In this article, we will explore the function of each component. Because injection molds are custom-made, they don’t all have identical parts. We’ll begin with the most common ones.
Common mold components
For better understanding, we divide the mold into 3 parts and let’s have a look one by one.
1. Basic mold structure
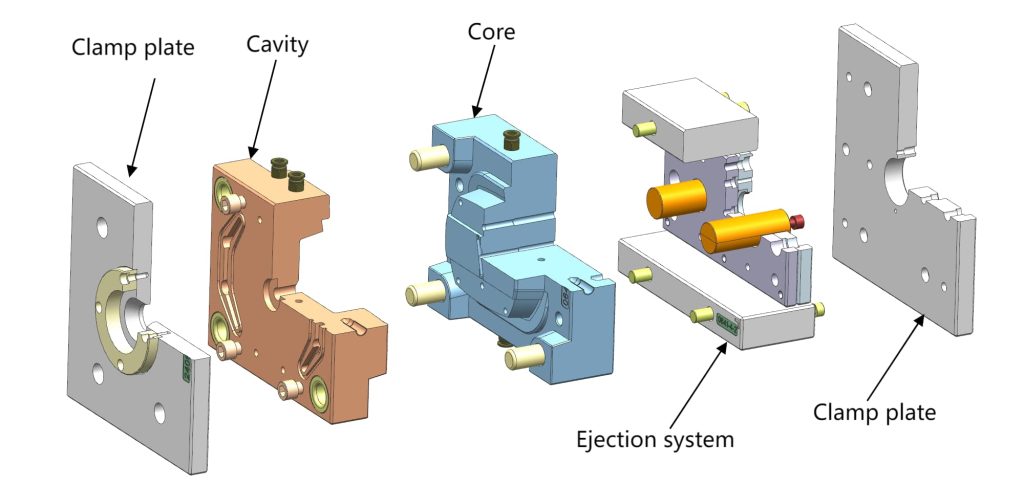
- Clamp
Primarily holds the mold in the platens of the injection machine while plastic is being injected.
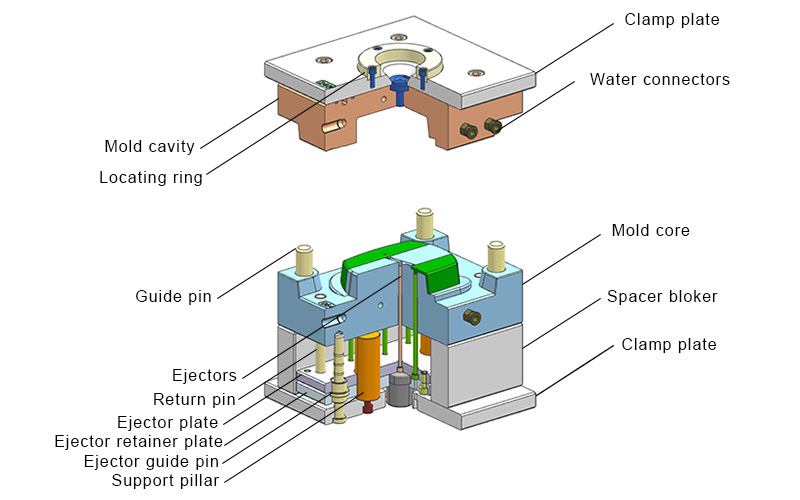
- Mold cavity & core
The mold cavity (plate A) & core (plate B) contain the specific geometry of the injected part. This can be made from a block or designed as an insert to allow future changes.
- Spacer bloker
The stripper plate is located between the fixed-side core plate and the mold base plate, allowing the movement of the ejector plates.
- Guide Pins
Injection mold guide pins are mounted in the mold and used to align and guide the movement of the mold during its opening and closing. They are designed to withstand heavy loads and help reduce wear and friction on the mold components.
- Guide bushing
Guide bushings complement guide pins by providing a precise and smooth bearing surface for the guide pillars to slide into.
- Locating Ring
The locating ring aligns the mold sprue with the nozzle of the injection machine. The outer diameter of the ring matches the hole in the machine’s platen.
2. Ejection system
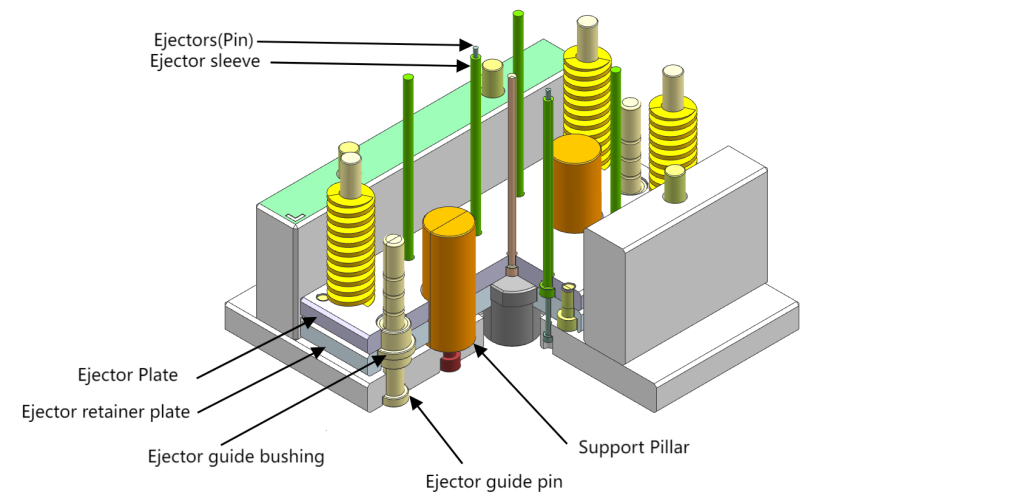
- Ejectors
These are the movable components that push the injected product out of the mold after the cooling process. They can be designed as pins or other shapes, such as an ejector ring.
