PC ABS, a blend of polycarbonate and ABS, combines strength and heat resistance. In this article, you’ll learn about its properties, comparisons with other plastics, and applications across various industries.
What is PC ABS?

PC ABS, or polycarbonate acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is a thermoplastic material renowned for merging the strengths of polycarbonate with the flexibility of ABS plastic. This fusion creates a material that exhibits enhanced mechanical performance, superior heat resistance, and improved processing capabilities, especially when comparing ABS alone.
Polycarbonate plastic contributes its renowned strength and optical clarity, while ABS material adds to the ductility and ease of processing, making PC ABS a versatile choice for a wide range of applications, such as ABS luggage, where durability and manufacturability are key.
The benefits become clear when comparing ABS to PC ABS, showcasing the latter’s superior strength and heat resistance.
Chemical Structure of PC ABS
The chemical structure of PC ABS is a fascinating blend of polycarbonate and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene. Polycarbonate, a general engineering plastic, is synthesized mainly through a melt transesterification process involving Bisphenol A and phosgene.
This results in a molecular structure featuring carbonate groups linked by Bisphenol A, contributing to its toughness and optical clarity.
When polycarbonate is combined with ABS, it forms PC ABS, which benefits from the combined properties of both materials, particularly its high heat resistance.
The molecular weight of polycarbonate within PC ABS significantly boosts its high heat resistance and durability, making it an ideal candidate for applications requiring robust performance under stress, such as durable luggage.
Key Properties of PC ABS
PC ABS is celebrated for its high impact strength, which ranges between 600-900 J/m. This makes it suitable for demanding applications where mechanical robustness is paramount. Additionally, PC ABS exhibits exceptional dimensional stability, surpassing that of pure ABS materials, which often share similar properties but lack the same level of resilience. This ensures that components made from PC ABS maintain their shape and functionality even under stress.
Another standout feature of PC ABS is its excellent heat resistance, thanks to the polycarbonate sheets within the material, especially when compared to materials with lower heat resistance like pure ABS. This is crucial for applications exposed to high temperatures.
Moreover, PC ABS allows for the creation of durable and clear complex components, emphasizing its resilience and versatility in various applications, even outperforming materials with lower heat resistance or similar properties.
Comparing PC ABS to Pure ABS
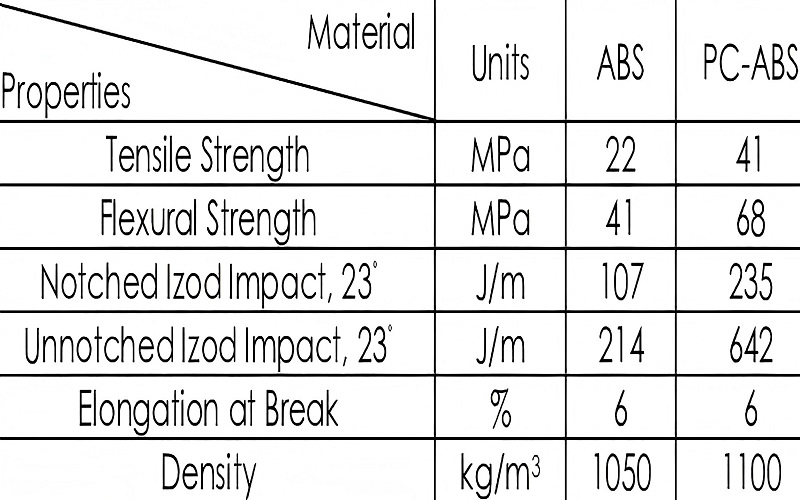
Comparing PC ABS to pure ABS reveals significant enhancements in mechanical and thermal properties. PC ABS merges the toughness of polycarbonate with the flexibility of ABS, resulting in improved impact resistance and flexibility.
These improvements make PC ABS suitable for applications demanding higher performance than what pure ABS can offer.
Mechanical Properties
PC ABS exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to pure ABS. Its improved toughness allows it to endure heavy impacts, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring high impact resistance, such as safety goggles.
Additionally, PC ABS demonstrates high tensile strength, excellent dimensional stability, and enhanced scratch resistance, ensuring reliable performance in various demanding applications like safety goggles where durability and clarity are essential.
Physical Properties
Physically, pc materials is denser and heavier than ABS, highlighting the distinct differences between the two materials. It also boasts a glossy, clear finish, in contrast to the typically opaque, matte finish of ABS, which comes in various colors.
Both materials, however, can be easily molded, formed, or 3D printed, offering flexibility in manufacturing processes and allowing for various shapes.
Cost and Availability
While PC ABS is generally more expensive than pure ABS, it offers better performance, making it a cost-effective choice for applications that demand enhanced properties.
The decision to opt for PC ABS should consider specific application requirements, manufacturing processes, and market availability to ensure it meets the desired performance and budget constraints.
Applications of PC ABS

