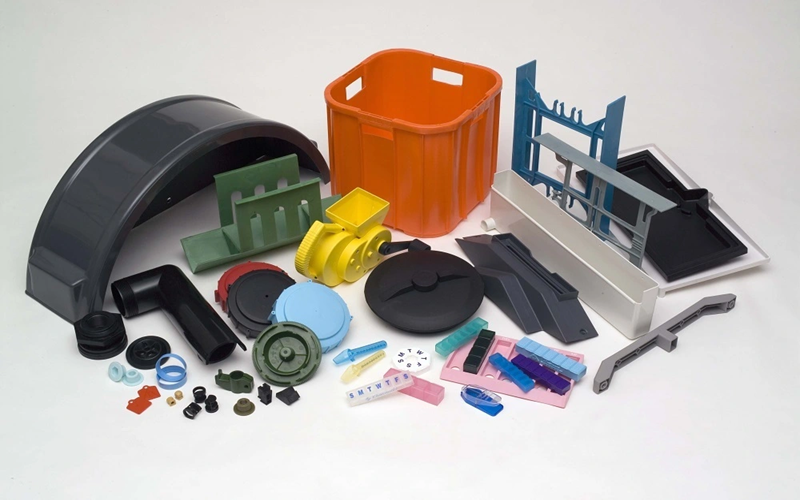
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) injection molding is a versatile and widely used manufacturing process that transforms this flexible, durable plastic into countless products, from packaging to medical devices.
Known for its excellent chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness, LDPE is a go-to material for industries seeking reliable, high-volume production.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding LDPE injection molding, covering its properties, process and applications, equipping readers with the knowledge to leverage this technology effectively.
What Is Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)?
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a flexible, lightweight thermoplastic polymer characterized by its low density and branched molecular structure.
Composed of ethylene monomers, LDPE offers excellent chemical resistance, good impact strength, and high flexibility, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Its properties allow it to be easily processed through various methods like injection molding and blow molding, where it is used to create products such as packaging films, containers, and medical components.
LDPE’s versatility, recyclability, and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice across industries, despite its lower tensile strength compared to other plastics like HDPE.
Key Characteristics Of LDPE Material
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is distinguished by several key characteristics that make it a preferred material for various applications.
Its low density, typically ranging from 0.910 to 0.940 g/cm³, contributes to its lightweight nature and flexibility, allowing it to bend without breaking.
LDPE exhibits excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for containers holding acids, bases, and other corrosive substances.
Additionally, it offers good impact strength, transparency in thin films, and ease of processing due to its low melting point, around 110-120°C.
The material also features a broad molecular weight distribution and notable melt flow index, which influence its flow behavior during injection molding.
While LDPE has lower tensile strength and heat resistance compared to other plastics like HDPE, its recyclability and cost-effectiveness enhance its appeal for injection molding and other manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, LDPE’s resistance to environmental stress cracking and its permeability to gases and moisture are important physical properties that affect its performance in various applications.
| Characteristic | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Density | 0.910 – 0.940 g/cm³ |
| Flexibility | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent |
| Impact Strength | Good |
| Transparency | High in thin films |
| Melting Point | 110°C – 120°C |
| Tensile Strength | Lower than HDPE |
Conditions Of LDPE Injection Molding Process
The injection molding process conditions for Low Density Polyethylene are critical to achieving high-quality molded products.
LDPE, also known as high pressure polyethylene due to its manufacturing process, requires precise control of parameters such as melt temperature, mold temperature, injection pressure, and cooling time.
Typically, the melt temperature ranges between 130°C to 200°C, while the mold temperature is maintained between 20°C and 40°C to balance flowability and solidification.
Injection pressure can reach up to 1500 bar to ensure complete filling of the mold cavities, especially when producing thin layer components.
LDPE’s broad molecular weight distribution and melt flow index influence its flow behavior during molding, requiring adjustments in injection speed and pressure.
A proper combination of these parameters is essential to optimize the molding process, as it helps decrease defects such as shrinkage and warpage, ensuring consistent product quality.
Additionally, LDPE’s permeability to gases and moisture must be considered when setting process conditions, particularly for applications like cable coating and packaging films.
Understanding and optimizing these injection molding process conditions is vital for harnessing LDPE’s unique properties and producing durable, flexible, and high-quality products.

Advantages Of LDPE Injection Molding
LDPE injection molding provides several key advantages that contribute to its widespread use in various industries.
Its low density and branched molecular structure result in products that are lightweight yet flexible, making them ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and durability.
The process benefits from LDPE’s relatively low melting temperature and favorable melt index, which allow for efficient molding cycles and energy savings.
Additionally, LDPE exhibits excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties, enhancing the performance and longevity of molded parts.
The material’s permeability to air and moisture can be an advantageous solution in specific applications, such as breathable packaging.
Furthermore, LDPE’s compatibility with different molding conditions, including lower mold temperatures and controlled holding pressure, enables manufacturers to optimize production quality and reduce defects like shrinkage and warpage, achieving an average improvement in product consistency.