- Ejector Plate
The main function of the ejector plate is to provide a flat and uniform surface on which the mold ejectors can be mounted and moved. They are equipped with a series of holes or slots that allow the ejectors to be securely inserted and fixed onto the plate.
- Ejector retainer plate
The ejector retaining plate holds the pins into the ejector plate, used to control the movement of the ejector pins.
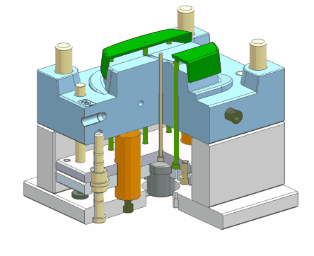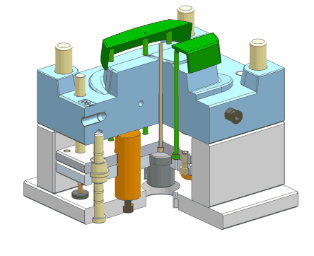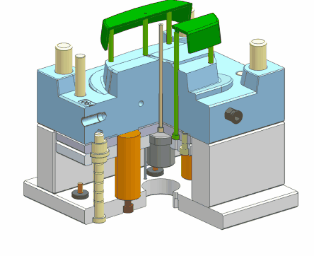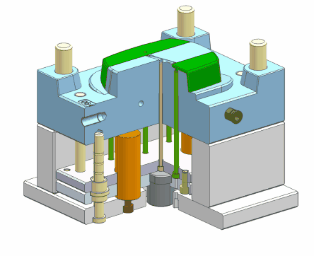
- Support Pillar
Prevents mold deformation under injection pressure, distributes load, and maintains mold shape and dimensions.
- Return Pin
Facilitates the return movement of mold parts, such as cores or ejector plates, after the molding cycle is complete.
- Ejector guide pins
Ejector guide pins are used to align and guide the movement of the ejector plate & ejector retainer plate during the ejection.