PC ABS is widely utilized across various industries, from automotive and electronics to consumer goods and medical devices. Its durability, impact resistance, and heat stability make it a versatile material choice, supporting innovative applications that demand high performance and reliability.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, PC ABS is highly valued for its impressive mechanical properties, particularly its high impact and temperature resistance. This material is commonly used in automotive interiors, including critical components such as instrument panels and door trims, where impact strength is crucial. Additionally, PC ABS’s chemical resistance is vital for parts exposed to various oils and fuels, ensuring durability and longevity.
For example, automotive headlights benefit from the combination of high impact strength and chemical resistance provided by PC ABS automotive parts, which offers higher impact resistance.
This ensures that the components withstand the rigors of daily use and exposure to harsh conditions, maintaining their functionality and appearance over time.
Consumer Electronics
PC ABS is extensively used in consumer electronics due to its durability and heat resistance. It is often employed in protective housings for electronic devices, where it needs to withstand both heat and impact. This makes PC ABS an ideal material for products that require reliable protection, such as smartphones, laptops, and other electronic gadgets.
Beyond protective housings, PC ABS offers a combination of strength and aesthetic flexibility, which is crucial for consumer electronics. This material allows manufacturers to create devices that are not only durable but also visually appealing, catering to the demands of modern consumers.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, PC ABS is ideal for equipment enclosures due to its chemical resistance and durability. These properties ensure that medical devices can withstand repeated sterilization processes and exposure to various chemicals, even at low temperatures, maintaining their performance and longevity. Applications include high-pressure syringes and disposable dental tools, where reliability and safety are paramount.
The unique properties of PC ABS, such as enhanced durability and resistance to household chemicals, make it a preferred choice for medical devices and medical equipment that require specific properties for consistent performance and long-term use. This ensures that medical professionals can rely on their equipment to function correctly under demanding conditions.
Manufacturing Processes for PC ABS
PC ABS can be processed using several manufacturing methods, including injection molding, fused deposition modeling (FDM), and extrusion.
These processes enhance the versatility and applicability of PC ABS in various industries, allowing for the creation of complex and detailed components.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a popular method for processing PC ABS due to its high processability. This technique involves injecting molten plastic into a mold, cooling it, and allowing it to solidify.
Injection molding allows for precise replication of intricate designs, making it ideal for producing detailed injection molded components with high impact strength and durability.

Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is another method used for processing PC ABS, particularly in the field of additive manufacturing. PC ABS provides improved flow characteristics during the 3D printing process, leading to smoother extrusion and better print quality.
This makes it a valuable material for creating complex shapes and advancing the capabilities of additive manufacturing in various industries.
Extrusion
The extrusion process is particularly effective for producing uniform cross-sectional shapes continuously. PC ABS can be extruded to create a variety of products, taking advantage of its enhanced flow characteristics and high impact strength.
This method is commonly used in manufacturing processes that require consistent and reliable material properties.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability of PC ABS

The environmental impact and recyclability of PC ABS are important considerations for sustainable manufacturing practices. While PC ABS exhibits low resistance to chemicals, ultraviolet light, and oxidation, additives can be used to improve its performance.
However, it does not biodegrade quickly, making recycling essential for reducing environmental impact.
Sustainability of PC ABS Production
The production of PC ABS materials involves significant resource usage and emissions, which raises concerns about environmental sustainability. Recycling processes, including mechanical and chemical recycling, aim to reduce waste and promote sustainable practices.
These efforts are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of PC ABS production and ensuring a more sustainable future.
Recycling Processes for PC ABS
Recycling PC ABS involves careful sorting and processing due to the complexity of its components. Polycarbonate is recyclable, but the process is more challenging compared to ABS, requiring meticulous handling. ABS is typically shredded into plastic chips, cleaned, and melted for remolding.
Both two materials and other materials can be reused, contributing positively to their overall recyclability and reducing environmental impact.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PC ABS

