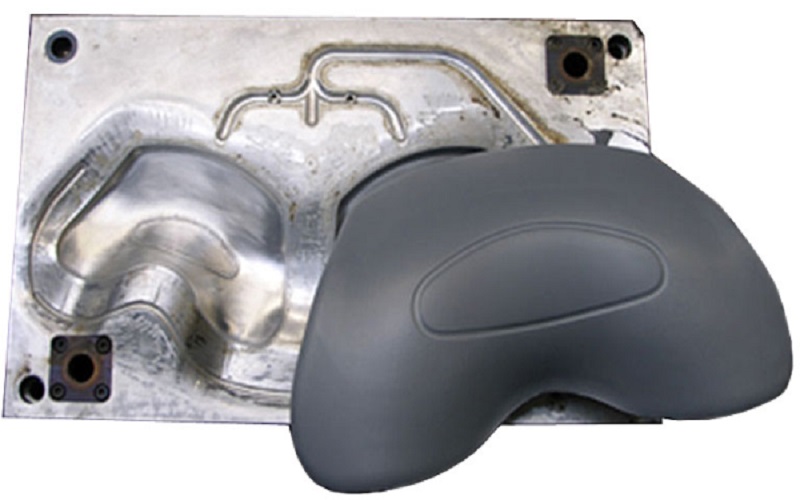
EVA foam is a superstar material for crafters, manufacturers, and designers.
Whether you’re building a cosplay costume, crafting comfy shoe soles, or designing protective gear, EVA foam molding is a skill worth mastering.
In this guide, we’ll break down what EVA foam is, how to mold it, and where it’s used in real-world applications.
We’ll keep it simple and practical so you can jump right in.
From the raw material like ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer to the final product, we’ll cover everything you need to create high-quality molded foam.
Understanding EVA Foam
Before we dive into molding techniques, let’s get to know EVA foam and why it’s so popular.
This versatile material has unique properties that make it stand out from other foams like latex or open-cell options.
What is EVA Foam?
EVA foam, or ethylene vinyl acetate foam, is made from ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer—a blend of ethylene and vinyl acetate.
This mix creates a soft, flexible, and durable foam with a smooth surface.
As a closed cell foam, its tiny, sealed air pockets block water, giving it excellent moisture resistance.
Unlike open-cell foams that soak up liquids, EVA stays dry and holds its shape, even in wet conditions.
It comes in sheets, rolls, or pre-cut forms, with different types varying in density and thickness for everything from thin craft layers to dense industrial blocks.
The production process starts by combining ethylene and vinyl acetate under heat and pressure to form the copolymer.
Then, it’s expanded into foam with agents that create those closed cells. The result is a lightweight, non-toxic material with great heat resistance and insulation properties.
Whether you’re working with flat sheets or curved designs, EVA foam’s ability to bend and stretch makes it perfect for custom shapes.
Key Properties of EVA Foam
EVA foam’s standout features make it ideal for molding. Its cushioning properties offer excellent shock absorption, perfect for footwear or protective pads.
The closed cell structure makes it resistant to chemicals, so it won’t break down when exposed to oils or cleaners.
With a low melting point, it’s easy to heat and shape but stays durable under normal conditions due to its heat insulation.
This foam is versatile in texture and form—soft for comfy mats or dense for structural pieces.
It’s lightweight, so your final product won’t feel heavy, and it’s easy to paint, glue, or combine with materials like fabric for added style.
Depending on the blend, some EVA foams offer extra flexibility for items that need to stretch or bend repeatedly.
These traits—durability, moisture resistance, and ease of use—make EVA foam a favorite for hobbyists and professionals alike.

EVA Foam Molding Techniques
Molding EVA foam involves using heat and pressure to shape it into the desired form.
Whether you’re a DIYer or running a production line, these techniques will help you create high-quality molded EVA foam.
Let’s explore the main methods, starting with tools you might already have.
Heat Molding with a Heat Gun
Using a heat gun is one of the easiest ways to mold EVA foam, especially for small projects like cosplay props or custom mats.
This method softens the foam so you can shape it by hand or press it into a mold.
Start in a well-ventilated area to avoid fumes, and wear gloves to protect your hands from heat.
Prepare your mold—something simple like a wooden form or even a curved household item works for DIY projects.
Hold the heat gun 4-6 inches from the foam’s surface, moving it slowly to heat evenly. As the foam nears its melting point, it becomes pliable without melting completely.
Once soft, press it into your mold or shape it by hand to get the right shape. For smooth surfaces, use your gloved hands to iron out wrinkles.
Let the foam cool in place for a few minutes, and it’ll harden into the desired shape.
This technique is great for creating patterns or curved pieces like armor or thin inserts. Test on a scrap piece first to avoid overheating, which can make the foam too thin or sticky.
Injection Molding for Mass Production
For large-scale projects, injection molded EVA foam is the go-to method.
This production process involves melting EVA foam and injecting it into a mold under high pressure.
It’s commonly used for items like footwear soles or medical device padding, where consistency and quality are key.
The process creates a smooth, precise final product with complex shapes, making it ideal for industries like fashion or healthcare.
Manufacturers use metal molds for durability and precision, ensuring the foam’s texture and density are just right.
This method is less hands-on than heat gun molding but requires specialized equipment, making it better suited for factories than home workshops.
