Injection moulding and thermoforming are two popular manufacturing methods with unique strengths.
When considering injection moulding vs thermoforming, it’s clear that injection moulding excels in producing intricate, high-volume parts, whereas thermoforming is cost-effective for simpler, large-scale items.
This article will guide you through their pros, cons, and best applications to help you choose the right one.
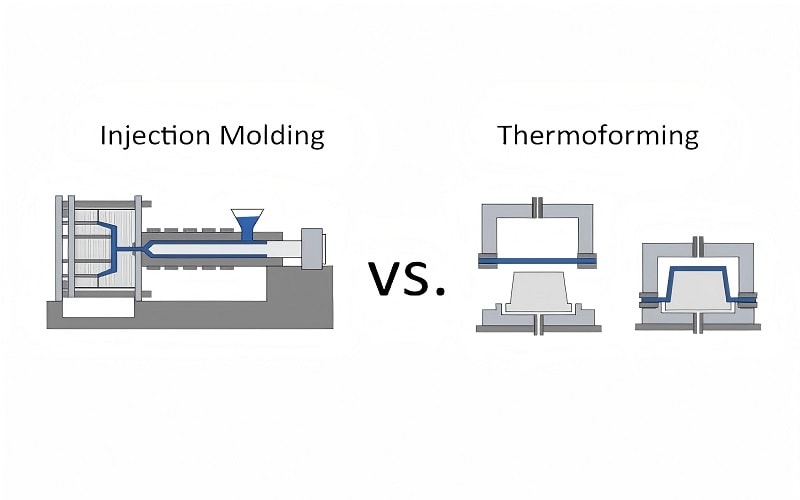
Understanding Injection Moulding and Thermoforming
Injection molding and vacuum thermoforming are the primary processes for producing plastic parts, including plastic injection molding. Widely utilized in the industry, these methods have revolutionized the plastic manufacturing process by offering distinct advantages based on specific requirements.
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into reusable molds under high pressure, creating highly detailed parts with precision.
Unlike injection molding, molten material thermoforming versus injection molding heats plastic sheets until pliable and then shapes them over molds using vacuum or pressure, making it ideal for simpler, larger components.
Grasping the nuances of these two processes aids in selecting the optimal approach for manufacturing needs.

What is Injection Moulding Process?
Injection molding is a meticulous process where plastic pellets are first heated and melted into a liquid state. This molten plastic is then injected into an injection mold cavity under high pressure using an injection molding machine, allowing it to take the shape of the mold.
The mold can be designed with one or multiple cavities, enabling the production of several parts simultaneously. After the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens, and the finished parts are ejected. This process is highly efficient for producing small, intricate parts with exceptional detail and precision.
The use of durable and reusable molds in injection molding contributes to its cost-effectiveness in production. The materials used for the molds, such as stainless steel or aluminum, ensure they withstand the high pressures involved.
Consequently, injection molding is favored for applications requiring complex designs and consistent quality, making it indispensable in industries like automotive, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
What is Thermoforming Process?
Thermoforming, in contrast, begins with heating a plastic sheet until it becomes pliable. This heated plastic sheet is then formed over a mold using vacuum pressure or mechanical force to take on the desired shape. Processes like vacuum forming and pressure forming are commonly used, each offering unique advantages depending on the specific application. Once the plastic cools, it solidifies, and the formed part is trimmed and finished.
One of the standout features of thermoforming is its ability to create parts with unique textures and finishes, enhancing product design and branding. The process allows for vibrant colors and customizable print options, making it an attractive choice for consumer products and packaging.
Thermoforming is particularly effective for producing large and simple shapes efficiently, often used in industries such as packaging, automotive, and construction.
