Why is injection molded ABS plastic so popular in manufacturing? Discover its key benefits, properties, and applications in injection molding. Learn how its durability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility can transform your production process.
Key Takeaways
- ABS plastic is a cost-effective and durable thermoplastic, featuring a unique composition that grants it excellent impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
- The injection molding process for ABS involves multiple stages, including mold design, material preparation, melting, injecting, cooling, and ejecting, all of which are critical for achieving high-quality components.
- While ABS plastic offers versatile applications across various industries, its production poses environmental challenges, necessitating improved recycling processes to mitigate negative impacts.
What is ABS Plastic?

Before: ABS plastic, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a popular thermoplastic known for its cost-effectiveness and high durability. As the name suggests, it is composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Each component imparts specific characteristics to ABS, making it a versatile thermoplastic suitable for various applications. Acrylonitrile enhances fatigue and chemical resistance, butadiene provides toughness across a wide temperature range, and styrene contributes to the material’s glossy finish and rigidity.
After: ABS plastic, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a popular thermoplastic known for its cost-effectiveness and high durability. It is composed of three monomers:
- Acrylonitrile, which enhances fatigue and chemical resistance
- Butadiene, which provides toughness across a wide temperature range
- Styrene, which contributes to the material’s glossy finish and rigidity
Each component imparts specific characteristics to ABS, making it a versatile thermoplastic suitable for various applications.
The material properties of ABS plastic include excellent impact resistance, making it a preferred choice for products subjected to physical stress. Its ability to maintain performance under various conditions, coupled with its affordability, makes ABS a go-to material for industries ranging from automotive to consumer electronics.
This blend of mechanical strength and aesthetic appeal underscores why ABS plastic is widely favored in plastic injection molding processes.
Key Benefits of Injection Molded ABS Plastic
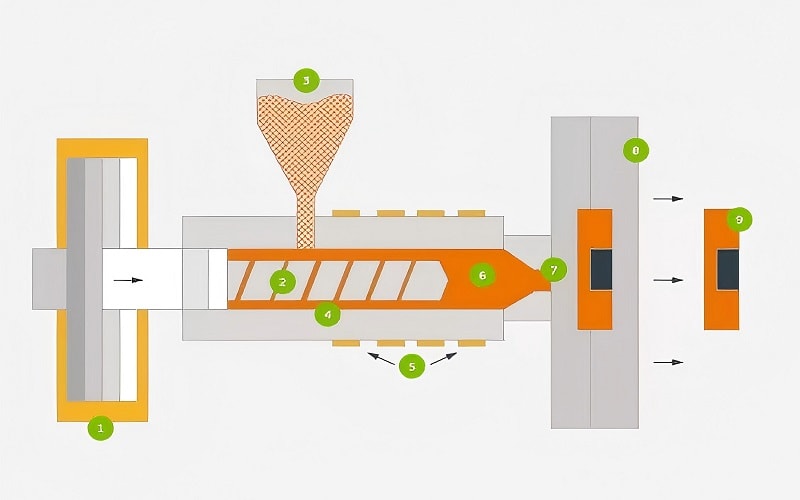
One of the standout benefits of ABS injection molding is its high impact resistance and rigidity, essential for parts that endure significant physical stress. This resilience ensures that products made from ABS can withstand daily wear and tear, making them reliable and durable. Moreover, ABS plastics offer excellent dimensional stability, crucial for maintaining tight tolerances in high-volume production. Additionally, abs plastic injection molding is an effective method for producing high-quality components.
Another significant advantage is the cost-effectiveness of ABS plastic. Compared to other injection-molded plastics, ABS is relatively inexpensive, which helps manufacturers manage production costs without compromising on quality. Additionally, the ABS injection molding process is energy efficient due to the lower processing temperatures required, further reducing production expenses.
The versatility of ABS plastic also extends to its aesthetic qualities. ABS can be molded into parts with a high-gloss finish, making it suitable for consumer electronics and automotive interiors. Whether it’s the sleek design of a computer keyboard or the sturdy build of household appliances, the key benefits of ABS injection molding make it an ideal choice for a wide range of products.
The Injection Molding Process for ABS Plastic
The ABS injection molding process is a meticulous procedure that requires careful regulation of injection pressure and temperature to ensure high-quality injection mold part production.
The process can be broken down into four major stages:
- Designing the mold
- Preparing the ABS material
- Melting and injecting the ABS
- Cooling and ejecting the part.
Each stage plays a crucial role in achieving the desired properties and dimensions of the final product.
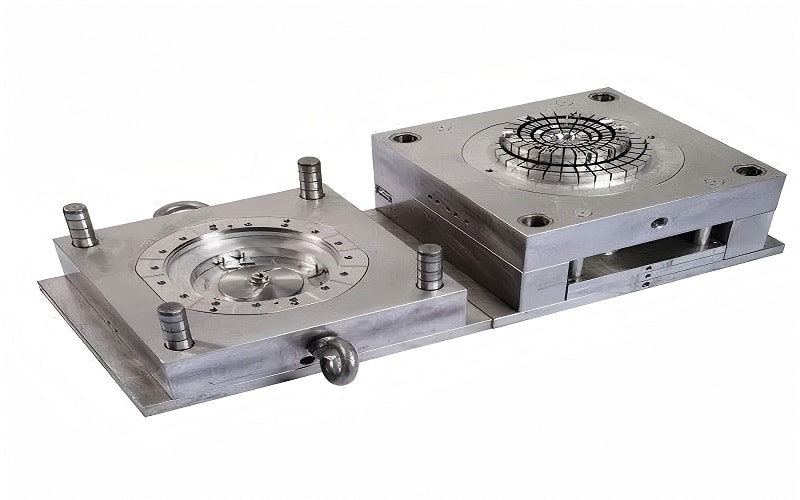
Designing the Mold for ABS
Designing the mold for ABS injection molding involves a deep understanding of ABS plastic properties. ABS, being an amorphous plastic, offers flexible molding capabilities compared to more crystalline polymers. The mold design must account for the material’s behavior under heat and cooling, ensuring that the molten ABS fills the mold cavity uniformly and solidifies without defects.
Attention to details like wall thickness is critical during the mold design phase. Variations in wall thickness can lead to flow lines and other surface defects. Therefore, a well-designed mold helps in minimizing defects and achieving consistent quality in the injection-molded parts.
Preparing ABS Material
Selecting the appropriate grade of ABS is crucial for achieving the desired mechanical properties and ensuring successful molding outcomes. Before the molding process begins, the ABS material must be dried to reduce its moisture content to 0.05% or less. Excess moisture can lead to surface defects and reduced mechanical properties in the final product.
Industrial-grade dryers are typically used to remove moisture from ABS material. The drying process involves subjecting the material to specific temperatures for a predetermined time, usually taking three to four hours.
Proper preparation ensures that the ABS material is in optimal condition for the injection molding process.

