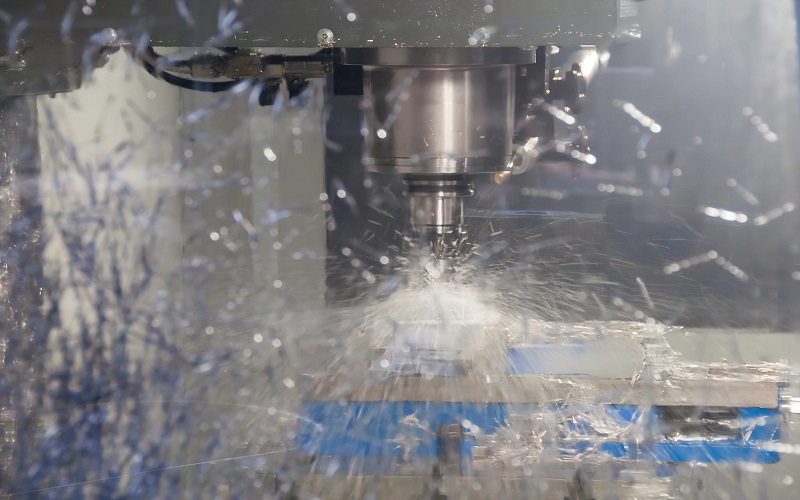
CNC technology is the engine behind modern manufacturing, turning raw materials into high precision parts like car components and medical implants.
Instead of relying on a human to move a cutting tool, cnc machines operate using pre-programmed computer software to dictate every movement.
But how does a cnc work? At its simplest, it’s like a high-tech sculptor that never gets tired and never makes a mistake.
In this guide, we’ll skip the overly academic lectures and break down the cnc machining process in plain English.
What is CNC Technology?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. It refers to the use of computerized software to control machine operations.
In the old days, a cnc machinist had to turn wheels and pull levers by hand (manual control)to move a cutting tool. It was slow, and if the operator’s hand slipped, the part was ruined.
Today, CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to dictate the movement of factory tools and machinery.
Think of it as complex machinery. You give the computer a set of instructions, and the cnc machine follows them to the millimeter.
Because it is a subtractive manufacturing process, it creates the desired shape by removing material from a solid workpiece—much like carving a statue out of marble.
How CNC Machines Operate?
To understand how cnc machines work, you need to know what’s under the hood.
It’s not just one motor; it’s a symphony of automated equipment working together.
The CNC Controller (MCU)
The Machine Control Unit (MCU) is the brain of the operation. It interprets the computer program (usually written in G code) and translates it into electrical signals.
In 2026, modern MCUs may incorporate AI for adjusting feeds and speeds based on real-time sensor feedback.
Servo Motors and Drive Systems
Once the brain sends a signal, servo motors move the machine parts along defined coordinates.
Most high-end cnc equipment uses a closed-loop system that adjusts movements in real time based on position feedback.
This means the cutting tool’s position is continuously monitored, allowing for immediate corrections to maintain accuracy during machining.
The Spindle and Bed
The spindle is a high-speed rotating component that holds and drives the cutting tool in CNC machines.
The machine bed serves as a rigid foundation where the workpiece is secured during machining.
The CNC Machining Process: From Design to Finished Part
The cnc machining process can involve multiple stages, including design, conversion, configuration, and execution.These machining processes all rely on CNC programming.
Step 1: Creating the Design (CAD)
The cnc machining process begins with creating a CAD model of the desired part. Using Computer Aided Design (CAD) software, an engineer draws a 3D version of the part. This CAD file is the digital blueprint.
Step 2: Translating the Design (CAM)
A cnc machine doesn’t understand a 3D drawing; it only understands coordinates. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create 2D or 3D designs that are converted into G-code by CAM (computer aided manufacturing cam) software. This G code is a list of number- and letter-based prompts that tell the machine exactly where to go.
Step 3: Setting Up the Machine
Before machining begins, the CNC machine must be properly configured and set up with the correct tools and workpiece. The cnc operator selects the right machining tools and secures the raw material. Modern CNC machines may include an Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) to reduce downtime during multi-step tasks.
Step 4: Execution
Once the machine is configured, the G-code is executed to begin the machining operation. The cnc machine tools move across the material, shaving off bits until the part is finished.The CNC machining process is automated, requiring minimal human intervention after setup.
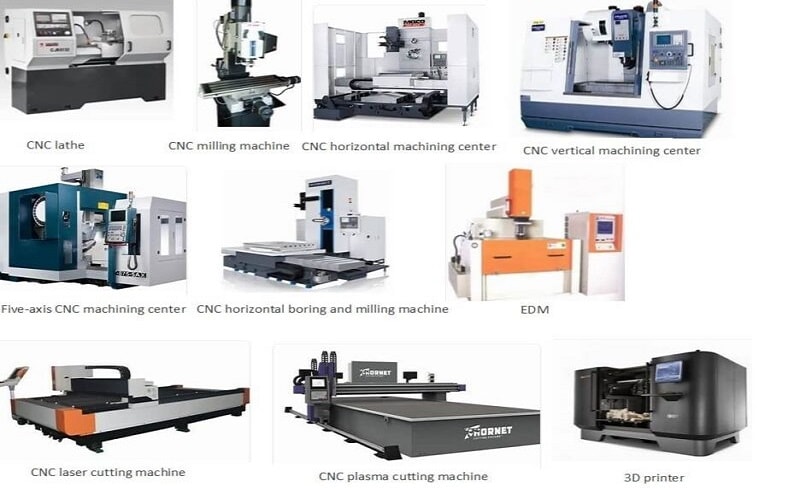
Types of CNC Machines
The manufacturing industry uses many types of cnc machines, each specialized for different machining operations.
