Choosing between PET and PETG involves understanding their differences, particularly in the context of PET vs PETG.
PET is strong and clear, perfect for food packaging, while PETG is flexible and impact-resistant, making it suitable for 3D printing and medical uses.
This article will cover their properties, uses, and environmental impacts, helping you decide which material is right for your project.
What Is Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)?

Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a widely used plastic material known for its high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and outstanding clarity.
Typical PET structure allows it to be used extensively in food packaging, beverage bottles, soap dispensers, and other materials requiring durability and product visibility.
Its clarity and strength ensure the safety and integrity of the contents, while PET filament and PET composite filaments serve industrial needs in 3D printing and manufacturing.
Moreover, PET is widely recycled and promotes sustainability by being transformed into recycled PET fibers or resin, effectively reducing environmental impact within the recycling stream.
What Is Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)?
PETG, or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, is a versatile thermoplastic known for its clarity, flexibility, and impact resistance.
PETG is widely used in applications such as 3D printing, medical packaging, food containers, and signage due to its food-safe properties, excellent chemical resistance, and ability to be easily injection molded.
Its polymer chains are arranged randomly, unlike the semi-crystalline polymers structure of PET, which contributes to PETG’s flexibility and impact resistance.
Additionally, PETG can absorb moisture to a lesser extent than PET, making it easier to maintain higher ambient temperatures during processing and printing.
Overall, PETG plastic combines the benefits of clarity, toughness, and processability, making it a preferred choice for mid-range temperature applications that require both strength and flexibility.

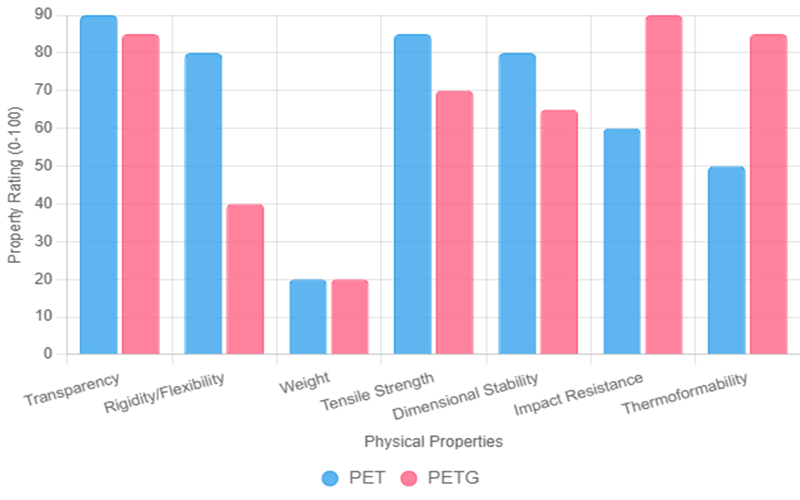
Main Properties Of PET And PETG
PET is a tough, non-toxic thermoplastic with low water absorption and good resistance to weak acids and organic solvents.
Its semi-crystalline nature causes a slightly higher working temperature than PETG and limits prolonged exposure to hot water or alkaline substances.
PET offers excellent electrical insulation but has reduced resistance to corona discharge due to its crystalline structure.
PETG is a glycol-modified PET where some ethylene glycol monomers are replaced with CHDM glycol units.
This change creates an amorphous polymer with randomly arranged chains, making PETG more flexible and impact resistant.
PETG is highly transparent, chemically resistant to household detergents, dilute acids, and alkalis, and provides a strong oxygen and carbon dioxide barrier.
Its melting point (180°C–200°C) allows excellent processability for injection molding and 3D printing.
While both share the same acid and glycol monomers, PETG’s glycol modification gives it unique physical properties and processing benefits, suiting different industrial and consumer uses.
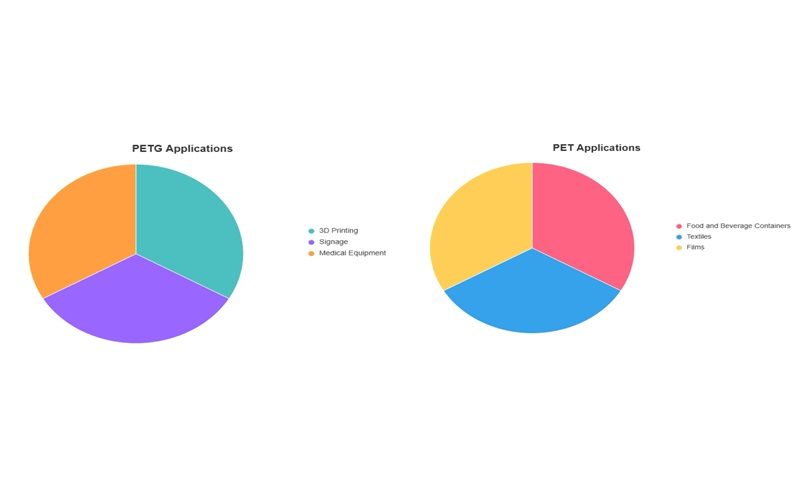
PET vs PETG: Application
PET and PETG serve distinct purposes due to their unique chemical properties and physical characteristics.
PET plastic, characterized by its semi-crystalline polymer chains and high tensile strength, is widely used in food and beverage containers such as water bottles, as well as in textiles like polyester fabrics and various electrical devices.
Its excellent chemical resistance and rigidity make it ideal for applications requiring durability, clarity, and thermal resistance.