- Ejector guide bushings
Ejector guide bushings complement guide pins by providing a precise and smooth bearing surface for the guide pillars to slide into.
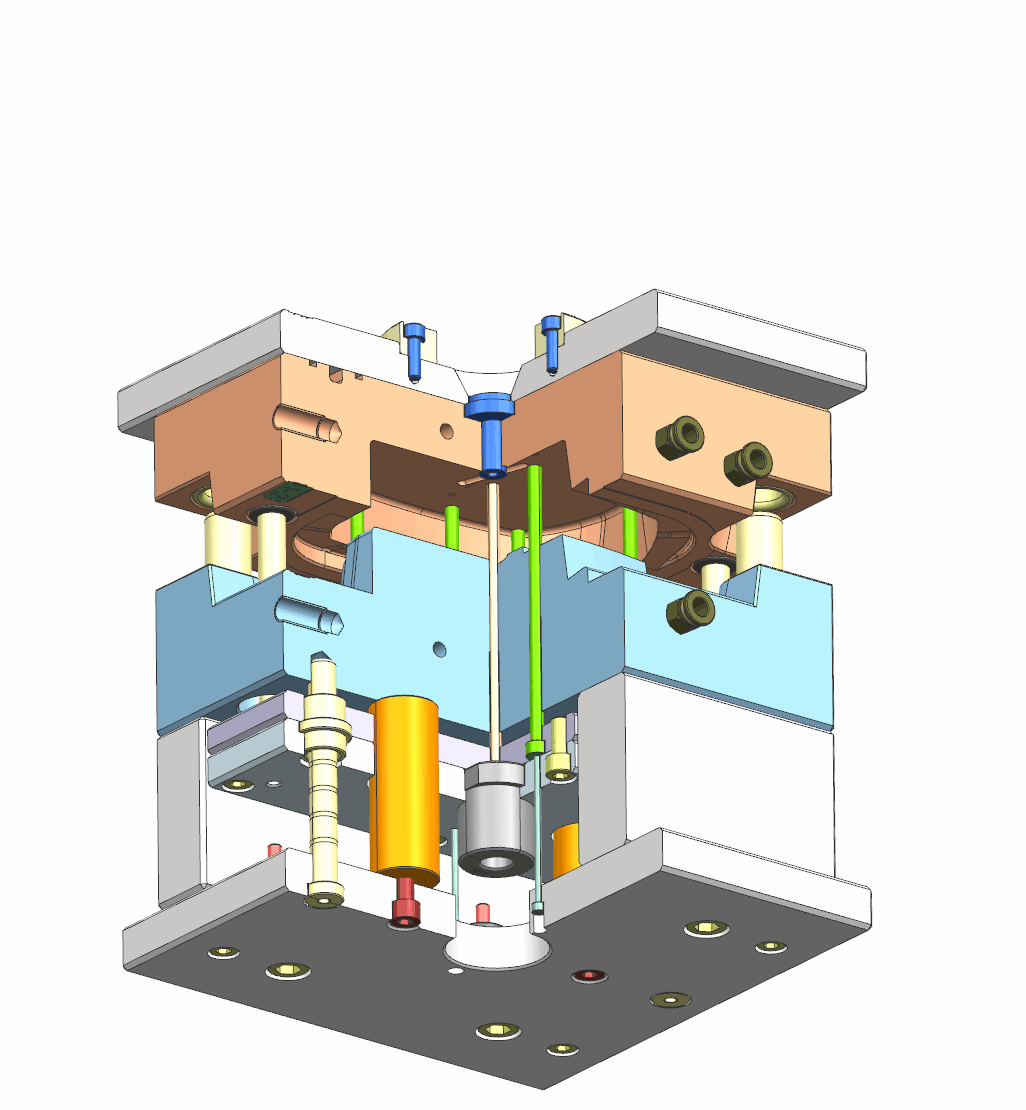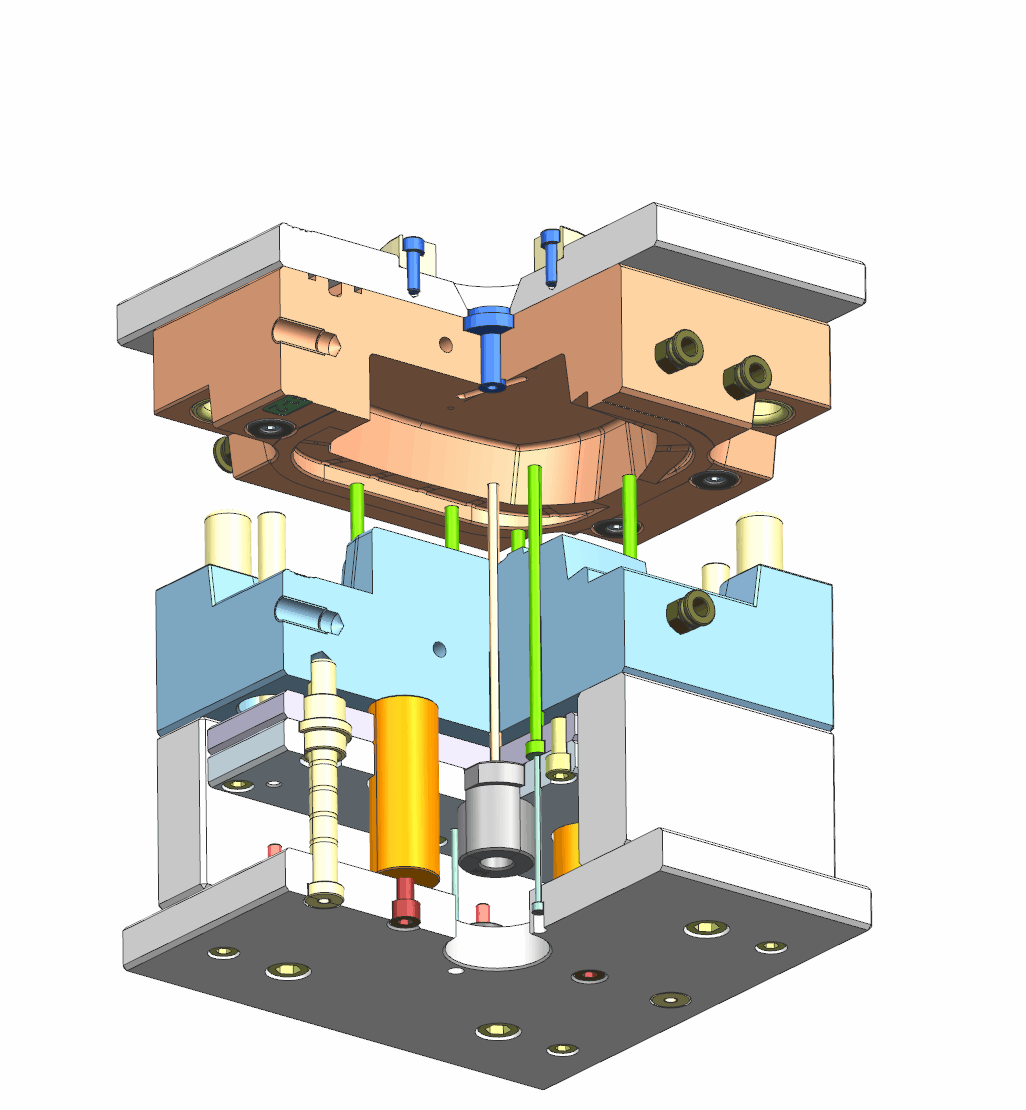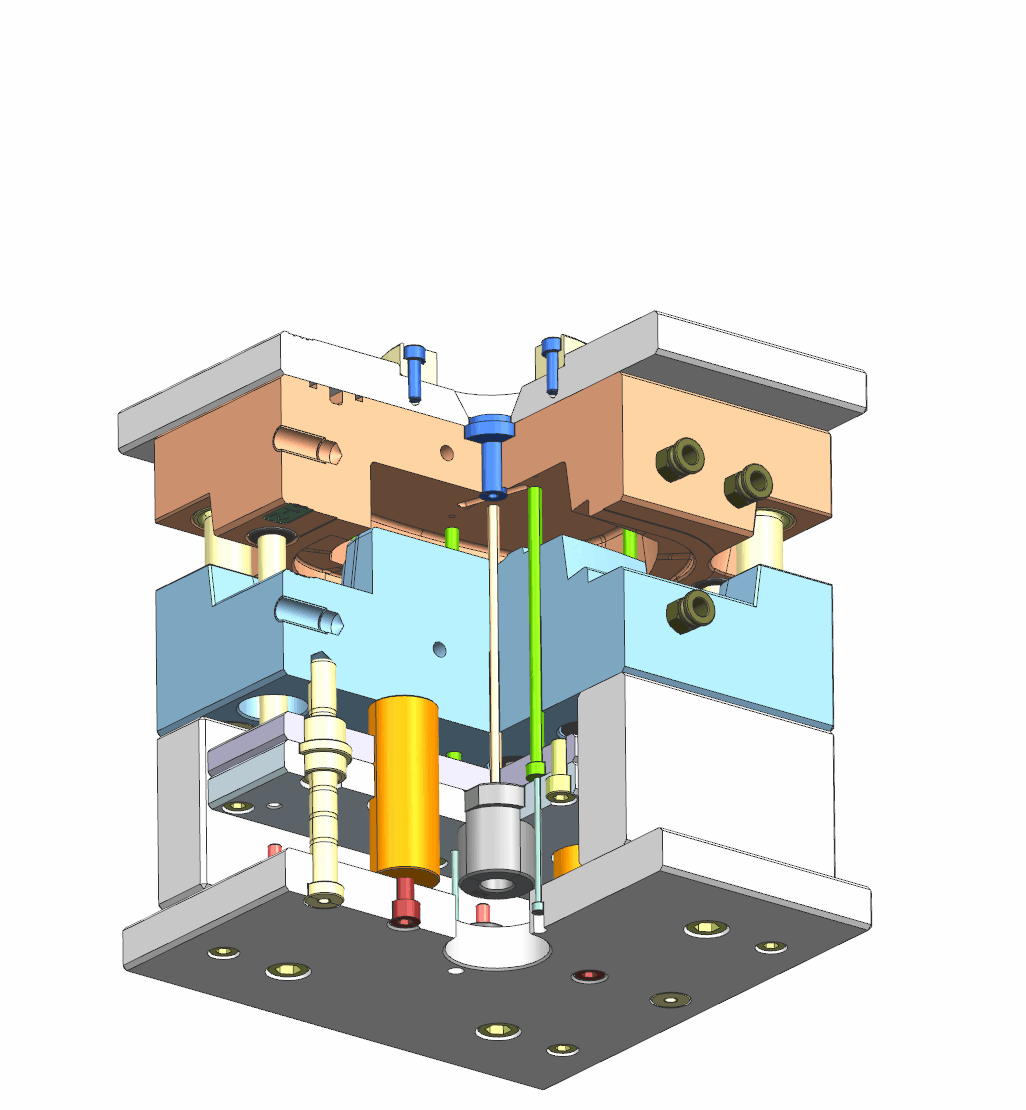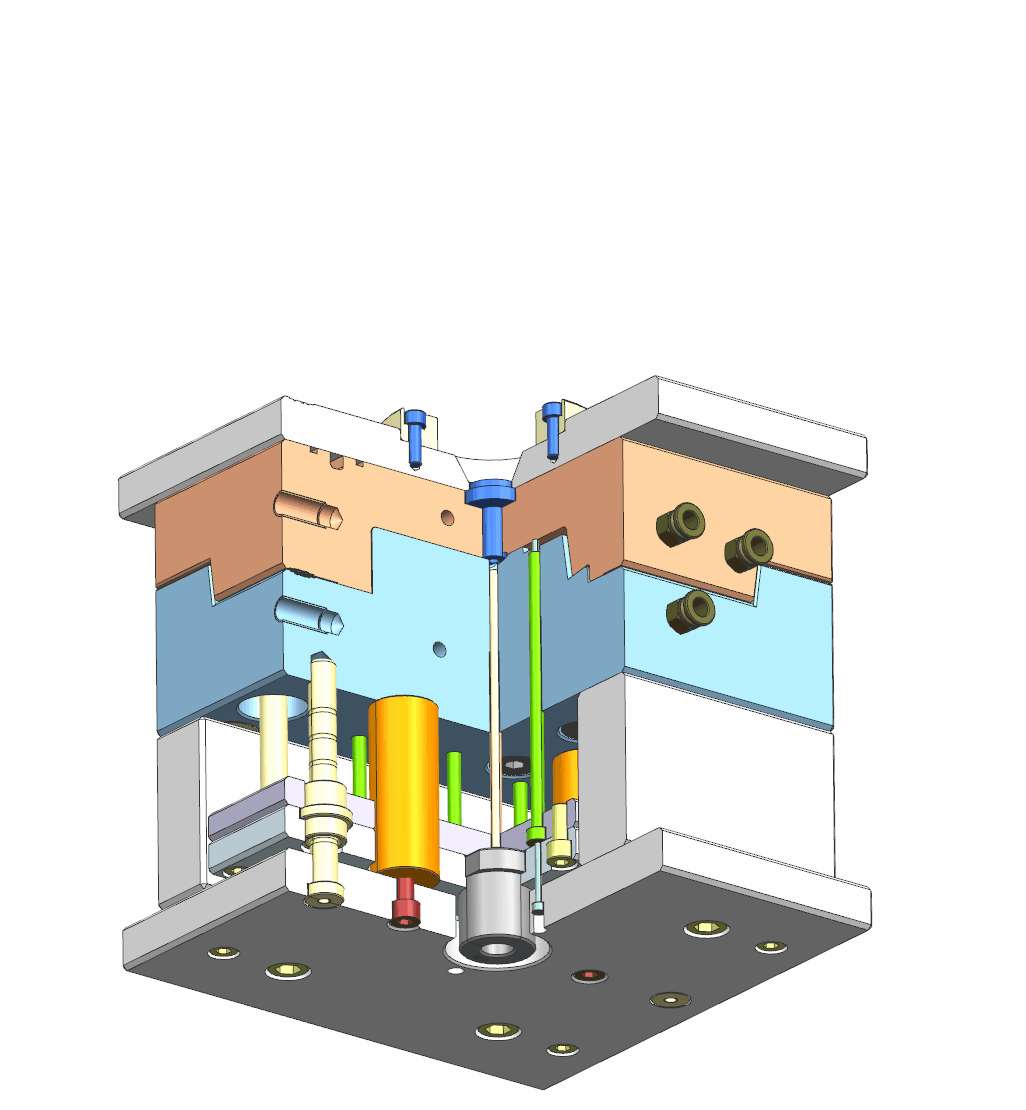
3. Injection & cooling system
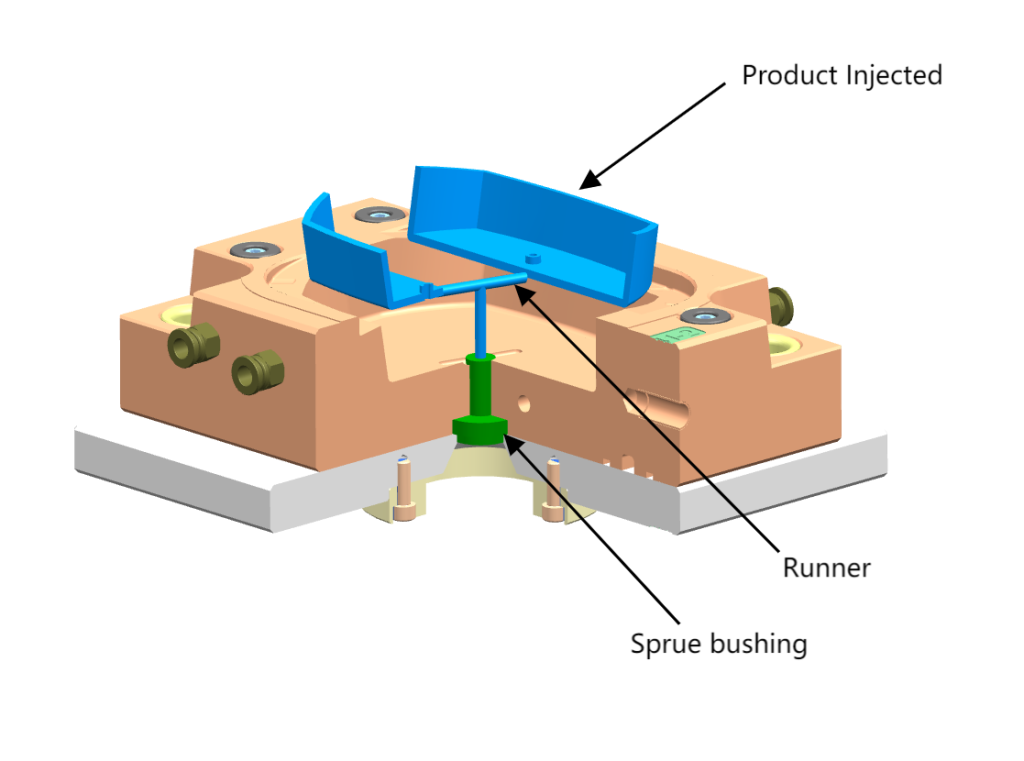
- Sprue Bushings
