Foreword
Engineering plastics are used to make a variety of products and parts,Polymethyl methacrylate(PMMA) and polycarbonate (PC)are high-performance plastics widely used in industrial environments.
Perhaps you are looking for a material that can be used in the production of transparent molds or in the production of optical lenses and car lighting. Finding the right ingredients for these products can sound like a daunting task.But fortunately, we can offer materials suitable for this production: polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polycarbonate (PC). Among plastics, polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polycarbonate (PC) have higher light transmittance and are generally transparent. PMMA surface gloss, good stability, light transmittance close to glass. Uv resistance is stronger than PC.These two categories of materials may fit your needs well.
It is not easy to choose the right materials and craftsmanship. There are many things to consider! Think about your budget, production time and design requirements. Here is a brief comparison of the mechanical, physical and chemical aspects of PMMA and PC to help you choose the right material.
Introduction of PMMA
Definition:
A very magical material: polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA for short). This name may be unfamiliar to everyone, but it is actually a common raw material for fish tanks in daily life. It is composed of methyl methacrylate monomers. Because of its extremely high light transmittance, it is also called “plexiglass”. PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) is a thermoplastic material. It was first produced by the company of chemist Otto Röhm in 1933 and has been widely used since then. The methyl group in it can increase the stiffness of PMMA, and the ester group can increase the resistance to ultraviolet rays. With the extension of the use time and the increase of ultraviolet rays, PMMA will turn yellow and the light transmittance will decrease.

The Main Advantage:
High transparency: The light transmittance of PMMA reaches 92%, making it almost as transparent as optical glass.
Anti-UV: It has excellent resistance to ultraviolet rays and does not turn yellow or deteriorate even with prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Strong weather resistance: PMMA can maintain stable performance and appearance in all weather conditions, making it suitable for outdoor use.
Hardness and rigidity: PMMA has high hardness and rigidity and can effectively resist scratches and wear.
Light weight: Although PMMA is light, its density is only about half that of glass.
Ease of processing: It can be processed into various shapes by processes such as injection molding, extrusion, blow molding and thermoforming, making it very suitable for complex designs and mass production.
Repairability: Even if the surface is scratched, it can be repaired with a simple polishing to maintain a good appearance.
Application case:
PMMA is cheaper than polycarbonate and has a higher gloss. It is often used in mass production (such as windows, decorative wall panels and dashboards) and is suitable for everyday use. Areas of daily use of PMMA include:
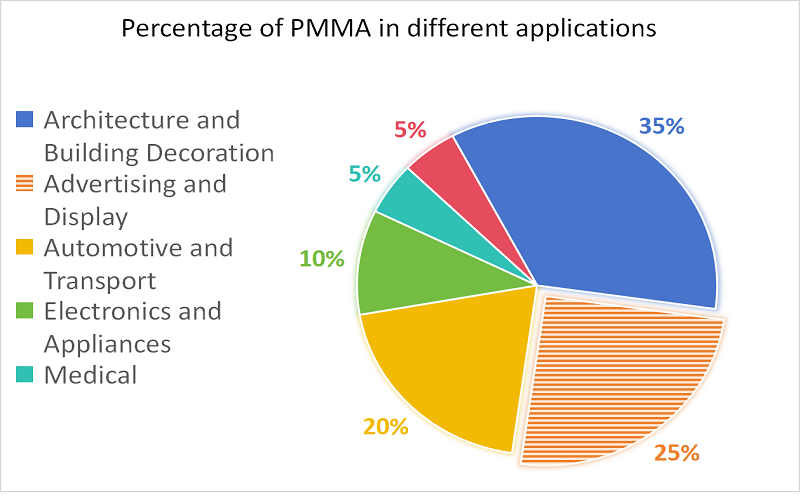
Introduction of PC
Definition:
The discovery of polycarbonate (PC) as a thermoplastic material dates back to 1898, but it was first successfully synthesized in 1953. Its chemical structure consists of bisphenol A (BPA) and carbonate monomers. This structure gives PC excellent optical properties, enabling it to exhibit high transparency comparable to silicate glass.
One of the most notable features of the PC is its excellent impact resistance. Its impact resistance is 250 times greater than ordinary glass, so it is widely used in the production of bulletproof glass, windows, ceilings and various types of screens and covers. However, the scratch resistance of PC is relatively low, which means that special attention must be paid to protecting the surface during use.
Due to its excellent physical properties, PC is widely used in fields such as medical equipment, auto parts, electronic products and building materials. Its high temperature resistance, chemical resistance and good mechanical properties make PC one of the necessary and important materials in today’s industrial and consumer markets.

