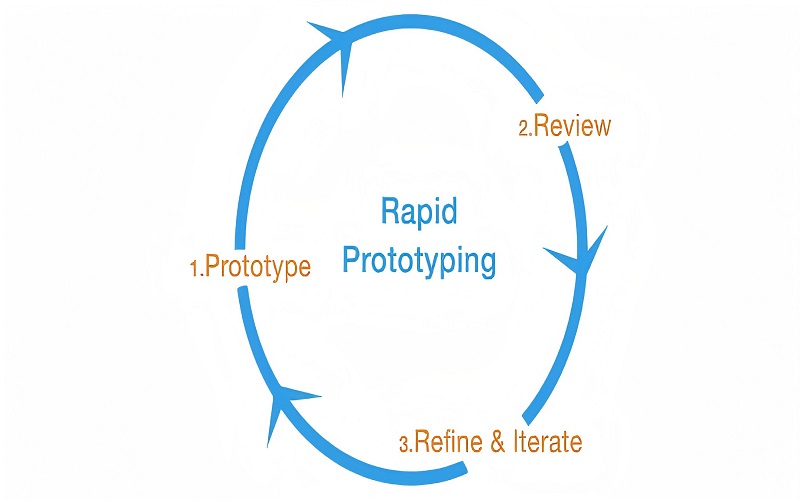
Visual Prototypes
Visual prototypes are powerful tools for bridging the gap between technical teams and non-technical stakeholders. They are utilized to effectively convey ideas and concepts to stakeholders who may lack technical expertise, ensuring that everyone has a clear personal understanding of the concepts being presented.
This alignment is crucial during the first stage of product development, where concepts are conceptualized and shared to establish a common ground. By using inexpensive materials, these prototypes can be created quickly and cost-effectively, making them ideal for early-stage ideation and feedback.
Gathering new insights from visual prototypes allows for early feedback that can influence design choices and improve the product outcome. By presenting a tangible representation of the innovative ideas and creative solutions generated during the ideation phase, visual prototypes facilitate user testing and feedback, which are critical for refining the design.
Ultimately, visual prototypes serve as a bridge that enhances communication and aligns vision, paving the way for a successful product development journey.
Alpha Prototyping
Alpha prototyping is where the rubber meets the road in the design thinking process. This phase focuses on developing functional prototypes that test feasibility and functionality, including the mechanical properties of materials to ensure durability and performance.
It’s an iterative process involving rigorous testing and modifications to gather feedback about the design. Activities such as swapping components and making design modifications are common, allowing teams to refine the prototype based on real-world feedback, often incorporating metal parts for enhanced structural integrity.
Early feedback gathered through visual prototypes in the previous stages allows teams to refine concepts for a deeper understanding before extensive development, addressing pain points identified during user interactions. Custom circuit boards, for instance, are an integral part of integrating electronic components into prototypes, assembled by shop technicians and engineers in the prototyping lab for more detail.
This stage is all about testing early and often to ensure that the first prototype meets user needs and expectations during the five stages of the design thinking process, including the define stage, test stage, prototyping stage, and key stages of development, to challenge assumptions in earlier stages, early prototypes, the previous stage, and the empathize stage in early stages. The prototype stage is crucial for refining ideas for real users.
Detailed CAD Designs
Detailed CAD designs are the backbone of alpha prototyping. These designs are crucial for mapping out both technological and aesthetic aspects prior to physical production. CAD software allows for precise manipulation of design elements, ensuring that the product is refined and ready for manufacturing.
The iterative prototyping process involves creating multiple T1 samples, allowing for continuous improvement of the product until it meets specifications. By ensuring that products are aligned with both functionality and aesthetic considerations, detailed CAD designs play a pivotal role in the successful development of high fidelity prototypes.
Material Selection
Material selection is a critical aspect of the alpha prototyping phase. Choosing the right materials ensures that prototypes meet specific performance and durability standards.
This careful selection process is essential for ensuring that the prototypes fulfill performance and specification requirements, setting the stage for successful product development.
Beta Prototyping