Its primary function is to direct the molten plastic from the injection molding machine’s nozzle into the mold cavity
- Water Connectors
Naturally, the mold has water channels for cooling the parts. The water connectors are for quick water connections.
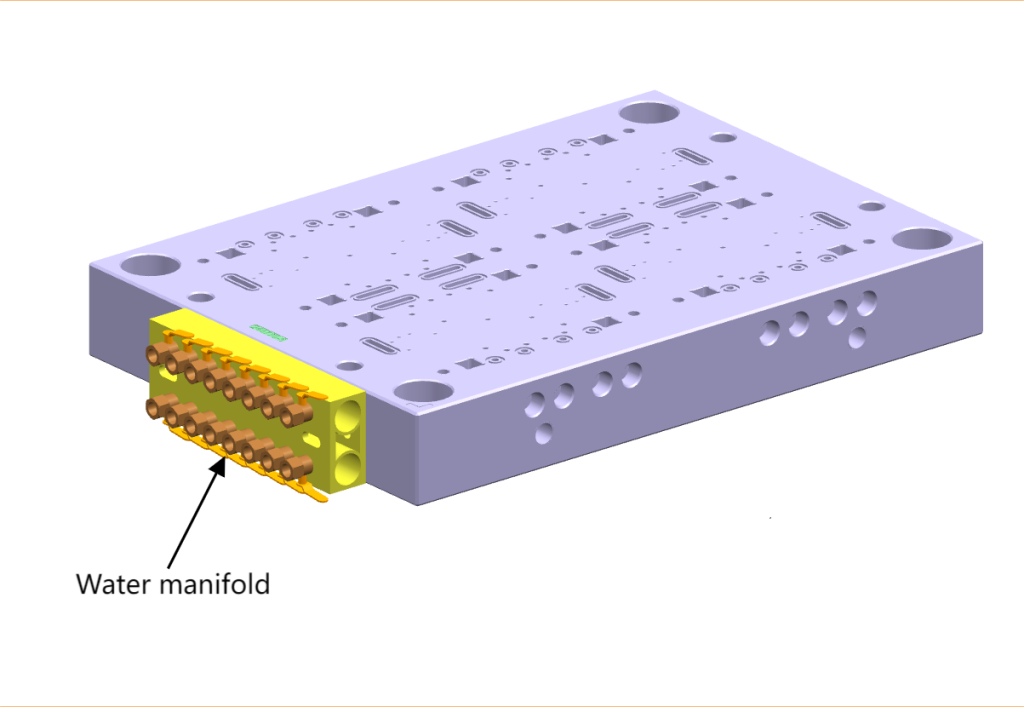
- Water Manifold
Water manifold connects the cooling channels of the mold to a centralized water supply, ensuring consistent temperature control during the molding process.
