Delrin vs Nylon: Which is right for your project? Delrin excels in machinability and stability, while Nylon offers greater strength and wear resistance. This article will break down these key differences to help you make an informed decision.
Delrin vs Nylon: Key Differences in Properties
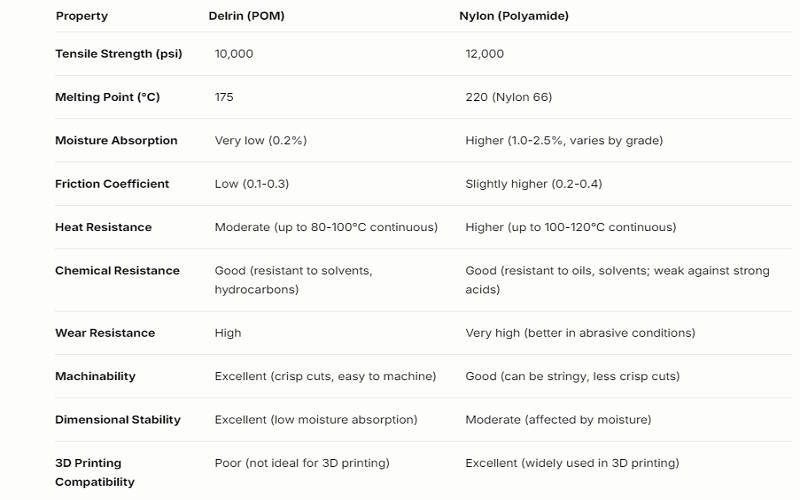
When comparing Delrin and Nylon, their distinct material properties must be considered. Delrin, known for its excellent machinability and specific applications, offers better dimensional stability and lower moisture absorption rates. Nylon, on the other hand, boasts higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-stress environments.
Both materials share excellent chemical resistance and a low friction coefficient, but their unique properties make them suitable for different chemical resistant uses.
Wear Resistance Comparison
Wear resistance is crucial for components subjected to constant friction. Nylon excels in this area with superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high wear resistance environments. Delrin, though slightly less abrasion-resistant, performs exceptionally well under pressure and in dry conditions, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Although both materials have their strengths, the ideal material and suitable material for the specific wear conditions of the application will determine the choice.
Friction Coefficient Analysis
Both Delrin and Nylon have low friction coefficients, making them excellent choices for moving and sliding parts. Delrin benefits from natural lubricity, particularly in grades like Delrin AF 100, which contains PTFE to further reduce friction.
This makes Delrin particularly suitable for applications requiring smooth, low-friction movement.
Tensile Strength Comparison
Nylon leads in tensile strength with 12,000 psi, roughly 20% higher than Delrin’s 10,000 psi. This higher tensile strength makes Nylon a better choice for applications requiring robust materials that can withstand significant stress and strain.
Machinability and Precision
Delrin is renowned for its machinability, high precision, and excellent dimensional stability. This makes it an ideal choice for producing precision parts with tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes.
Delrin’s properties ensure accurate and reliable delrin components, whether through injection molded processes or injection molding delrin or CNC machining, including delrin parts.
3D Printing Feasibility
Nylon stands out as the easier material to work with in 3D printing. Its adaptability for creating complex geometries and overall flexibility make it a preferred choice over Delrin in additive manufacturing processes.
Temperature Tolerance
Nylon’s superior temperature tolerance makes it more suitable for high-temperature environments compared to Delrin. While Delrin may deform under high heat, Nylon can withstand elevated temperatures without significant flow, particularly in grades like Nylon 6,6.
Moisture Absorption
Moisture absorption significantly affects material performance, especially in humid environments. Delrin absorbs moisture significantly less (0.2% to 0.5%) than Nylon, which can absorb moisture between 2% and 9% depending on the grade.
Low moisture absorption allows Delrin to maintain its mechanical properties and dimensional stability better than Nylon in wet conditions.
Understanding Delrin

Delrin, also known as polyoxymethylene, is a type of acetal polymer first mass-produced in 1960. Known for its precision parts, low friction, and high structural integrity, Delrin is widely used in manufacturing applications such as laser machining and injection molding.
We will explore the different grades, mechanical and physical properties, thermal properties, and common applications of this thermoplastic material.
Types of Delrin Grades
Delrin grades are engineered to optimize specific mechanical properties for various machining applications. For instance, Delrin AF 100 contains 13% PTFE, significantly enhancing its friction and wear properties.
Tailored grades ensure that Delrin meets the demands of precise specifications for specific industrial requirements.
Mechanical and Thermal Properties
Delrin has impressive mechanical and thermal properties, including a tensile strength of 10,000 psi and high rigidity. Its excellent dimensional stability and resistance to warpage make it ideal for precision parts. Delrin, an engineering thermoplastic, can operate continuously at a wide operating temperature range from 180 to 190 degrees Fahrenheit, with a melting point of 175 °C.
Adding PTFE to specific grades further enhances its frictional performance.
Common Applications of Delrin
Delrin is widely used across various industries. In the automotive sector, it’s utilized for gears and fuel systems due to its strength and durability. It’s also common in mechanical applications such as gears, screws, bushings, and bearings.
Low moisture absorption and FDA-certified grades make Delrin ideal for food industry applications. Additionally, it’s employed in electronics, medical devices, and high-impact parts.
Advantages of Using Delrin

