This article delves into the detailed comparison of Polypropylene and Polystyrene, two widely used thermoplastic polymers, to determine which material best suits your needs based on their unique properties, applications, and performance under various conditions.
What Is Polypropylene (PP)?
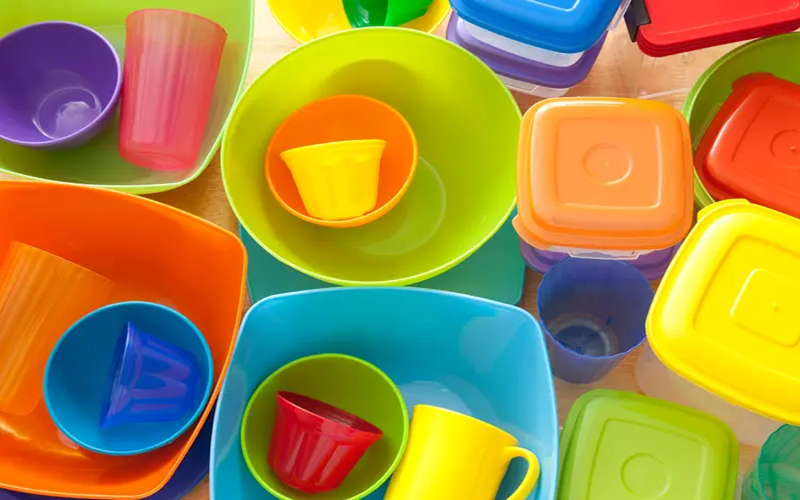
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer derived from propylene monomers, widely used for its durability, lightweight properties, and excellent chemical resistance.
With a semi-crystalline structure featuring crystalline regions, it exhibits outstanding mechanical properties including high tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility.
PP has a relatively high melting point of around 160°C, which contributes to its superior heat resistance compared to many other plastics.
Commonly found in food packaging, automotive parts, medical containers, and laboratory equipment, PP is valued for its recyclability and cost-effective production.
Its moisture-wicking properties and resilience make it a popular choice in the textile industry, especially for polypropylene fibers used in thermal clothing and sportswear.
Additionally, PP is widely used in manufacturing dishwasher safe food containers and disposable syringes.

What Is Polystyrene (PS)?
Polystyrene (PS) is a versatile synthetic polymer derived from styrene, widely recognized for its clarity, lightweight and economical solutions, and cost-effectiveness.
It is commonly used in its rigid form for packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation boards, as well as in expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam for protective packaging and construction materials.
Polystyrene generally offers excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for clear protective packaging and even optical devices.
Its malleability when heated allows for molded packaging and complex packaging needs, including the production of model assembly kits and other consumer products.
Despite its many advantages, PS is a brittle material with lower heat resistance compared to polypropylene, limiting its use in high-temperature applications.
It also exhibits poor chemical resistance and limited recyclability, contributing to concerns over plastic pollution.
Polystyrene’s capacity for insulation and lightweight properties makes it popular in the food service sector and insulation boards, but careful disposal is necessary due to environmental impact.

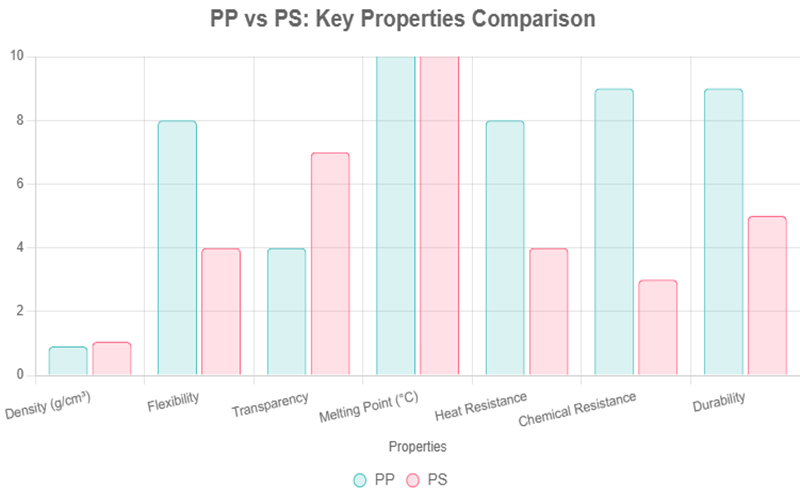
PS vs PP: Key Properties Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) and Polystyrene (PS) are two widely used plastics with distinct properties that influence their suitability for various applications.
Mechanical Properties
When comparing polypropylene vs polystyrene, mechanical properties play a crucial role in determining their suitability for various applications.
Polypropylene exhibits good tensile strength, high impact resistance, and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for products that require durability and repeated use.
It also exhibits good resistance to fatigue and stress cracking, which enhances its longevity in demanding environments.