| Machine Type | Primary Function | Best Used For |
| CNC Mills | Uses a rotating milling tool to cut material. | Complex shapes, shoulder milling. |
| CNC Lathes | Rotates the workpiece against a stationary tool. | Cylindrical parts, modern lathes vs manual lathes. |
| CNC Routers | CNC routers are similar to CNC milling machines but are designed for cutting various materials in three dimensions. | Wood, plastic, and soft metals. |
| CNC Plasma Cutters | CNC plasma cutters use a plasma torch to cut material, primarily applied to metal materials. | Heavy metal sheets, plasma cutting. |
| EDM Machines | Electric discharge machines (EDM) mold workpieces into particular shapes with electrical sparks. | Extremely hard metals, sinker edm, wire edm. |
CNC lathes cut workpieces as they rotate and offer precision and compactness compared with manual lathes.
Meanwhile, CNC milling machine systems (or a cnc mill) are the workhorses of the cnc industry, capable of handling everything from flat surfaces to deep pockets.

What Materials Can CNC Machine Cut?
One of the biggest myths is that cnc machinery is only for metal.
In reality, CNC machining can be performed on practically any material with sufficient hardness.
Metals and Alloys: CNC machines can work on metal alloys just as well as metals, including aluminum, steel, and titanium.
Plastics: CNC machining can also be used to shape plastic parts, offering higher precision than injection molding for small batches.
Wood: Wood is another common material used in CNC machining, especially for custom fabrication and furniture.
Composites: CNC machines can cut through composites such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, essential for the aerospace sector.
Why CNC Machining is the Industry Standard?
Why do companies spend thousands on cnc systems instead of using traditional methods?
Because CNC machining provides superior levels of versatility, efficiency, and precision relative to other manufacturing methods.
1. Unmatched Precision
CNC machines often achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches, essential for high-precision industries.
Using feedback systems like sensors or encoders, the machine ensures the cutting tool never strays from its path.
This results in high precision parts that fit together perfectly every time.
2. Speed and Repeatability
CNC machining can produce parts exponentially faster than traditional manufacturing methods.
Once the cnc programs are loaded, the machine can run 24/7.
This automation in CNC machining reduces the likelihood of human error, leading to fewer rejections during quality control.
3. Complexity Made Simple
CNC machining allows for the production of complex parts that would be difficult or impossible to achieve manually.
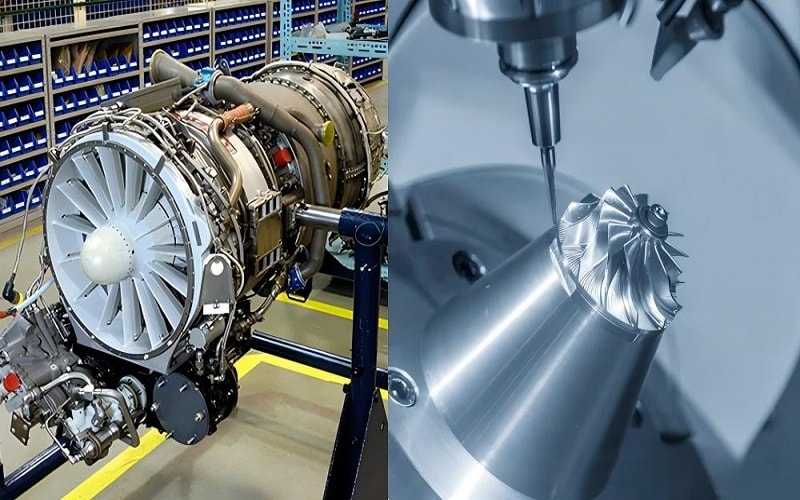
From turbine blades for jet engines to tiny components for medical device manufacturing, CNC can handle it all.
Applications Across Industries
The cnc machining market is expected to grow significantly, driven by increased demand in sectors such as semiconductors and medical equipment.
Aerospace: Creating lightweight, complex shapes for aircraft.
Automotive: Producing engine blocks, pistons, and custom valves.
Medical: CNC machining is often used in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries to create biocompatible implants and surgical tools.
Electronics Industry: Making tiny enclosures and heat sinks for smartphones and computers.

Summary
CNC machining technology is considered a pillar of modern manufacturing, transforming raw materials into complex components.
By using pre-programmed software and numerical control, we have moved away from the limitations of manual control and into an era of automated equipment.
Whether it’s laser cutting, spark machining, or water jet cutting, CNC machines can perform a variety of tasks including cutting, drilling, milling, and more with minimal human intervention.
As cnc technology continues to evolve—incorporating AI and faster cnc controller systems—it will remain the heart of the manufacturing industry.

