LDPE plastic, or low-density polyethylene, is a flexible, lightweight, and transparent thermoplastic widely used in everyday products such as plastic bags, squeeze bottles, and cling film.
This article explores what LDPE plastic is, its key properties including its characteristic density range and chemical resistance.
It also covers how it’s made, its common applications across various industries including packaging and plastic parts for computer components, and its environmental impact.
What Is Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) Plastic?
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic that has become ubiquitous in our everyday lives.
It is made from ethylene monomers and is known for its flexibility and transparency, making it an ideal material for a variety of applications.
The chemical formula of LDPE, (C2H4)n, signifies its polymeric nature, where ethylene units are repeated to form long molecular chains.
Unlike high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which is more rigid and strong, LDPE boasts a lower density and greater flexibility.
This makes it perfect for products like plastic bags and plastic parts that require a certain degree of pliability and transparency.
LDPE’s ability to be easily molded and its resilience also contribute to its widespread use in various industries.
These fundamental characteristics of LDPE, including its flexibility, toughness, and excellent chemical resistance, translate into a wide range of practical applications.
This makes LDPE a preferred choice over other plastics in industries such as packaging, manufacturing plastic bags, squeeze bottles, and various containers, where durability and adaptability are essential.

LDPE Plastic Properties
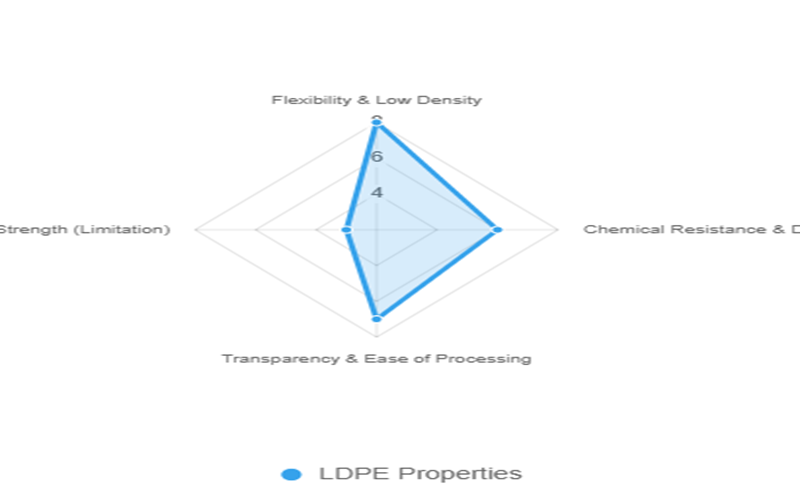
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is renowned for its unique properties that make it a widely used material across various applications.
Physical Properties
LDPE is characterized by its low density (0.910–0.940 g/cm³) and high flexibility, allowing it to bend, stretch, and absorb impact without breaking.
This toughness makes it ideal for applications like plastic films, plastic bags, and flexible packaging.
Its relatively low melting point (105–115°C) and translucent appearance further enhance its utility in lightweight, flexible products that require durability and good chemical resistance.
Additionally, LDPE offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for containers and bottles that store various chemicals and food products.
Chemical Resistance
LDPE exhibits excellent chemical resistance and offers good chemical resistance against a wide range of substances including acids, alcohols, and bases without degrading.
This toughness and durability ensure that LDPE remains stable and reliable under various environmental and chemical exposure conditions.
This makes it highly suitable for packaging, plastic bottles, squeeze bottles, and storage solutions where chemical resistance is a critical factor.
Ease Of Processing
LDPE is easy to process due to its low melting point and malleable nature.
It can be efficiently molded through techniques such as extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding, allowing for the creation of complex and precise shapes with minimal energy consumption.
This ease of processing not only reduces manufacturing costs but also supports high production rates and scalability.
Furthermore, LDPE’s toughness and flexibility during processing help minimize material waste and enhance the durability of finished products.
These processing benefits make LDPE a highly cost-effective and versatile material choice for a wide range of applications across various industries.
Manufacturing Process Of LDPE Plastic
The production of LDPE involves a series of sophisticated processes that transform ethylene gas into a versatile polymer.
LDPE is produced through the polymerization of ethylene, a hydrocarbon derived from natural gas or petroleum.
This process involves linking ethylene monomers into long polymer chains under controlled conditions.
Free-radical polymerization, initiated by catalysts such as organic peroxides, is commonly used to create the branched structure characteristic of LDPE, which contributes to its flexibility and low density.
The most prevalent method for producing LDPE is the high-pressure process, which operates at pressures between 1,000 and 3,000 bar and temperatures of 200–300°C.
In this technique, ethylene gas is compressed and heated in a reactor, where initiators trigger the formation of polymer chains.
Two primary systems are used: the autoclave process, which allows for continuous mixing in a single vessel.
The other is the tubular process, which uses long, heated tubes for greater control over molecular weight.
These methods ensure LDPE’s unique properties, such as flexibility and transparency, are consistently achieved.

