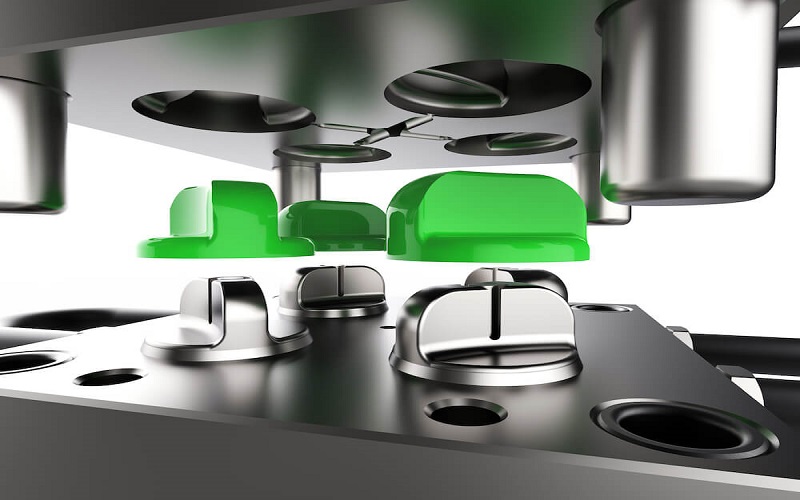
Prototype plastic injection molding quickly creates plastic prototypes for testing before full production. This method helps validate designs, reduce risks, and control costs. In this article, we’ll cover the benefits, applications, and comparisons with other methods like 3D printing.
Key Takeaways
- Prototype plastic injection molding accelerates product development by enabling rapid creation and testing of high-quality prototypes across various industries.
- Comparative advantages highlight that 3D printing is ideal for early-stage prototypes, while injection molding is more suitable for larger quantities and real-world testing.
- Key considerations in prototype design include material selection, wall thickness management, and ensuring consistent quality to facilitate effective transitions from prototype to production.
Understanding Prototype Plastic Injection Molding
Prototype plastic injection molding rapidly and efficiently creates a prototype mold using prototype tooling, essential for testing designs before full-scale production. This process offers reduced lead times and the ability to quickly produce high-quality, functional prototypes.
Various industries, such as automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods, use this process to validate designs and functional requirements.
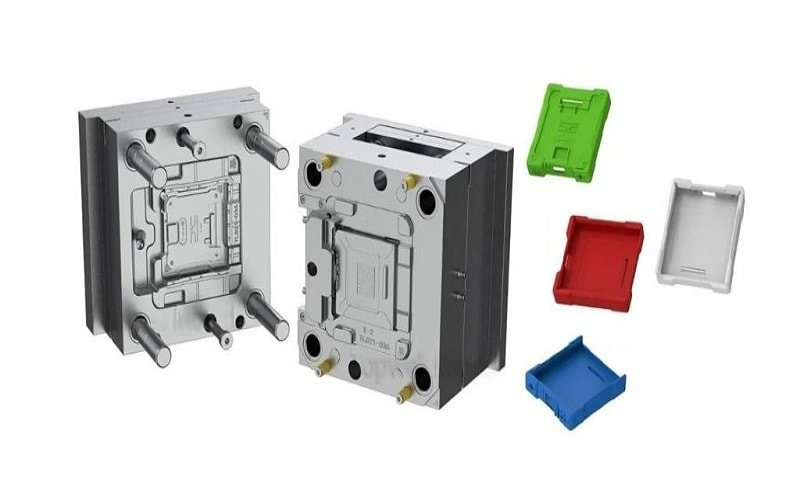

What is Prototype Plastic Injection Molding?
Prototype injection molding creates physical plastic prototypes for testing and refining designs before full-scale production. This process mitigates risks, ensuring high-quality output and allowing evaluation of functional and critical appearance features before prototype molding and mass production.
Options for prototype injection molds closely resemble those for long-term production projects, providing versatility in design. Prototypes can use a wide selection of plastic materials, including engineering plastics like PEEK for specific applications. Prototype molds often use softer materials like aluminum or semi-hardened steel, speeding up production.
Benefits of Prototype Plastic Injection Molding
A key benefit of prototype plastic injection molding is its cost-effective solution for testing complex product designs without extensive tooling investments. This method significantly cuts down product development time by enabling faster testing and iteration.
Additionally, prototype injection molding lowers design risk, shortens time-to-market, and enhances design and performance.

Applications Across Industries
Various industries, including aerospace and medical devices, utilize injection molding. Sectors like consumer goods, energy, electronics, automotive, robotics, and toys also employ it for diverse applications. For example, injection-molded parts are used in medical IVD testing and clinical trials.
A practical example is the development of the bow alignment tool Tuning ForksTM by Keith Shetler using injection molding services. This wide range of applications highlights the versatility and importance of prototype plastic injection molding across various sectors.
Comparing 3D Printed Prototypes to Injection Molded Prototypes

Both 3D printing and prototype injection molding offer unique advantages for prototyping. 3D printing excels at initial prototypes and designs requiring flexibility and rapid iteration. Injection molding, however, is more efficient for larger quantities due to its faster cycle times.
It’s important to note that 3D-printed prototype molds don’t represent true production injection molding conditions.
Advantages of 3D Printing for Prototypes
3D printing significantly cuts setup and lead times compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Without tooling costs, production becomes more economical, especially in low quantities. Designers can create complex geometries that are difficult or impossible with injection molding.
Overall, the speed, cost-effectiveness, and design flexibility of 3D printing make it an advantageous method for early-stage prototypes.