Disadvantages Of LDPE Injection Molding
While LDPE injection molding offers many benefits, it also has some notable disadvantages.
The material’s lower mechanical strength and heat resistance compared to other polyethylene, such as HDPE or linear low density polyethylene, limit its suitability for applications requiring high durability or thermal stability.
LDPE’s branched molecular structure can lead to higher shrinkage and warpage during the molding process, which may affect dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Additionally, its permeability to gases and moisture can be a drawback for packaging applications needing strong barrier properties.
The material is also prone to environmental stress cracking under certain chemical exposures or mechanical stresses, which can reduce the lifespan of molded parts.
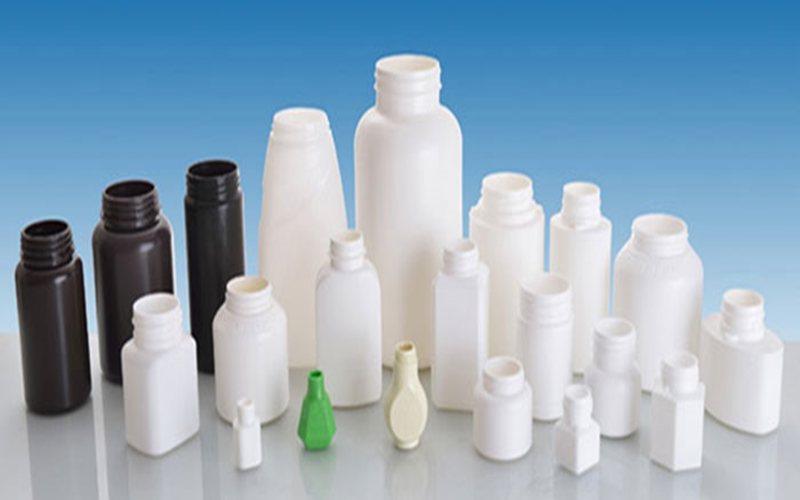

Applications Of LDPE Injection Molding Parts
Low Density Polyethylene injection molding is widely utilized across various industries due to its flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The process enables the production of high-quality, durable products tailored to specific needs.
Packaging Industry
LDPE is extensively used for producing flexible containers, lids, and closures, such as squeeze bottles and food storage containers, leveraging its excellent chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and good barrier performance.
Its permeability to gases and moisture makes it especially suitable for packaging applications requiring breathability, while maintaining product freshness and safety.
Medical Sector
The material’s excellent biocompatibility and flexibility make it ideal for manufacturing medical components such as syringe stoppers, tubing connectors, and soft, disposable containers.
Additionally, LDPE’s chemical resistance and ease of molding contribute to producing reliable and safe medical products.
Cable And Wire Coating
LDPE’s excellent electrical insulation properties, combined with its flexibility and chemical resistance, make it an ideal choice for coating wires and cables.
Its permeability to gases and moisture requires careful control during the injection molding process to maintain durability and ensure long-lasting performance in electrical applications.

LDPE Injection Molding vs HDPE Injection Molding
LDPE injection molding and HDPE injection molding differ primarily due to the distinct molecular structures and resulting physical properties of these two materials.
LDPE, with its highly branched polymer chains, has a lower density and offers greater flexibility, making it suitable for producing soft, pliable products such as squeeze bottles, flexible packaging, and thin-walled containers.
Its injection molding process typically operates at lower melt and mold temperatures, with moderate injection pressure to accommodate its flow characteristics and reduce defects like shrinkage and warpage.
In contrast, HDPE features a more linear and crystalline structure, resulting in higher density, strength, and rigidity. This makes HDPE ideal for manufacturing hard, durable items such as large containers, automotive parts, and industrial components.
HDPE injection molding requires higher melt and mold temperatures, increased injection and holding pressures, and longer cooling times to achieve optimal crystallization and mechanical performance.
Additionally, HDPE exhibits better resistance to environmental stress cracking and solvents compared to LDPE, which is more permeable to gases and moisture.
Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate resin and optimizing process conditions to meet specific application requirements and ensure product quality.

Summary
LDPE injection molding is a versatile, cost-effective, and widely adopted manufacturing process that leverages the unique properties of Low-Density Polyethylene, such as excellent flexibility, superior chemical resistance, and recyclability.
It is used to produce a broad spectrum of products—from flexible packaging and blown film applications to medical components and cable coatings.
By thoroughly understanding the material’s characteristics and optimizing key injection molding process conditions, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, durable parts with minimal defects like shrinkage and warpage.
Compared to High-Density Polyethylene, LDPE offers greater flexibility and better impact resistance but has lower tensile strength and heat resistance, making it ideal for specific applications that benefit from its softness and permeability.
As sustainability concerns grow and technological advancements continue, LDPE injection molding remains a critical and evolving process for innovative, efficient production across various industries.
It combines the benefits of low density polyethylene with precise molding techniques to yield superior performance and cost savings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Optimal Injection Molding Process Conditions For LDPE?
The optimal conditions typically include a melt temperature between 130°C and 200°C, mold temperature between 20°C and 40°C, and injection pressure up to 1500 bar. These parameters help achieve high quality molded parts with minimal defects.
What Are The Key Differences Between High Density Polyethylene And Low Density Polyethylene In Injection Molding Applications?
HDPE, with its denser, linear molecular structure, offers higher tensile strength and rigidity, making it ideal for rigid containers and durable parts, while LDPE’s branched structure provides greater flexibility and transparency, suited for flexible packaging and soft products.
What Are The Main Advantages And Disadvantages Of LDPE Injection Molding?
Advantages include lightweight, flexibility, excellent chemical resistance, and cost effectiveness. Disadvantages involve lower mechanical strength, higher shrinkage and warpage, and susceptibility to environmental stress cracking.
What Types Of Products Are Commonly Made Using LDPE Injection Molding?
Common products include flexible packaging films, squeeze bottles, medical components like tubing connectors, and wire and cable coatings due to LDPE’s flexibility and electrical insulation properties.
How Can Process Parameters Be Optimized To Reduce Defects Like Shrinkage And Warpage In LDPE Injection Molding?
Controlling mold temperature, injection pressure, cooling time, and using appropriate mold designs can minimize shrinkage and warpage. Maintaining consistent drying and optimizing injection speed also contribute to better product quality.