Delrin plastic is notable for its impressive great dimensional stability and offers excellent dimensional stability, low friction properties, and good dimensional stability. Its low moisture absorption enhances performance in humid environments, showcasing the delrin material properties and the properties of delrin grade.
We will explore these advantages in more detail.
Lightweight yet Strong
Delrin’s light weight combined with high tensile strength makes it an excellent alternative to heavier materials. Incorporating 30% glass into Delrin enhances its impact resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications.
High Machinability
One of Delrin’s standout features is its high machinability. Its unique qualities and higher flow rates facilitate easy molding and shaping for various applications.
These qualities make Delrin ideal for achieving tight tolerances in machining projects.
Low Friction and Wear Resistance
Delrin copolymer exhibits a lower coefficient of friction compared to Nylon, making it highly effective for applications involving motion. Industrial bearings often use Delrin due to its low friction and wear resistance, which ensures high durability.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Low moisture absorption makes Delrin ideal for applications where moisture presence is a concern. Its high strength and dimensional stability contribute to its performance under various conditions.
These characteristics make Delrin suitable for applications requiring moisture resistance and durability against various chemicals.
Understanding Nylon

Nylon, known as polyamide, is synthesized through condensation polymerization using dicarboxylic acids and diamines. Although it can be more challenging to machine than some alternatives, Nylon is a versatile engineering synthetic material used in various industrial applications.
We will explore the different grades, mechanical and chemical properties, and common applications of Nylon.
Types of Nylon Grades
Nylon grades vary based on the number of carbon atoms in the dicarboxylic acid and diamine used during synthesis, affecting the material’s properties in both nylon types. This variation, especially when considering filled nylon, affects the material’s properties, making each grade suitable for different applications.
Mechanical and Chemical Properties
Nylon’s mechanical strength varies significantly among its grades, influencing its suitability for different applications, such as valve components. It is known for its exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring robust materials. Additionally, Nylon’s low density and chemical resistance to neutral chemicals enhance its usability in various industries.
Though not the strongest material, nylon material can endure significant wear and tear, thanks to its high crystalline composition, making it suitable for long-lasting applications like valve components and proving it is made from a sturdy material.
Common Applications of Nylon
High strength and durability make Nylon a preferred material in multiple industries. In automotive components applications, it’s favored for components requiring heat resistance.
Its ability to form complex shapes makes Nylon an excellent choice for 3d printed 3D printing solutions.
Advantages of Using Nylon

Nylon is widely used due to its beneficial properties, including high durability and tensile strength. Its ease of fabrication allows for efficient manufacturing processes.
We will delve into these advantages in more detail.
High Strength and Durability
Nylon’s high tensile strength makes it well-suited for applications requiring resistance to distortion. The strongest grade, Nylon 6,6, exhibits excellent mechanical properties, high stiffness, and superior mechanical properties.
Adding materials like glass or carbon fiber can further improve Nylon’s tensile strength.
Lightweight Material
Nylon’s lightweight nature makes it particularly suitable for weight-sensitive applications. However, moisture absorption can compromise its performance. Preconditioning treatments can mitigate these issues, ensuring Nylon retains its properties in various environments.
Versatile and Easy to Fabricate
Nylon’s versatility extends to various machining operations, including traditional methods and modern 3D printing techniques, as well as the manufacturing process. It offers fast drying and easy machining, making it suitable for efficient production. Low moisture absorbency further enhances Nylon’s machinability.
Nylon materials offer customization options with various finishes, enabling manufacturers to achieve desired aesthetics for their products.
Choosing Between Delrin and Nylon
The choice between Delrin and Nylon depends on the specific requirements of the application. Delrin is ideal for high-moisture environments and precision applications, while Nylon excels in high-temperature and high-stress environments. In the discussion of nylon vs delrin, it’s important to consider these factors, including nylon and delrin.
Both materials offer distinct advantages, and the choice ultimately depends on balancing two materials, versatile materials, material properties, and other materials, as well as the desirable material, manufacturing materials, and good material production methods, and application needs.

Best Uses for Delrin
Delrin’s low moisture absorption and high dimensional stability make it ideal for wet environments. Its properties, such as greater impact resistance and chemical stability, ensure it performs well in precision applications requiring high accuracy and consistent performance.
Best Uses for Nylon
Nylon is better suited for high-temperature environments and applications requiring robustness and heat resistance. Its robustness and ability to withstand significant wear and tear make it ideal for industrial applications where durability and thermal resistance are paramount. When considering materials, it’s essential to evaluate nylon vs other options for specific needs.
Summary
In summary, both Delrin and Nylon offer unique advantages tailored to specific applications. Delrin excels in environments requiring high precision, low moisture absorption, and chemical resistance. Its machinability and dimensional stability make it ideal for precision parts and components used in various industries.
On the other hand, Nylon’s high tensile strength, durability, and lightweight nature make it suitable for high-stress and high-temperature environments. Its versatility in 3D printing and ease of fabrication further enhance its applicability.
Choosing the right material between Delrin and Nylon involves understanding the specific needs of your project. Whether it’s the precision and stability of Delrin or the strength and versatility of Nylon, each material has distinct advantages that can lead to successful outcomes.
As you navigate through your material selection process, consider the properties and applications discussed in this guide to make an informed decision that aligns with your project requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between Delrin and Nylon?
Delrin excels in machinability and has lower moisture absorption, whereas Nylon boasts higher tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance. Therefore, the choice between them depends on specific application requirements.
Which material is better for high-temperature environments, Delrin or Nylon?
Nylon is the better material for high-temperature environments, as it offers superior temperature tolerance compared to Delrin.
Why is Delrin preferred for precision parts?
Delrin is preferred for precision parts due to its high machinability, excellent dimensional stability, and low friction properties. These characteristics ensure optimal performance and accuracy in applications.
Can Nylon be used for 3D printing?
Nylon can indeed be used for 3D printing, providing exceptional flexibility and the ability to create intricate designs effectively.
What are the common applications of Delrin?
Delrin is commonly applied in automotive components, electronic devices, medical devices, and the food industry because of its strength, durability, and low moisture absorption. Its versatility makes it a valuable material across various sectors.