Conversely, PETG, a modified version of PET with glycol additive incorporated into its polymer chain, transforms the material into an amorphous PETG polymer with polymer chains arranged randomly.
This chemical modification enhances PETG’s flexibility, impact resistance, and ease of processing, making it a preferred choice for 3D printing, medical packaging, signage, and other applications demanding toughness and aesthetic versatility.
PETG’s improved thermoformability and reduced susceptibility to stress cracking compared to PET allow for more complex shapes and designs through injection molding.
Both materials are produced using the same monomers—acid monomers and glycol monomers—but the substitution of ethylene glycol with CHDM glycol units in PETG alters its chemical structure and physical properties significantly.
While PET is favored for rigid, high-strength applications with stringent packaging needs, PETG excels in projects requiring flexibility and resistance to impact and extreme adhesion during processing.
By understanding these key differences in chemical structures, material properties, and application suitability, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize product performance, durability, and environmental sustainability.
PET vs PETG: Recycling And Environmental Impact
PET is widely recycled, benefiting from well-established recycling streams and infrastructure that efficiently transform used bottles and packaging into new products such as textiles, containers, and fibers.
This extensive recyclability makes PET generally considered an environmentally friendly option, significantly reducing plastic waste and conserving resources.
In contrast, PETG, while recyclable, presents more challenges due to its glycol-modified amorphous structure and the presence of other additives, which complicate the recycling stream and require specialized facilities that are less common.
As a result, PETG often experiences lower recycling rates and limited reuse opportunities.
However, PETG’s superior impact resistance and flexibility make it valuable in specialized applications like medical packaging and 3D printing, where its durability can contribute to longer product lifespans and potentially reduce environmental impact when managed properly.
Overall, while both materials are durable and useful, PET’s semi crystalline PET nature and broader recyclability give it an edge in sustainability, especially in large-scale food packaging and other materials with high volume usage.

The Differences Between PET And PETG
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) differ primarily in their chemical composition and properties.
PET is rigid, strong, and highly transparent, making it ideal for applications like beverage bottles and textiles.
PETG, modified with glycol, offers greater flexibility, impact resistance, and ease of thermoforming, suiting it for 3D printing and medical packaging.
While PET excels in recyclability and cost-effectiveness, PETG provides superior durability and processing versatility for specialized uses.
Understanding these differences can guide you in selecting the right same material based on your specific needs.

How To Choose Between PET And PETG?
Selecting the right material between PET and PETG hinges on the specific requirements of your project.
PET is the preferred choice for applications demanding high strength, rigidity, and excellent recyclability, making it ideal for food-grade containers, textiles, and other packaging needs where durability and environmental friendliness are priorities.
Its semi-crystalline PET structure provides superior thermal resistance and mechanical properties compared to its totally amorphous counterpart, PETG.
Additionally, recycled PET contributes significantly to reducing plastic waste within the recycling stream, highlighting its environmental benefits.
On the other hand, PETG, known for its amorphous structure and glycol modification, represents a versatile alternative with enhanced flexibility and superior impact resistance.
This modified version of PET plastic incorporates CHDM glycol units, which disrupt crystalline regions and improve processability.
PETG excels in 3D printing, medical packaging, and signage applications that require toughness, aesthetic versatility, and easier thermoforming.
Its reduced susceptibility to moisture absorption allows for maintaining higher ambient temperatures during processing, improving print quality and durability.
When deciding, consider key factors such as low cost, processing parameters—including following PETG parameters for optimal results—mechanical resistance, and environmental impact to ensure you select the material that best matches your application’s demands.
It is important to note that not all glycols used in these polymers have the same effects, and the substitution of ethylene glycol with different glycol monomers plays a crucial role in defining the physical properties of these two polymers.