Beta prototyping is the last step before manufacturing, focusing on refining prototypes for marketing and technical evaluation. Creating multiple beta prototypes allows for thorough testing and improvements. Parts are sanded, painted, and decals added to closely resemble finished products, preparing them for mass production.
The prototyping phase aims to uncover issues in the design before mass production, optimizing the design for manufacturability and cost-efficiency, as outlined in the problem statement. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the final product is not only functional but also appealing to the target market.
Functional Testing
Functional testing in beta prototyping assesses a prototype’s functionality and regulatory compliance. This phase evaluates adherence to industry standards, durability, and functionality, identifying design flaws that need addressing before full-scale production.
By testing early and often, teams can ensure that the prototype meets user needs and expectations, paving the way for a successful product. This process helps in refining the prototype based on user feedback and creating prototypes that truly resonate with the target audience.
Iterative Improvements
Iterative improvements define a successful beta prototyping phase, involving:
- Continuous enhancements based on user feedback and test results
- Ensuring alignment with user expectations
- Focusing on refining prototypes to enhance usability and functionality.
Based on the learnings from the testing phase, improvements should be made to the prototype to address any identified issues. This cycle of testing and refining continues until the prototype meets all necessary criteria, ensuring a successful product launch.
Pre-Production Prototyping

Pre-production prototyping transforms ideas into tangible forms for testing and feedback. This phase ensures that the final design meets user needs. Multiple manufacturing iterations refine the product, verifying the assembly process through T1 samples.
Feedback ensures that the final design aligns with user expectations before full user centered design product development. This design process focuses on perfecting the design and preparing for large-scale production.
Manufacturing Tooling
Manufacturing tooling is critical in pre-production prototyping, significantly impacting manufacturing efficiency and quality. Creating jigs and tooling enhances production efficiency and maintains product quality.
Selecting suitable materials and manufacturing methods produces durable advanced tools that withstand production rigors, ensuring a smooth and efficient transition to mass production.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance checks in pre-production detect and address defects before large-scale manufacturing. Implementing quality control procedures maintains product standards during production, ensuring a successful final product.
Production and Launch

In the production phase, the final product is created, with all components ready for market introduction. Quality assurance procedures maintain product standards, ensuring the existing products meet specified design and performance criteria. Regular inspections identify defects before market release, ensuring a successful launch.
Beta prototypes are utilized to evaluate market interest and technical performance, providing valuable insights for the final product launch. This phase focuses on creating a finished product that is ready to hit the store shelf and capture the target users’ interest.
Final Prototype Product Testing
Comprehensive product testing is essential to verify that the final product fulfills all specified design and performance standards. This testing ensures that the final solution meets user needs and expectations for the end user, paving the way for a successful product launch with effective test solutions.
Market Readiness
Finalizing marketing strategies and distribution plans ensures a seamless product launch, effectively reaching the target audience and leading to success.
Summary
Summarize the key points covered in the blog post, highlighting the importance of each prototyping phase in the product development process.
Conclude with an inspiring phrase that encourages the reader to implement the discussed strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the ideation phase in prototyping?
The ideation phase is essential for generating a wide array of ideas and potential solutions, establishing a robust foundation for the product development process. This collaborative approach ensures that diverse perspectives contribute to innovative outcomes.
Why are visual prototypes important in the design thinking process ?
Visual prototypes are essential in the design process as they clearly communicate ideas to stakeholders, facilitate early feedback, and align the team’s vision, ultimately leading to a more successful product development outcome.
What is the role of alpha prototyping?
Alpha prototyping plays a crucial role in evaluating the feasibility and functionality of a design through the creation of functional prototypes, which undergo rigorous testing and modifications to gather valuable insights. This process helps identify issues early, ensuring a more refined final product.
How does functional testing contribute to beta prototyping?
Functional testing is essential for beta prototyping as it evaluates the prototype’s functionality and ensures compliance with regulatory standards, thereby identifying design flaws that must be rectified before proceeding to full-scale production. This process enhances the overall quality and reliability of the final product.
Why is quality assurance important in pre-production prototyping?
Quality assurance is crucial in pre-production prototyping as it identifies and resolves defects early, ensuring that product standards are upheld before large-scale manufacturing begins. This proactive approach helps maintain quality throughout the production process.