Melting and Injecting ABS
The melting and injecting phase of ABS plastic involves heating the material to a temperature range between 170°C and 320°C, depending on the specific grade used. The liquefied ABS, now molten ABS, is then injected into the mold cavity. Maintaining the correct injection pressure is critical; too low can lead to mold shrinkage and inferior quality components, while too high can cause defects like jetting and flash.
The injection molding process for ABS has three key stages. These are filling, packing, and holding. During these stages, the speed and pressure must be carefully controlled to prevent issues such as thermal decomposition, poor glossiness, and weld lines. Properly managing these parameters ensures that the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
Cooling and Ejecting the Part
Cooling channels integrated into the mold design are essential for ensuring that molten ABS cools uniformly, preventing defects like warping and sink marks. Once the part has cooled sufficiently, ejection pins help release it from the mold. The cooling and ejection phase is critical for maintaining the dimensional stability and surface quality of the injection-molded parts.
After ejection, each component undergoes a visual and dimensional inspection to ensure it meets quality standards. Any excess material is trimmed, and the parts are prepared for further processing or assembly. This meticulous cooling and ejection process is vital for producing high-quality ABS molded parts.
Applications of ABS Injection Molded Parts
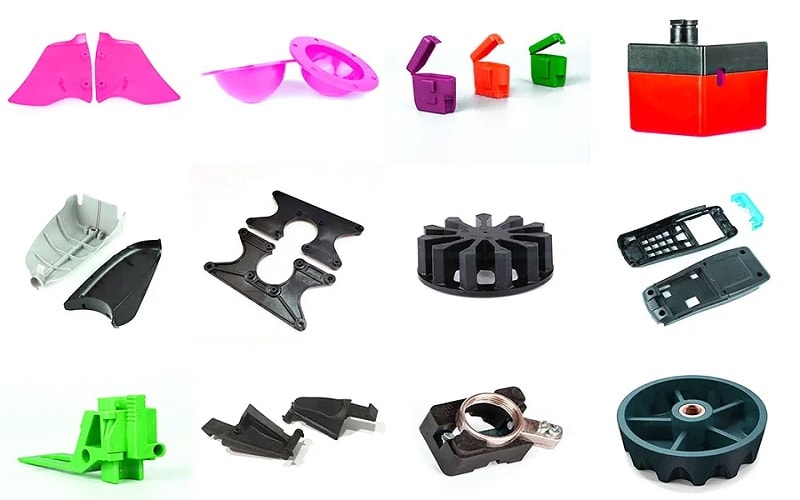