Material Considerations in Injection Moulding and Thermoforming
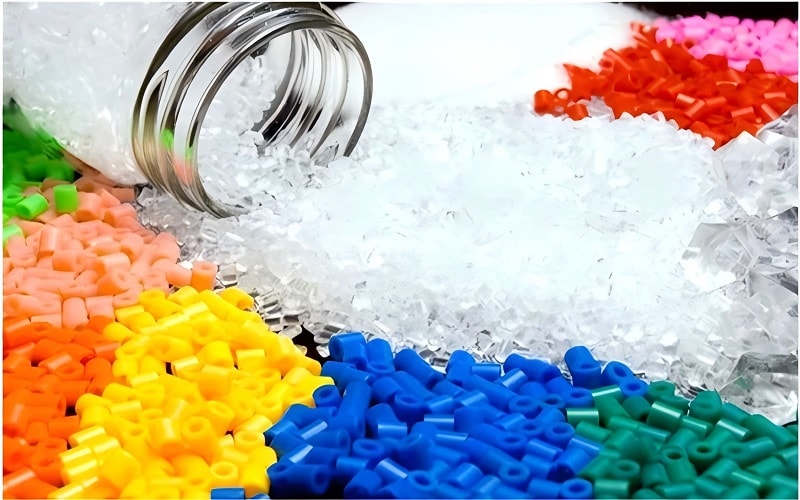

Selecting the right material is crucial for achieving the desired properties and performance in plastic parts. Both injection molding and thermoforming utilize a variety of materials, but the form and type of these materials differ. Injection molding typically uses plastic pellets, which are ideal for creating durable and complex parts.
Thermoforming, on the other hand, relies on plastic sheets, which offer flexibility and ease of processing for larger, simpler shapes. These material considerations optimize the manufacturing process for cost, efficiency, and product quality.
Suitable Materials for Injection Moulding
The quality of the final product and manufacturing efficiency heavily rely on material choice. Thermoplastics like polypropylene, polystyrene, and polycarbonate are common in injection molding for their durability and versatility.
Additives such as impact modifiers and colorants can be incorporated to enhance specific properties of the plastics, making them suitable for a wide range of applications from automotive parts to medical devices.
Suitable Materials for Thermoforming
Before:
Thermoforming often utilizes materials such as High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) due to their excellent forming characteristics. PETG is favored for its clarity and impact resistance, making it ideal for packaging and display items. Acrylic is another popular choice for thermoforming, valued for its clarity and ability to be formed into complex shapes.
After:
Thermoforming often utilizes materials such as:
- High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) due to its excellent forming characteristics
- Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG), which is favored for its clarity and impact resistance, making it ideal for packaging and display items
- Acrylic, which is valued for its clarity and ability to be formed into complex shapes
The use of thinner plastic sheets in thermoforming can also lower material consumption and waste, contributing to cost-efficiency and sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Injection Molding vs Thermoforming
Cost is a critical factor when choosing between injection molding and thermoforming. The overall expenses of each method are influenced by tooling, production volume, and material types. While thermoforming typically has lower tooling costs, injection molding’s higher initial investment can be offset by lower per-unit production costs in large volumes.
Analyzing these cost factors helps in making an informed decision based on the project’s budget and production requirements.
Injection molding and vacuum thermoforming are the primary processes for producing plastic parts, including plastic injection molding. Widely utilized in the industry, these methods have revolutionized the plastic manufacturing process by offering distinct advantages based on specific requirements.
Tooling Costs
Tooling costs vary significantly between injection molding and thermoforming processes. Injection molding involves higher initial tooling costs due to the need for durable molds made from materials like stainless steel or aluminum to withstand high pressures. These molds are designed for repeated use and can produce large volumes of parts over their lifespan, making the initial investment worthwhile for production.
In contrast, thermoforming molds, typically made from aluminum, are less costly and quicker to produce, leading to lower tooling costs.
Production Costs
Injection molding usually achieves lower per-unit costs when producing large quantities due to faster cycle times. For high volume production runs, injection molding becomes more cost-effective, as the high initial tooling costs are distributed over a large number of parts.
Conversely, thermoforming is a better choice for small production runs as it offers lower setup costs and flexibility in design changes. Thus, the choice between the two methods often hinges on the scale of production and the budget available.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
Design flexibility and complexity are vital considerations in manufacturing. Injection molding is capable of producing highly detailed and complex parts through the use of multi-cavity molds and techniques. In contrast, thermoforming allows for easier modification of designs, making it suitable for producing large and simple shapes efficiently.
Recognizing these design capabilities aids in choosing the right method for specific project needs.
Complexity in Injection Moulding
Injection molding excels at creating highly detailed and complex parts, making it ideal for intricate designs. The high pressure used during the injection molding process ensures precision and consistency in manufactured parts. Multi-cavity molds further enhance the capability to produce complex shapes efficiently, allowing for simultaneous production of multiple items.