In contrast, polystyrene is a brittle material with lower impact resistance and tensile strength, making it more prone to cracking and breaking under stress.
However, its rigidity and ease of molding make it suitable for disposable items and applications where shape retention is important.
These differences polypropylene exhibit highlight why polypropylene is favored in automotive parts and reusable containers, whereas polystyrene is commonly used for disposable cutlery and packaging.
Heat Resistance
When comparing polypropylene vs polystyrene, heat resistance is a critical factor that influences their application.
Polypropylene boasts a higher melting point, typically around 160°C, allowing it to withstand higher temperatures without significant deformation.
This exceptional resistance makes PP ideal for applications such as dishwasher-safe food containers and automotive parts exposed to heat.
In contrast, polystyrene has a lower melting point, generally near 100°C, which limits its use in high-temperature environments.
Its lower heat resistance means PS can undergo significant deformation when exposed to elevated temperatures, restricting its suitability to disposable items and packaging that do not require heat tolerance.
Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance is a crucial factor when comparing polypropylene vs polystyrene.
Polypropylene exhibits exceptional resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including strong alkalis like sodium hydroxide, which makes it highly suitable for laboratory equipment, medical containers, and automotive components exposed to harsh substances.
Its molecular structure provides stability against chemical reactions and significant degradation, ensuring durability in demanding environments.
In contrast, polystyrene generally has poor chemical resistance, especially to solvents and acids, which limits its use in applications where exposure to such chemicals is frequent.
This difference in chemical resistance significantly influences the choice between these two versatile polymers for various industrial and consumer applications.
Moisture Resistance
Both polypropylene and polystyrene exhibit low moisture absorption, making them excellent choices for applications where moisture resistance is critical.
Polypropylene’s semi-crystalline structure contributes to its superior moisture resistance, preventing water penetration and maintaining its mechanical properties even in humid environments.
This makes PP ideal for food packaging and medical containers that require hygiene and durability. Polystyrene, while also resistant to moisture, is more prone to brittleness when exposed to prolonged moisture or environmental stress.
Despite this, its low water absorption still allows for effective use in insulation boards and disposable food service items where moisture exposure is limited.
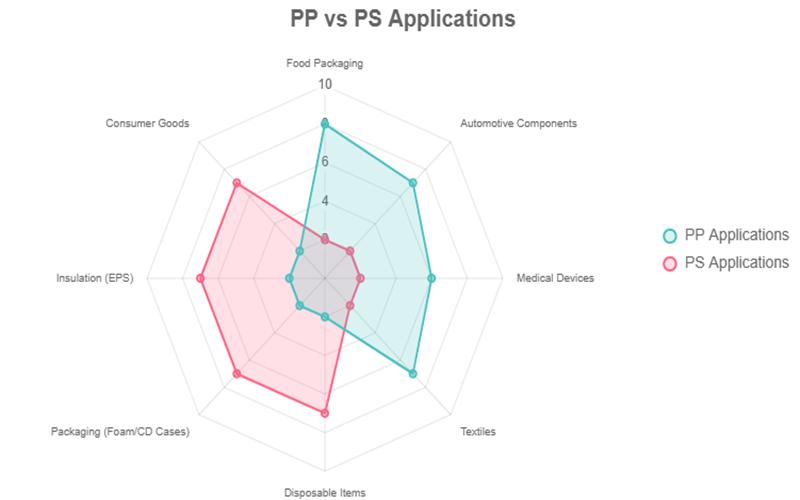
Applications Of Polypropylene And Polystyrene
Polypropylene (PP) and polystyrene (PS) are both widely used thermoplastic polymers, but their applications differ significantly due to their unique molecular structures and resulting properties.
PP is extensively favored in the automotive industry, medical containers, and food packaging because of its excellent mechanical properties, exceptional chemical resistance polypropylene offers, and superior heat resistance PP can withstand.
Its high melting point and crystalline regions contribute to its durability and ability to endure higher temperatures without significant deformation.
Additionally, its good electrical resistance and role as a reliable insulator make it a preferred material in the electrical and electronics industry for manufacturing electronic components and electrical components.
The versatility of polypropylene fibers also makes it popular in the textile industry for moisture-wicking thermal clothing and sportswear.