When to Choose Injection Molded Prototypes
Injection molded prototypes are essential when the final manufacturing process will involve injection molding. They suit complex designs or innovative products with unknowns. Injection molding is preferred for real-world testing due to its consistent part production. It benefits the validation of designs with intricate features or materials.
Higher production volumes justify the initial tooling costs of injection molding. Injection molding also offers a lower cost per unit for larger quantities compared to machining or 3D printing.
Key Considerations in Prototype Injection Mold Design
Design ensures the functionality, aesthetics, materials, and overall performance of injection molded parts. Maintaining a constant wall thickness and alignment with the mold opening is important in injection mold design. Effective material flow management avoids voids and incomplete filling in large injection molded parts, ensuring quality.
Common challenges in prototype injection molding include warping and shrinkage, often due to material selection and mold design. Prototype molds can be modified by plugging the metal and machining new geometry for iterative design improvements.
A thorough stress analysis during design can identify potential weaknesses affecting part dimensions.
Material Selection for Prototype Injection Molds
Material choice greatly impacts the performance and durability of prototype molds. Abrasive injection molding materials like glass-filled nylon cause quicker wear in prototype injection molds. This causes the molds to deteriorate faster. Low-shrinkage materials like amorphous polymers can minimize shrinkage and warping in injection molded parts.
MUD tooling enables quick changes in mold inserts, facilitating rapid design adjustments. Mold-flow simulation tools help assess manufacturability during injection molding projects.

Gate Design and Placement
Choosing the right gate type and location is crucial in prototype injection molding for even mold cavity filling and consistent part quality. Proper gate positioning ensures the even distribution of plastic during the injection process.
Design adjustments for gates and runners can reduce flow lines and other surface imperfections in molded prototypes. Proper venting in molds can prevent surface defects by allowing trapped air to escape during the injection process.
Prototype injection molding enables testing of gate type or location. This approach offers valuable insights into design considerations.
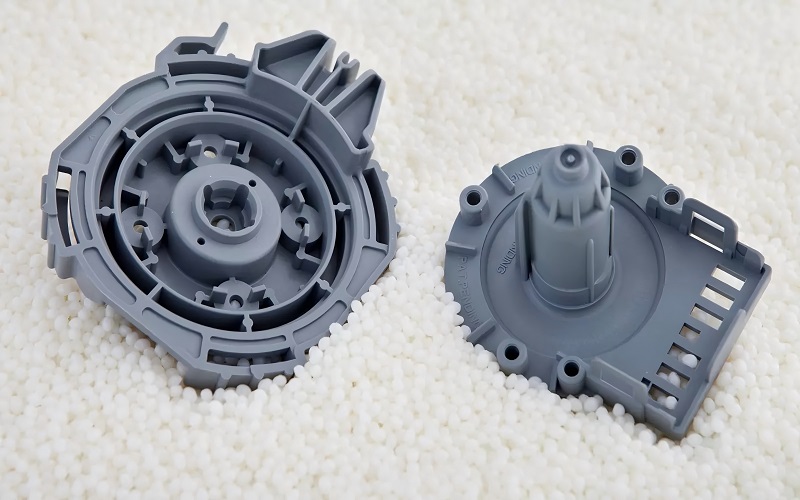

Managing Wall Thickness and Surface Finish
Consistent wall thickness optimizes the structural integrity of molded parts. Inconsistent wall thickness may cause structural weaknesses. Uniform wall thickness in part design reduces the likelihood of shrinkage and warping.
Controlling temperature and pressure during the injection process can mitigate surface defects like sink marks and flow lines.
Rapid Prototype Injection Molding Techniques
Rapid injection molding uses faster tooling processes than traditional methods, providing quicker access to prototypes. Rapid injection molding often accommodates design complexity, offering flexibility in prototype creation.