Hot runner Components
A hot runner is a resin distributor incorporated into the mold, equipped with heaters and thermocouples to keep the resin melted during production.

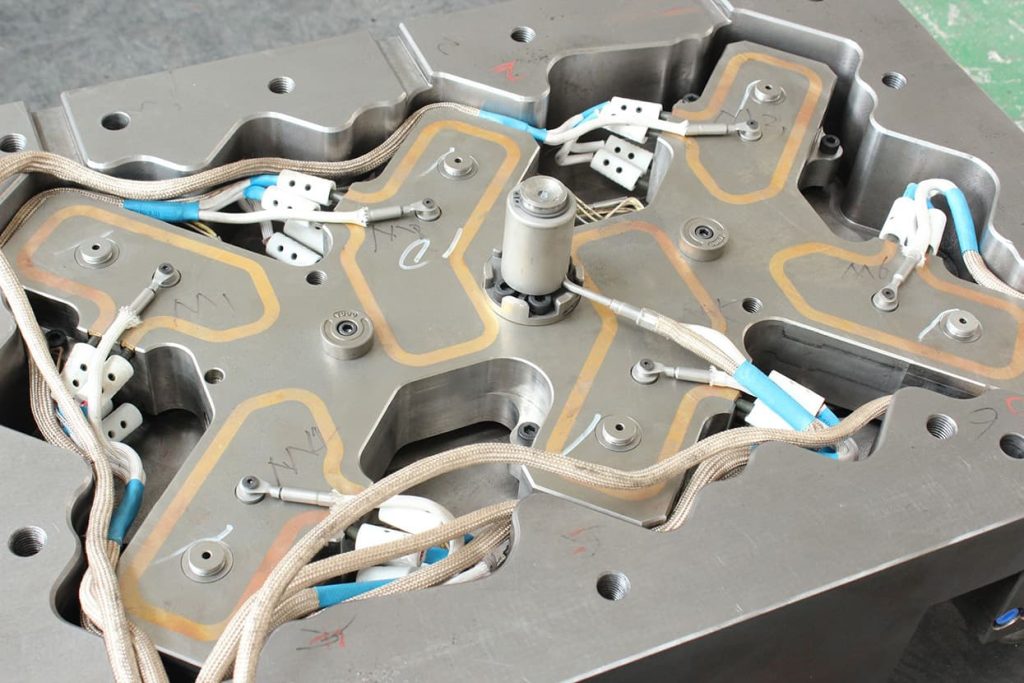
- Water jacket
Water jacket regulates temperature by circulating coolant, preventing overheating. This ensures even flow of molten material and enhances both production efficiency and product quality
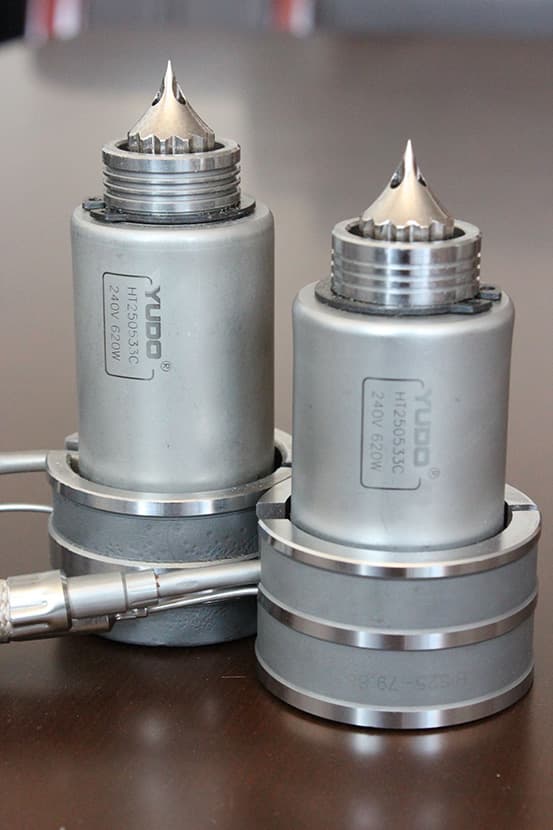
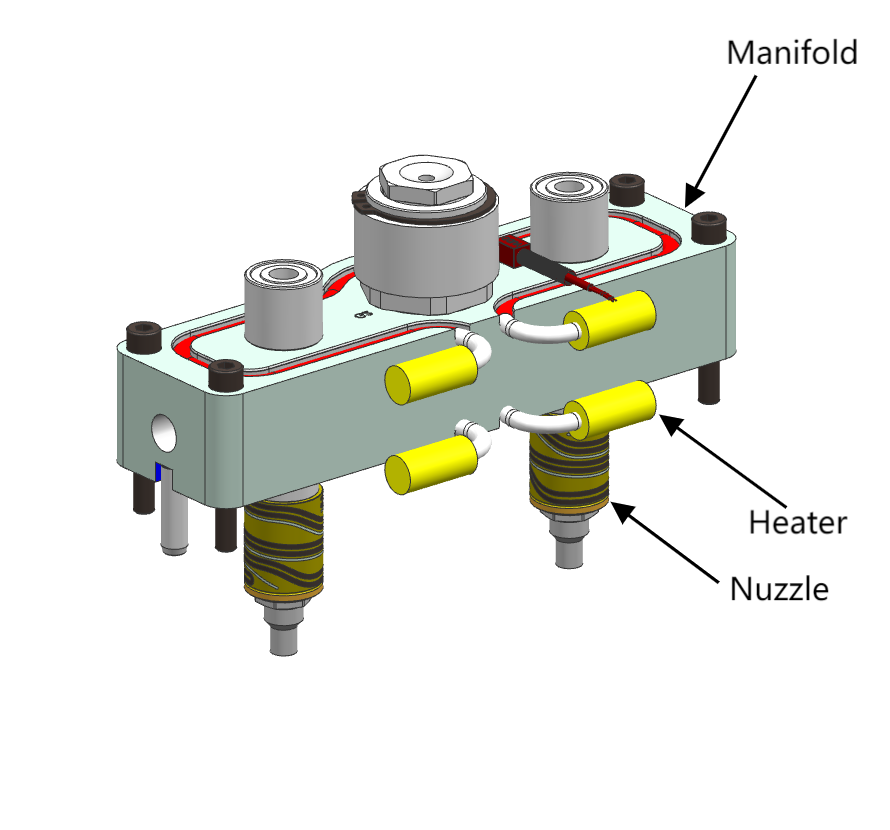
- Nozzles
Nozzles connect to the hot runner and point to the product surface. They also have heaters to keep the resin melted during production.