This makes injection molding indispensable for industries that require high precision and detail, such as automotive and medical devices.
Flexibility in Thermoforming
Thermoforming offers significant flexibility in design, allowing for quick modifications with minimal cost. Changing thermoforming molds is easier and less expensive than altering injection molds, making thermoforming suitable for producing large, simple shapes and low-volume production.
This process is particularly effective for applications such as packaging, automotive panels, and construction materials where design changes are often required. The fast lead times and aesthetic possibilities further enhance the appeal of thermoforming for various industries.
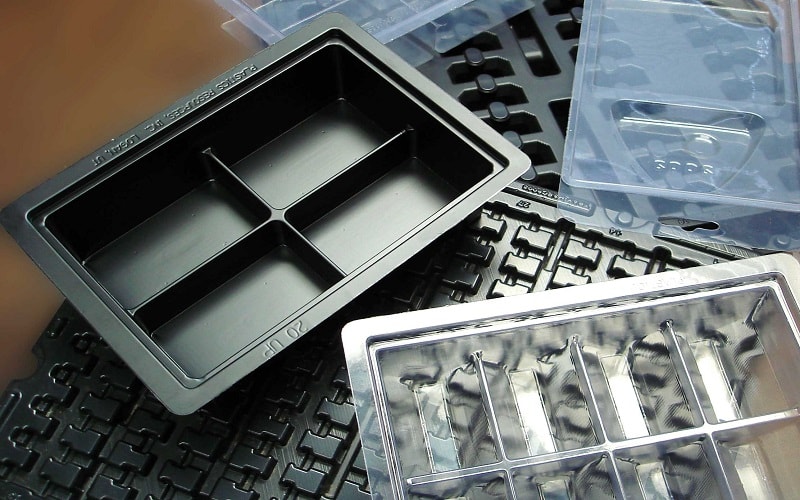

Production Volume and Efficiency
Production volume and efficiency are crucial factors in determining the suitability of manufacturing processes. Efficiency injection molding is preferred for high-volume production due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness in producing detailed parts.
Thermoforming, on the other hand, is ideal for smaller production batches, offering lower setup costs and flexibility in design changes. Understanding these factors helps in selecting the most efficient method for specific production needs.
High Volume Production Runs
Injection molding is ideal for mass production due to its efficiency in producing large quantities. Multi-cavity molds enable simultaneous production of multiple items, enhancing output. Higher upfront costs are offset by lower per-part costs in large volumes, making it cost-effective for high-volume orders.
This process is particularly suited for industries requiring precise and repeatable manufacturing of components, such as automotive and consumer electronics.
Small Batch Production
Thermoforming is ideal for producing smaller production quantities, offering lower setup costs and quick changes between different part designs. This process allows for big components to be produced quickly, making it suitable for low-volume orders and rapid prototyping.
The lower material costs and flexibility in design changes make thermoforming a more economical choice for small batch production. This approach is often favored for packaging, medical trays, and custom-designed panels.
Applications and Use Cases

Both injection molding and thermoforming and injection molding have diverse applications across various industries. Thermoforming is typically more suitable for larger designs and lower production volumes, making it ideal for packaging and automotive panels.
Injection molding is widely used in the construction sector for producing durable components like fasteners and tools. Understanding these applications helps in leveraging the strengths of each method for specific industry needs.
Common Uses for Injection Moulded Parts
Injection molding is particularly effective for creating complex and intricate designs using high precision. Common products made through injection molding include automotive components, medical devices, and consumer goods.
For instance, in the automotive industry, parts like dashboard panels and fasteners are often injection molded to meet stringent quality and durability standards, supported by injection mold tooling. An injection molded product can significantly enhance the efficiency of production processes.
Similarly, medical devices that require high precision and consistency, such as syringes and diagnostic tools, are frequently produced using injection molding. This versatility makes injection molding a go-to method for industries that demand high-quality, detailed parts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is a growing concern. Injection molding generally utilizes less material and generates less waste compared to thermoforming, making it more environmentally friendly in terms of material usage.