Aluminum Molds for Rapid Prototyping
Aluminum prototype injection molds are a better choice than 3D-printed molds for prototype injection molding. Aluminum molds showcase their effectiveness, dispelling the stigma that they are only suitable for prototyping.
Rapid prototype injection molds offer considerable cost advantages compared to traditional molds. Aluminum molds can be produced in about half the time of steel molds, significantly speeding up prototyping. Typically, aluminum molds last around 10,000 cycles before requiring replacement.
Using aluminum molds can lower initial tooling costs by up to 66%.
Utilizing MUD Tooling for Prototypes
Master Unit Die (MUD) tooling provides a standard mold frame. It includes customized, removable inserts, enhancing its versatility. This setup allows for quick changes and adjustments, making it efficient for rapid prototype injection molding.
Achieving Production Quality with Rapid Prototyping
Maintaining high-quality standards in rapid prototyping ensures parts meet production specifications. Rapid prototyping can produce parts with cycle times as short as 45 seconds, significantly boosting efficiency.
A robust quality control system catches defects early in the production process.
Transitioning from Prototype to Production Injection Molding
While not a high-volume production process, prototype injection molding is crucial for developing production-ready components. Maintaining high-quality standards during the transition to production molds is crucial.
Upon receiving an order for injection molding prototypes, a review is conducted and a case manager is assigned. Initiating an injection molding project requires material specifications, surface finish preferences, production volume estimates, and delivery dates.
Inexpensive materials like polyphenylsulfone (PPSU) can effectively create functional, works-like prototypes.
Scaling Up: From Prototype Molds to Production Molds
Prototype injection molding experience equips teams with knowledge for production. The typical injection molding cycle time is 45-60 seconds, crucial for maintaining production pace. Molded parts can be shipped in as little as five business days, facilitating quick turnaround.
In designing production injection molds, the focus should be on achieving the fastest cycle times and highest quality parts. Engineering changes may be required to adapt prototype designs for mass production. Depending on project complexity, one or more engineering changes may be necessary during the transition to production.
Ensuring Consistent Quality in Production Parts
To achieve representative samples for production, it is essential to use the same material and process planned for full-scale production. Common causes of failure in production injection molding are often related to wall thickness. Walls can be too thick, too thin, or non-uniform.
Conducting a design for manufacturability assessment using mold-flow simulation tools is key to ensuring that designs are production-ready. Maintaining quality and consistency during the transition to production molds is crucial for the success of the final product.
Cost Management in Production Injection Molding
The cost of initial tooling with MUD molds can be significantly reduced, making them budget-friendly options for prototyping. Understanding and optimizing production parameters can lead to significant cost savings during mass production. Effective cost management is crucial for balancing budgets and ensuring a successful transition from prototype to mass production.
Implementing cost-effective production tooling and optimizing production processes are key strategies for managing costs in production injection molding.
Common Challenges in Prototype Injection Molding and How to Overcome Them
Successful transition to mass production requires thorough evaluation of prototypes to ensure they meet design specifications. Optimizing mold production is essential to prevent issues such as warping and ensure efficient production.
Establishing standard operating procedures for process parameters helps in achieving consistency during production.
Addressing Material Shrinkage and Warping
Shrinkage and warping in injection molded parts are influenced by the type of plastic used, the design of the mold, and various processing parameters. Real-time monitoring is vital to detect and address quality issues promptly during production.
Utilizing low-shrinkage materials and thorough mold-flow simulations helps minimize these issues, ensuring better quality parts.
Preventing Surface Defects
Common surface defects in injection molded parts include sink marks, flow lines, and gate imperfections. These can be mitigated by optimizing the manufacturing process, selecting appropriate materials, and implementing design changes to ensure a high-quality surface finish.
Proper venting and maintaining consistent temperature and pressure during the injection process are also crucial in preventing surface defects.
Ensuring Accurate Critical Dimensions
Achieving tight tolerances in injection molded parts is essential for ensuring they function correctly in their intended applications. Dimensionally tight tolerances are important for injection molded part to perform properly.
There are two main types of tolerances in injection molding: commercial and fine tolerances. Non-uniform or unreasonable wall thickness can lead to many production failures in injection molded parts. Utilizing multiple gates can enhance the filling process, leading to improved dimensional accuracy in complex parts.
Summary
In summary, prototype plastic injection molding is an invaluable tool in the product development process. It allows for rapid testing and iteration, reduces risks, and speeds up time-to-market. By understanding the key considerations in mold design, material selection, and rapid prototyping techniques, manufacturers can ensure a smooth transition from prototype to production. Embracing these best practices will not only enhance product quality but also provide a competitive edge in various industries. As you embark on your next injection molding project, remember the insights shared in this guide to achieve success and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is prototype plastic injection molding?
Prototype plastic injection molding is a rapid manufacturing process that produces physical plastic prototypes, allowing designers to effectively test and refine their products prior to full-scale production.
What are the benefits of prototype plastic injection molding?
Prototype plastic injection molding offers reduced lead times and cost-effective testing for complex designs, enabling the rapid production of high-quality, functional prototypes. This approach significantly enhances efficiency in the product development process.

How does 3D printing compare to prototype injection molding?
3D printing excels in creating initial prototypes due to its design flexibility and rapid iteration capabilities, while prototype injection molding is more efficient for producing larger quantities with consistent part quality.
What materials are commonly used for prototype injection molds?
Prototype injection molds are commonly made from softer materials such as aluminum or semi-hardened steel, as these materials enable quicker production and allow for iterative design refinements.
How can I ensure consistent quality in production parts?
To ensure consistent quality in production parts, utilize the same materials and processes as planned for full-scale production, perform design for manufacturability assessments, and implement thorough quality control systems. These measures will help maintain high standards throughout the production process.