What Is LDPE Plastic Used For?
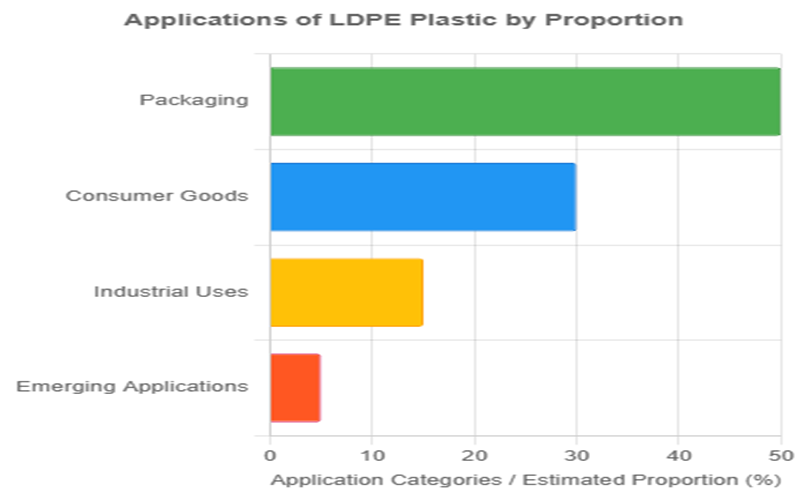
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a highly versatile material used across a wide range of industries due to its flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Packaging
LDPE is a cornerstone of the packaging industry, widely used for producing plastic bags, films, and various containers.
Its flexibility, toughness, and good chemical resistance make it ideal for grocery bags, shrink wraps, cling film, and food packaging films, ensuring products are protected while allowing visibility.
LDPE containers, such as squeeze bottles and wash bottles, are also popular for their lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant nature.
Additionally, LDPE is used in six pack rings and other flexible packaging solutions, highlighting its versatility in protecting and preserving food products and consumer goods.
Consumer Good
LDPE is commonly used in manufacturing everyday consumer products like bottles and toys.
Its flexibility, toughness, and good chemical resistance make it suitable for producing squeeze bottles for cosmetics, household cleaners, and food products.
Additionally, LDPE’s safety, moldability, and moisture resistance allow it to be used in children’s toys and other household items.
These products require durability, lightweight properties, and good resistance to various chemicals.

Industrial Use
In industrial settings, LDPE is widely employed for applications such as pipes, coatings, and protective films.
Its excellent chemical resistance and toughness make it suitable for low-pressure piping systems, particularly in agriculture for irrigation and water management.
LDPE is also used as a protective coating for cables and wires, providing effective insulation and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and corrosion.
Additionally, LDPE’s flexibility and durability make it ideal for manufacturing various industrial packaging materials and liners, contributing to its reputation as a versatile and reliable plastic material.
Low Density Polyethylene vs High Density Polyethylene
When comparing low-density polyethylene (LDPE) to high-density polyethylene (HDPE), several key differences emerge.
LDPE is known for its greater flexibility, thanks to its molecular structure, which allows for more movement and bending without breaking.
This makes LDPE suitable for applications like plastic bags and flexible tubing where pliability is essential.
On the other hand, HDPE is stronger and more durable than LDPE.
Its tightly packed molecular structure gives it higher tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for products that require robustness, such as heavy-duty containers and pipes.
This strength and hardness make HDPE a better choice for applications where durability and resistance to impact are crucial.
These structural differences between LDPE and HDPE highlight why certain products are made from one type over the other.
While LDPE excels in flexibility and ease of processing, HDPE stands out in strength and durability, each serving distinct roles in the plastics industry.
| Feature | LDPE | HDPE |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Structure | Branched, more flexible | Tightly packed, rigid |
| Flexibility | High, bends easily | Low, stiff |
| Strength | Lower tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Durability | Moderate | High, impact-resistant |
| Applications | Plastic bag, flexible tubing | Heavy-duty containers, pipes |
Recycling And Environmental Impact Of LDPE
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is widely used, but its environmental impact and recyclability are important considerations.
LDPE is assigned the recycling number 4, indicating it is recyclable. However, it is less commonly recycled compared to plastics like PET (No. 1) or HDPE (No. 2).
This is partly due to challenges in collection and processing of flexible LDPE products such as plastic bags and cling film.
Despite this, many recycling programs and supermarkets have started initiatives to collect and recycle LDPE films and bags, helping to reduce plastic waste.
From an environmental perspective, LDPE is durable and resistant to chemicals, but it can take hundreds of years to degrade in landfills.
When exposed to sunlight, LDPE breaks down slowly and can release greenhouse gases such as methane and ethylene, contributing to environmental pollution.
Therefore, increasing recycling rates and developing biodegradable alternatives are crucial steps towards minimizing LDPE’s ecological footprint.
Consumers can contribute by reusing LDPE products like grocery bags and participating in local recycling programs.
Manufacturers are also exploring options to incorporate recycled LDPE content into new products, reducing the demand for virgin plastic.

Summary
In summary, low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a highly versatile and widely utilized plastic known for its unique combination of flexibility, toughness, and excellent chemical resistance.
These distinctive properties make LDPE an ideal material for a broad range of applications, including plastic bags, cling film, squeeze bottles, food packaging, and various containers used across multiple industries.
Its lightweight nature and ability to withstand temperatures and impact further enhance its appeal for both consumer and industrial uses.
Moreover, LDPE’s ease of processing and availability in translucent and opaque variations provide manufacturers with considerable design flexibility.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, increasing recycling efforts and developing sustainable alternatives for LDPE are essential to minimize its ecological footprint.
By embracing responsible usage, recycling, and innovation, we can continue to benefit from this remarkable material while promoting a greener and more sustainable future.