ABS injection-molded parts find applications in various industries due to the material’s excellent properties. In the automotive sector, ABS is used for interior components like instrument panels and door linings, thanks to its rigidity and formability. The material’s impact resistance and ability to withstand harsh chemicals also make it suitable for industrial applications.
Household appliances like refrigerators and washing machines often incorporate ABS plastic for its durability and aesthetic appeal. In the medical field, ABS is used for surgical instruments and casings for medical devices, benefiting from its compatibility with sterilization processes.
The versatility of ABS plastic makes it an invaluable material across various industries.
Challenges and Solutions in ABS Injection Molding

One of the primary challenges in ABS injection molding is managing moisture content. Excess moisture can lead to surface defects and reduced mechanical properties. To mitigate this, ABS material must be thoroughly dried before processing. Proper moisture management ensures improved performance and longevity of injection-molded ABS parts.
Another challenge is controlling the injection pressure and temperature. Incorrect settings can result in defects like sink marks, weld lines, and thermal decomposition. By closely monitoring and adjusting these parameters, manufacturers can produce high-quality ABS molded parts with minimal defects.
Addressing these challenges effectively leads to superior end products.
Partnering with Experts for ABS Injection Molding
Collaborating with experienced manufacturers for ABS injection molding projects brings numerous benefits. These experts have industry-specific knowledge and understand the unique requirements of different projects. Effective communication between technicians and mold-building teams is crucial for a successful injection molding process.
Manufacturers can also assist in selecting the appropriate materials based on factors like durability requirements and environmental conditions. Choosing an injection molding partner with ISO certification ensures that quality standards are consistently met. Partnering with experts guarantees a smoother, more efficient production process.
Comprehensive ABS Plastic Molding Services
A reliable injection molding company should offer a full-service package, covering:
- Consultation
- Design
- Prototyping
- Production
These services ensure that all aspects of the project are handled professionally, from initial concept to finished product.
Advanced manufacturers provide program management to optimize cost and quality control for production orders. High-quality ABS molding services often include secondary operations such as CNC machining and finishing services. With quick turnaround times, some companies can deliver prototypes in as little as one day.
Environmental Impact and Recycling of ABS Plastic

The production of ABS plastic heavily relies on petroleum, contributing to environmental issues such as habitat destruction and pollution. Additionally, the chemical components of ABS can leach into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. These factors highlight the importance of considering ABS’s environmental impact.
Recycling ABS plastic is a complex process due to its mixed material composition and potential contaminants. While ABS can be melted down and reformed or recycled, its poor thermal stability can lead to degradation and the release of toxic fumes during recycling. Despite these challenges, recycling remains a viable option to reduce the environmental footprint of ABS plastic production.
Microplastics generated from degrading ABS can contaminate water and soil, entering the food chain and potentially impacting human health. Addressing these environmental concerns requires a concerted effort from manufacturers and consumers to improve recycling processes and reduce the use of virgin materials.
Summary
In summary, ABS injection molding offers numerous benefits, including high impact resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness. The detailed molding process, from designing the mold to cooling and ejecting the parts, ensures high-quality production. Despite challenges like moisture management and precise control of injection parameters, solutions exist to mitigate these issues.
ABS plastic continues to be a versatile and reliable material across various industries, from automotive to medical applications. As we move forward, addressing the environmental impact and improving recycling processes will be crucial. Embracing the benefits of ABS injection molding can lead to innovative solutions and sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ABS plastic?
ABS plastic, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a durable and impact-resistant thermoplastic that is both versatile and cost-effective. Its properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
What are the key benefits of injection-molded ABS plastic?
The key benefits of injection-molded ABS plastic are its high impact resistance, excellent dimensional stability, cost-effectiveness, and its capability to produce parts with a high-gloss finish. These attributes make it an ideal choice for various applications requiring durability and aesthetic appeal.
What challenges are faced in ABS injection molding?
ABS injection molding faces challenges such as managing moisture, regulating injection pressure and temperature, and avoiding defects like sink marks and weld lines. Addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring quality in the final product.
How is ABS plastic recycled?
ABS plastic is recycled by melting it down to reform into new products, although this process can be complicated due to its mixed composition and potential contaminants.
Why is it important to partner with experts for ABS injection molding?
It is crucial to partner with experts for ABS injection molding as they ensure a smoother production process, appropriate material selection, and compliance with quality standards, ultimately leading to superior end products.