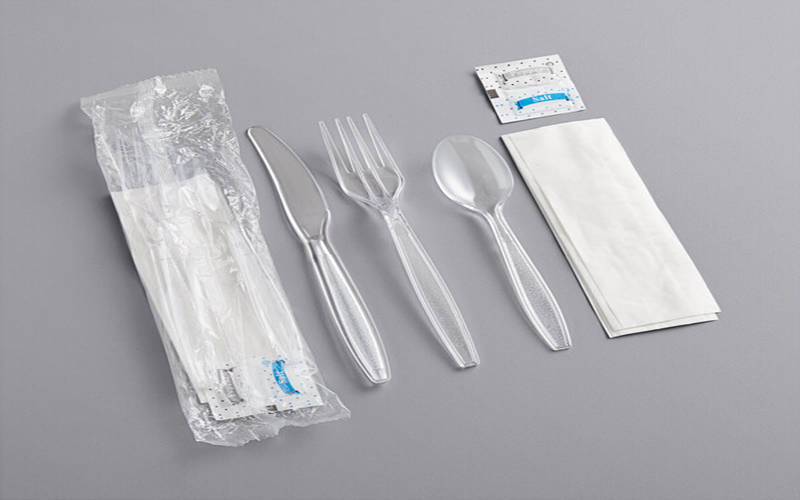
On the other hand, polystyrene is commonly used in disposable cutlery, molded packaging, insulation boards, and clear protective packaging, benefiting from its affordability polystyrene offers and excellent optical clarity.
Its malleability when heated allows for complex packaging needs and the production of model assembly kits and other consumer products.
Furthermore, recycled polystyrene is gaining attention for sustainable packaging applications, despite PS’s lower heat resistance compared to PP.
However, its brittle nature and lower chemical resistance limit its use in high-stress or chemically demanding environments.
Understanding these distinct applications highlights the importance of selecting the right polymer based on specific mechanical properties PP and PS exhibit, thermal properties, and intended use cases.
PP vs PS: Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages Of PP
Polypropylene (PP) is a lightweight, cost-effective, and highly durable thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, making it ideal for a wide range of applications including containers, packaging, automotive parts, and medical equipment.
Its excellent fatigue resistance allows it to withstand repeated bending and mechanical stress without breaking, enhancing the longevity of products made from PP.
Additionally, its semi-crystalline structure contributes to superior moisture resistance and thermal stability, enabling it to withstand higher temperatures without significant deformation.
Polypropylene is also easy to recycle due to its thermoplastic nature, supporting sustainability efforts by reducing plastic pollution.
Its versatility extends to the textile industry, where polypropylene fibers are valued for their moisture-wicking properties in thermal clothing and sportswear.
Disadvantages Of PP
While polypropylene (PP) offers many advantages, it does have some limitations.
PP has lower impact strength compared to polycarbonate (PC), particularly at low temperatures, which can make it less suitable for applications requiring extreme toughness.
Additionally, PP is prone to UV degradation when exposed to prolonged sunlight, necessitating the use of UV stabilizers or additives for outdoor applications to maintain its durability.
Its relatively lower clarity restricts its use in transparent or optical-grade products.
Furthermore, despite its good heat resistance, PP’s melting point limits its performance in very high-temperature environments, making it less ideal for applications demanding exceptional thermal stability.
Advantages Of PS
Polystyrene (PS) offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for a variety of applications. Its affordability polystyrene offers makes it an economical solution for mass-produced and disposable products, such as disposable cutlery and molded packaging.
PS is lightweight and provides excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for clear protective packaging and optical devices.
Additionally, its malleability when heated allows for easy molding into complex shapes, which is beneficial for manufacturing model assembly kits and other consumer goods.
Despite its lower heat resistance compared to polypropylene, polystyrene’s insulating properties and ease of fabrication make it a versatile polymer in the food service sector and insulation boards.
Furthermore, recycled polystyrene is increasingly used to support sustainability efforts, helping to reduce plastic pollution.
Disadvantages Of PS
Despite its many advantages, polystyrene (PS) has several notable disadvantages that limit its applications.
As a brittle material, PS is prone to cracking and breaking under mechanical stress, which reduces its durability compared to more resilient polymers like polypropylene.
Its lower heat resistance means it can deform or warp at relatively low temperatures, restricting its use in environments requiring thermal stability.
Additionally, polystyrene generally exhibits poor chemical resistance, especially to solvents and certain acids, which can lead to significant degradation when exposed to harsh chemicals.
Environmental concerns also arise from PS’s limited recyclability and its contribution to plastic pollution, particularly with expanded polystyrene products that are difficult to collect and recycle effectively.

How To Choose, Polypropylene Or Polystyrene?
Choosing the right material for your project involves several considerations. Durability, flexibility, and transparency are paramount application requirements.
For projects demanding high durability and chemical resistance, polypropylene is the better choice. Conversely, if transparency and ease of molding are crucial, versatile materials like polystyrene might be more suitable.
Environmental conditions also significantly influence the choice. Polypropylene’s higher heat resistance makes it ideal for high-temperature applications, while polystyrene’s lower heat resistance might limit its use.
Cost constraints also play a role, with polypropylene generally being more cost-effective for durable goods and polystyrene offering economical solutions for disposable items.
All in all, Polypropylene (PP) is better for durable, chemically resistant applications, while Polystyrene (PS) excels in low-cost, transparent, single-use products.
Careful consideration of these factors helps ensure the success and efficiency of your manufacturing process project.