The Main Advantage:
Extremely transparent: Computer light transmission reaches 89%, allowing you to create ultra-transparent objects!
Exceptional impact resistance: 200 to 300 times stronger than ordinary glass and does not break easily, even with heavy impacts.
High heat resistance: PC can be used for a long time at temperatures from -40°C to 120°C and is extremely resistant.
Fire resistance: It is also flame retardant and does not burn or ignite easily, making it very safe.
Durability: Highly resistant to ultraviolet rays and various climate changes, does not yellow and does not age, especially suitable for outdoor use.
Ease of processing: PC can be processed in a variety of ways, including injection molding, extrusion and blow molding, and is suitable for making objects with various complex shapes.
Electrical insulation: Due to its good electrical insulation, it is widely used in electronic equipment.
Application Case:
PC is a very strong plastic because it is less likely to break, can withstand high temperatures and is not easily ignited. Therefore, it is widely used in construction, automobiles, electronic equipment, medical equipment and some particularly safe daily necessities. The following table describes its distribution in different areas:
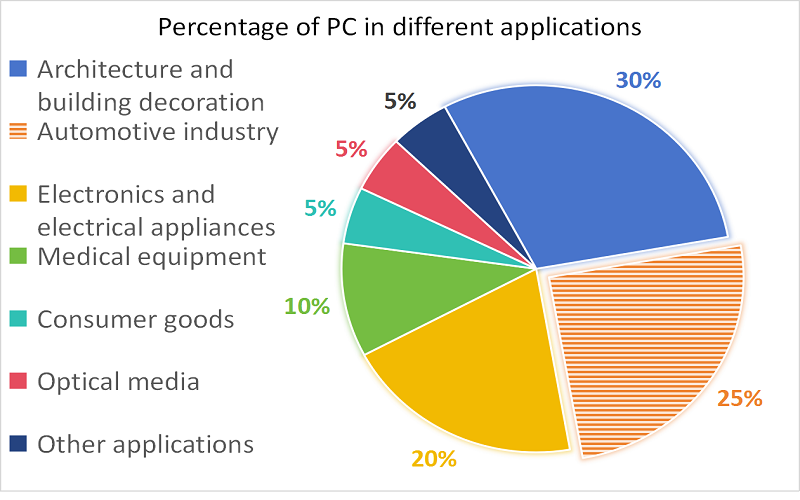
Comparison the Properties of PMMA and PC
This table compares the detailed parameters of polycarbonate (PC) and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in terms of light transmission, usable temperature range, strength and density. In this table you will find the information you need to determine which plastic best suits your needs.
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
| Light Transmission | 89% | 92% |
| Impact Strength | 640 J/m | 16 J/m |
| Operating Temperature | -40℃ to 120℃ | -40℃ to 80℃ |
| Flammability | UL94 V-0 rating, flame retardant | Non-flame retardant, flammable |
| Tensile Strength | 60-70 MPa | 48-76 MPa |
| Density | 1.20-1.22 g/cm³ | 1.18 g/cm³ |
| Flexural Strength | 90-100 MPa | 75-110 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 2.0-2.4 GPa | 3.0-3.3 GPa |
| Hardness | Rockwell Hardness M70-M85 | Rockwell Hardness M95 |
| Water Absorption | 0.15-0.35% | 0.3-0.4% |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 130℃ (at 0.45 MPa) | 100℃ (at 0.45 MPa) |
| Electrical Insulation | Dielectric Strength: 30 kV/mm | Dielectric Strength: 20 kV/mm |
Alternative Materials to PMMA and PC
In light of market changes, especially instability in commodity prices and supply, there is a need to use other materials as substitutes. This allows companies to reduce their reliance on specific materials, reduce cost risks and increase their competitiveness and responsiveness. Here are two common plastic types that can replace PMMA and PC.
1.Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG):
Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) is also a thermoplastic. It can be transparent up to 90% like PMMA or PC. In addition, it is very durable and does not break easily. PETG can be used to make a variety of transparent products such as displays and other products, and it is also very suitable to be produced using methods such as blow molding or injection molding.

2.Polyethylene terephthalate (PET):
PET is a cheap, translucent plastic that is often used to make water bottles, food boxes, and other lightweight items. Although not as transparent as other plastics, it transmits about 80% light, which is enough for many uses.

PMMA vs PC: Cost
Each of these plastic materials has its own characteristics. Polycarbonate(PC) is harder and less susceptible to damage by chemicals, but it is also more expensive. You can expect to pay between $3.50 and $5.00 per kilogram for polycarbonate sheets. PMMA is similar to polycarbonate in that it is transparent, tough, strong, and has a smooth surface. However, it is cheaper at $2.00 to $3.00 per kilogram. These price differences depend on the shape of the product and how much is made. In general, PC is about twice as expensive as PMMA.
PMMA is relatively cheap and is suitable for places where price is very sensitive and things need to look transparent. PC is relatively expensive, but it is very strong, not easily affected by impact, and can withstand high temperatures. Therefore, it is chosen in places that require high strength and durability.
Conclusion
This article talks about the characteristics of PMMA and PC and discusses when to use these two materials in the manufacturing process. If you want to save money and make more money, it is recommended to choose PMMA. However, if your product requires strong impact resistance and high temperature resistance, such as security equipment, bulletproof glass or car parts, you should choose PC. To know more about PMMA and PC, you can visit our website to learn more or request a free quote.