- Manifold
Manifold distributes molten material from the nozzle to multiple cavities, ensuring uniform flow and consistent filling across all cavities.
- Heater
Heater maintains the temperature of the hot runner system by heating the manifold and nozzle.
Complex ejection components
In addition to the basic parts, some injection molds have complex ejection system depending on the characteristics of the parts.
- Sliders
Sliders are parts that move to facilitate the demolding of negative draft features in injected parts. They can be driven by mechanical systems, pneumatic pistons, or hydraulic cylinders.
- Ejector ring
Ejection ring is circular, ring-like component that apply force evenly around the perimeter of a part to eject it from the mold. Typically used for parts with a circular cross-section and are ideal for maintaining the integrity of delicate or thin-walled parts.
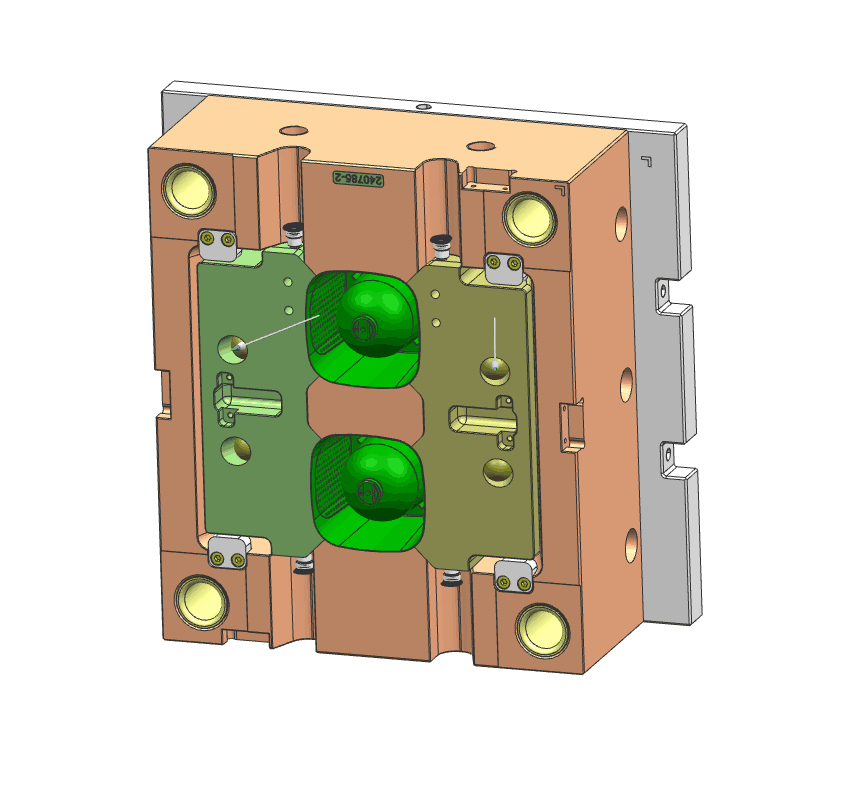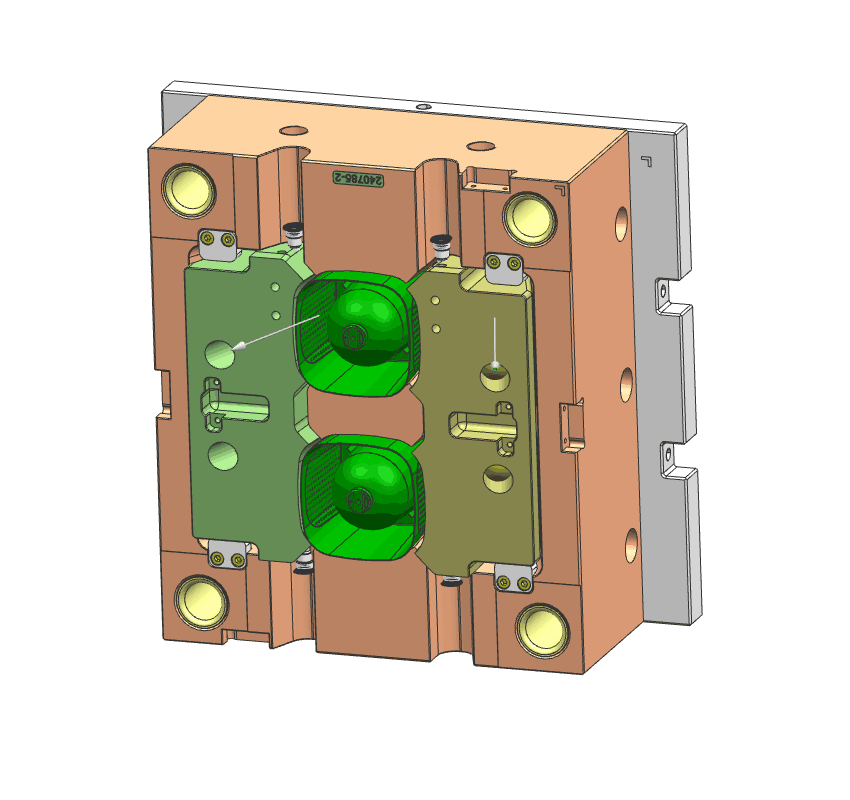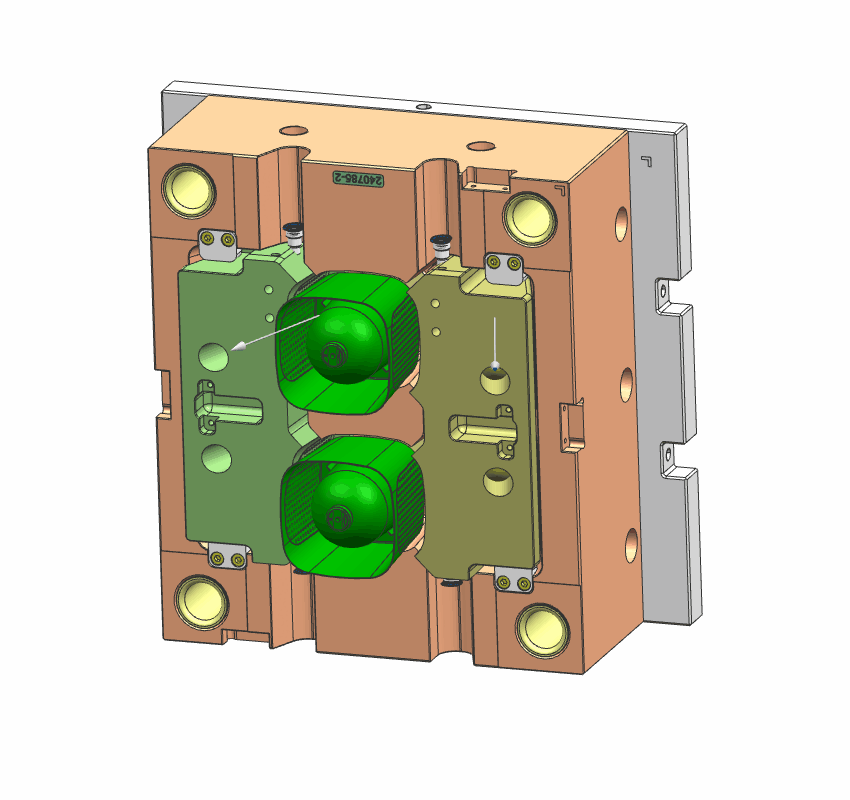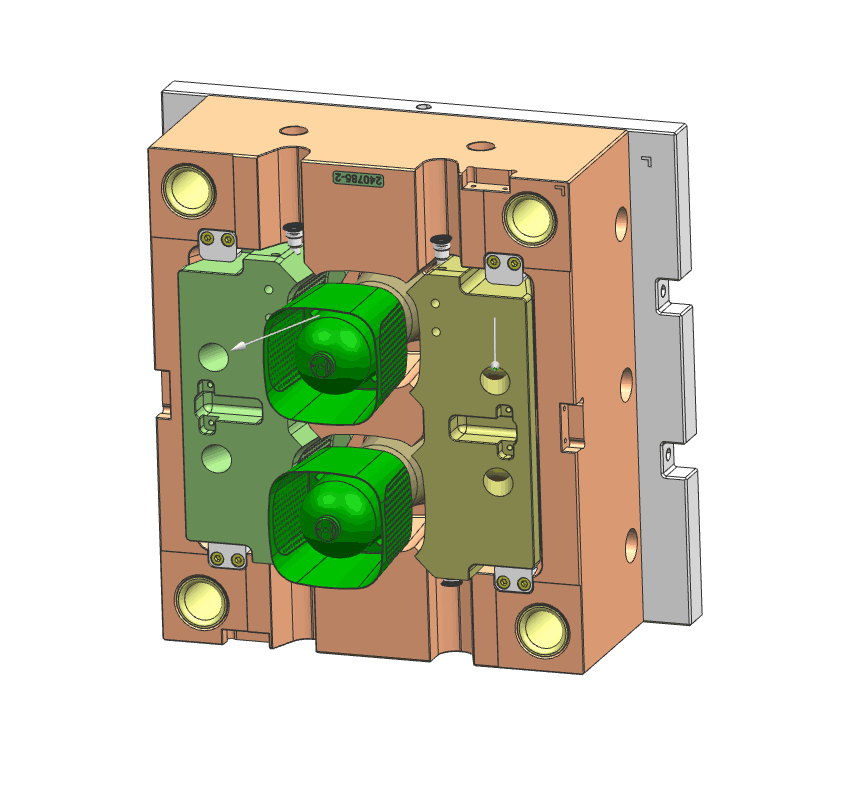
- Lifter
lifter is a mechanism that moves a part of the mold to eject molded components with undercuts or complex shapes. It helps in removing the part from the mold cavity by pushing it out or separating it from the mold core.