PC ABS offers numerous distinct advantages, including high impact strength, excellent durability, and good heat resistance. However, it also has some disadvantages, such as higher cost and processing complexity.
Understanding these pros and cons is essential for making informed decisions about using PC ABS in various applications.
Advantages
One of the main advantages of PC ABS is its exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for parts that require durability. It also exhibits excellent heat resistance and thermal stability, maintaining its shape under higher temperatures. Additionally, the property abs of this material contributes to its overall performance.
Additionally, PC ABS offers high transparency and dimensional stability, ensuring reliable performance in precision-driven applications.
Disadvantages
Despite its many advantages, PC ABS has some drawbacks. It is more expensive than many other thermoplastics, which may limit its accessibility. Achieving a smooth surface finish can be challenging, requiring additional processing for aesthetic applications.
PC ABS is also not suitable for extremely high-temperature environments and has relatively low fatigue endurance, which may limit its use in certain structural applications.
PC ABS vs Other Plastics
PC ABS stands out when compared to other common thermoplastics due to its superior mechanical properties, impact resistance, and heat stability. By understanding how PC ABS measures up against materials like Nylon, PET, and HIPS, manufacturers can make informed decisions about which material best suits their needs.
PC ABS vs Nylon
Nylon typically exhibits superior tensile strength compared to PC ABS. However, PC ABS offers better impact resistance and heat stability, making it more suitable for applications requiring robust performance under stress.
Both the best material and another material find extensive use in automotive and consumer electronics, but the choice between them often depends on specific application requirements and cost considerations.
PC ABS vs PET
When comparing PC ABS to PET, PC ABS demonstrates superior heat resistance and chemical durability. PET is less chemically resistant, making it unsuitable for applications exposed to harsh chemicals.
The enhanced heat resistance of PC ABS allows it to perform better in high-temperature environments, solidifying its role in demanding highly resistant heat resistant applications, and it stays solid in these conditions, showcasing its high toughness and high heat deflection temperature.
PC ABS vs HIPS
PC ABS offers superior impact resistance compared to HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene), making it preferable for high-stress applications. This increased durability and mechanical performance ensure that PC ABS is often chosen over HIPS for components that require high strength and reliability.
Safety and Certifications for PC ABS
Safety and regulatory compliance are critical when using PC ABS in various industries. Adhering to safety equipment standards and obtaining necessary certifications ensures the material can be used safely and effectively in its intended applications.
PC ABS must meet rigorous standards to be deemed suitable for widespread use.

Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for PC ABS
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for PC ABS provide essential information on handling and processing the material safely. These documents include emergency procedures, first-aid measures, and guidelines for proper storage and handling to prevent accidents and ensure user safety.
SDS are crucial for anyone working with PC ABS to understand the potential hazards and how to mitigate them.
Industry Certifications
PC ABS must obtain various industry certifications to ensure quality and safety. ISO 9001 certification indicates adherence to quality management standards throughout the production process. Additionally, obtaining UL certification demonstrates compliance with safety standards for electrical products, ensuring PC ABS meets the necessary quality and safety requirements for various applications.
Summary
In conclusion, PC ABS is a highly versatile material that combines the best properties of polycarbonate and ABS plastic. Its superior mechanical and thermal properties, along with its wide range of applications, make it a valuable choice for various industries.
While it has some disadvantages, such as higher cost and processing complexity, its benefits often outweigh these drawbacks.
Understanding the material’s properties, manufacturing processes, environmental impact, and safety considerations can help manufacturers make informed decisions about using PC ABS in their products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PC ABS?
PC ABS is a thermoplastic that merges the strengths of polycarbonate and ABS, resulting in superior mechanical performance and heat resistance. This combination makes it a valuable material for various applications.
How does PC ABS compare to pure ABS?
PC ABS excels over pure ABS by providing superior impact resistance, flexibility, and thermal stability, making it more suitable for demanding applications.
What are the key applications of PC ABS?
PC ABS is predominantly applied in automotive interiors, consumer electronics, and medical devices because of its durability, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. This makes it a valuable material in industries where performance and reliability are critical.
What manufacturing processes are used for PC ABS?
PC ABS is typically processed using injection molding, fused deposition modeling (FDM), and extrusion, which facilitates the production of intricate and detailed components.
What are the environmental considerations for PC ABS?
PC ABS has significant environmental considerations due to its slow biodegradation, highlighting the necessity for effective recycling processes, both mechanical and chemical, to mitigate its ecological impact. Prioritizing these sustainable practices is essential for reducing waste.