However, thermoforming contributes to less plastic waste by allowing for efficient recycling of excess materials. Both methods have their sustainability benefits, but the choice often depends on the specific environmental goals of the project.
Waste Management in Injection Moulding
Injection molding generates several waste types, including excess plastic, defective parts, and leftover materials. Ineffective machine calibration can lead to waste by causing overfilling or incomplete mold cavities.
However, recycling and reusing molded parts can significantly decrease the demand for raw materials, reducing the environmental footprint. Innovations like biodegradable materials and smart manufacturing techniques aim to further reduce waste in the injection molding process, making it a more sustainable option.
Sustainability in Thermoforming
The thermoforming process allows for the recycling of excess plastic, helping to reduce environmental impact. By recycling excess materials, manufacturers can significantly lessen their carbon footprint and contribute to a circular economy.
This process not only minimizes waste but also promotes sustainable practices by reusing materials, making thermoforming an eco-friendly choice for many applications.
Choosing Between Injection Moulding and Thermoforming
Choosing the optimal manufacturing process requires understanding each method’s key distinctions and advantages. Engineers and designers significantly contribute to design, prototyping, and selecting the best method for specific project needs.
Thermoforming allows quicker design modifications compared to injection molding, making it ideal for projects needing frequent changes. Considering factors like volume, complexity, cost, and lead time helps make an informed decision aligned with project goals.
Factors to Consider
Key factors to consider when choosing between injection molding and thermoforming include:
- Volume
- Complexity
- Cost
- Lead time
Injection molding is best suited for greater production quantities, whereas thermoforming is more cost-effective for smaller production quantities due to simple tooling and setup efficiency.
Thermoform molds are easier to design, fabricate, and modify, making them suitable for complex designs with design for manufacturing (DFM) assistance to optimize production. Cost-effectiveness differs between the methods; injection molding usually has higher tooling costs, while thermoforming molds are quicker and easier to produce.
Case Studies
Real-world examples highlight the practical decision-making scenarios in selecting between injection molding and thermoforming. For instance, injection molding is commonly used for automotive components, medical devices, and consumer goods due to its ability to produce detailed and high-precision parts.
On the other hand, thermoforming is often chosen for packaging, trays, and large panels due to its lower setup costs and quicker mold changes. Per-unit production costs for thermoforming can be lower for small runs, making it an attractive option for certain applications.
Overall cost analysis indicates that both processes have distinct cost implications, influencing choice based on project budget.

Summary
In summary, injection molding and thermoforming each offer unique advantages and are suited for different applications. Injection molding excels in producing high-precision, complex parts suitable for high-volume production, making it ideal for industries like automotive, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
Thermoforming, on the other hand, offers significant flexibility in design changes and is more cost-effective for smaller production quantities.
Ultimately, the choice between injection molding and thermoforming depends on the specific requirements of your project. By considering factors such as production volume, design complexity, cost, and environmental impact, you can select the method that best aligns with your goals and ensures the success of your product.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between injection molding and thermoforming?
The main differences between injection molding and thermoforming lie in their processes and applications. Injection molding is suited for high-precision, complex parts through high-pressure injection of molten plastic, whereas thermoforming is ideal for creating larger, simpler shapes by heating plastic sheets and forming them over molds.
Which materials are suitable for injection molding?
Thermoplastics such as polypropylene, polystyrene, and polycarbonate are highly suitable for injection molding. Incorporating additives like impact modifiers and colorants can further improve the material properties.
What are the typical applications of thermoformed plastics?
Thermoformed plastics are typically applied in packaging, automotive panels, construction materials, and medical trays due to their lightweight and sturdy nature. This versatility makes them ideal for a variety of industries.
How do tooling costs compare between injection molding and thermoforming?
Injection molding generally incurs higher initial tooling costs due to the need for durable molds, while thermoforming benefits from lower and quicker mold production, resulting in reduced tooling expenses. Thus, for projects prioritizing cost efficiency in tooling, thermoforming may be the more advantageous choice.
What factors should be considered when choosing between injection molding and thermoforming?
When choosing between injection molding and thermoforming, consider production volume, design complexity, cost, and lead time. Injection molding excels in high-volume, precise applications, whereas thermoforming is more economical for smaller runs and allows for faster design modifications.