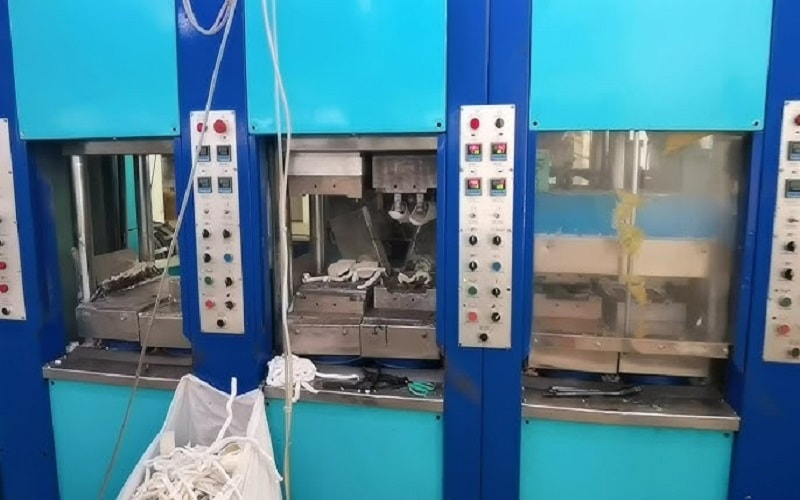

Oven Molding for Larger Pieces
For bigger sheets or uniform shapes, oven molding is a solid choice.
Heat the EVA foam in an oven at a low temperature (200–250°F, depending on the foam’s composition) to make it pliable.
Then, drape it over a form or press it into a mold. Monitor the temperature closely to avoid melting the foam. Once shaped, let it cool to lock in the form.
This technique works well for large, curved pieces like costume armor or padding for sports gear.
It’s a bit trickier than using a heat gun, so practice with small pieces first to get the hang of timing and temperature.
The Design Process for EVA Foam Molding
A good molded EVA foam piece starts with a smart design process.
Whether you’re crafting for fun or producing on a large scale, planning helps you avoid mistakes and wasted materials.
Planning Your Project
Begin by sketching your design or creating patterns on paper.
Think about the final product’s purpose—does it need to be lightweight for a costume or dense for a shoe sole?
Choose the foam’s thickness and density based on your needs.
For example, thin foam is great for detailed crafts, while denser foam suits structural parts. Decide if you’ll need to glue pieces together or paint them for a polished look.
Choosing the Right Mold
The mold determines your foam’s final shape, so pick one that matches your vision.
For DIY projects, you can make molds from wood, plastic, or even everyday objects like bowls for curved shapes.
In industrial settings, metal molds are used for injection molding to ensure durability and precision.
The mold’s surface affects the foam’s texture, so choose one that gives you the desired finish—smooth for sleek designs or textured for grip.
Testing and Refining
Before committing to a full project, test your design with a small piece of foam.
Experiment with different heat levels, molding times, or pressure to find what works.
If the foam doesn’t hold the right shape, tweak the temperature or try a different mold. This trial-and-error step saves time and ensures a high-quality final product.
Applications of Molded EVA Foam
Molded EVA foam is everywhere, thanks to its versatility. From everyday products to specialized gear, here’s where it shines.
Footwear and Orthotics
EVA foam is a star in the footwear world. Its cushioning properties and shock absorption make it perfect for shoe soles and insoles.
Injection molded EVA foam creates lightweight, durable soles that handle daily wear while keeping your feet comfy.
In orthotics, EVA foam provides support and cushioning for medical devices, helping people with foot conditions stay comfortable.
Cosplay and Crafting
Cosplayers love EVA foam for its flexibility and ease of use.
You can cut it into thin sheets, shape it with a heat gun, and paint it to create stunning armor, props, or costumes.
Its lightweight nature means you can wear it for hours without strain, and it’s easy to glue or combine with other materials for added style.
Whether you’re crafting a sword or a helmet, EVA foam lets you bring your designs to life.
Sports and Protective Gear
From yoga mats to helmet padding, EVA foam is a go-to for sports gear.
Its closed cell structure offers moisture resistance and durability, perfect for sweaty environments.
Molded EVA foam is used in knee pads, shin guards, and gym flooring, providing cushioning and shock absorption.
Its ability to hold up under impact makes it ideal for protective equipment.
Industrial and Medical Uses
EVA foam’s heat resistance and non-toxic nature make it a fit for industrial and medical applications.
It’s used in packaging to protect delicate equipment, in medical devices for cushioning, and in automotive parts for heat insulation.
The ability to mold it into precise shapes ensures it meets the needs of these high-demand fields.
Tips for Working with EVA Foam
To get the best results, keep these practical tips in mind:
- Stay safe: Work in a well-ventilated area when heating foam, and wear gloves to avoid burns.
- Pick the right foam: Choose a density and thickness that fits your project—soft for cushioning, dense for structure.
- Finish it right: Use flexible paints to avoid cracking, and seal the foam for a polished look.
- Practice makes perfect: Start with small pieces to master shaping and heating before tackling big projects.
Why EVA Foam Stands Out
Compared to materials like latex, EVA foam is more durable, resists chemicals better, and doesn’t absorb water.
Its versatility lets it be soft for mats or rigid for gear. It’s easy to cut, glue, and shape, making it a favorite for both hobbyists and manufacturers.
Plus, its lightweight and non-toxic nature adds to its appeal across industries.
Conclusion
EVA foam molding opens up a world of possibilities.
Whether you’re using a heat gun for a cosplay prop or injection molding for mass-produced footwear, EVA foam’s lightweight, durable, and flexible properties make it a top choice.
By understanding the material, mastering molding techniques, and exploring its many applications, you can create high-quality products that look great and perform even better.

