Polyurethane resin plays a vital role in SLA 3D printing because of its accuracy and strength. This article dives into what polyurethane resin is, its key attributes, and why it’s favored for creating detailed 3D printed parts. We’ll also explore the types of polyurethane resins and their uses in different industries.
What is Polyurethane Resin?

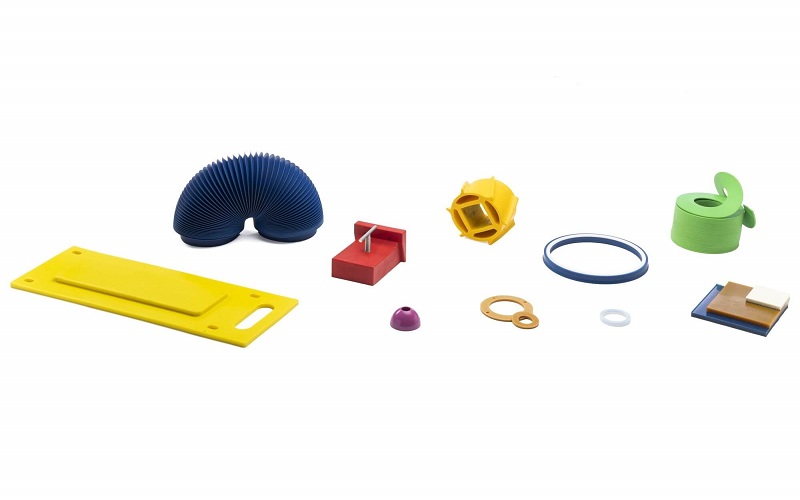
Polyurethane resin is a thermoset liquid material widely used in stereolithography (SLA) technology to create plastic parts with tight tolerances and intricate geometries.
This material, including specialized formulations like custom medical appliances resin and rigid ceramic filled resin, offers exceptional accuracy, resolution, and a high level of detail, making it highly desirable for 3D printing applications. Industries such as product design and dentistry commonly utilize polyurethane resins due to their remarkable properties, biocompatibility certifications for medical applications, and application versatility.
The curing process of polyurethane resins, known as photopolymerization, involves exposing the liquid resin to light, which solidifies it into a durable plastic. This transformation from liquid to solid is crucial for creating parts that are both precise and robust, whether using castable resins for molding applications or transparent resins for clear components.
The ability to cure liquid resin efficiently and effectively makes polyurethane resins a preferred choice for SLA 3D printing.
Key Properties of Polyurethane Resins
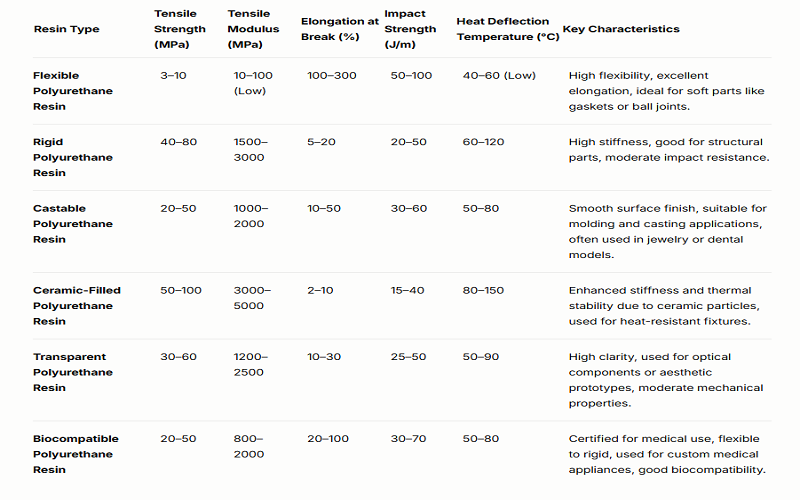
Polyurethane resins boast several key properties that make them ideal for 3D printing. Their superior performance in terms of toughness, durability, and heat resistance sets them apart from other 3d printing materials. These resins are resistant to stress, capable of withstanding shocks and impacts, and offer high thermal stability, essential for creating reliable and long-lasting components.
The subsequent subsections will delve deeper into these properties, exploring their significance and applications.
Toughness and Durability
Polyurethane resins are celebrated for their excellent mechanical properties, including:
- High toughness
- Flexibility
- High impact strength, making them suitable for rigorous applications where durability is paramount
- High elongation at break, ensuring that parts can withstand significant deformation without breaking
This makes them ideal for functional prototypes, mechanical assemblies, and heat resistant fixtures that require resilience and robustness, utilizing various manufacturing methods. The incorporation of ceramic particles in some formulations enhances specific properties like stiffness and thermal stability, though these resins may exhibit a low heat deflection temperature, limiting their use in high-temperature environments.
The mechanical properties of durable resins for SLA printing include the highest impact strength and elongation at break, essential for creating rugged prototypes and mechanical assemblies.
These castable SLA resins are also known for their smooth surface finish and the ability to create thin walls, contributing to their versatility in various applications. Despite their strengths, some formulations may have a low tensile modulus, which can affect rigidity in certain designs, yet their overall appearance and mechanical properties of SLA resin material properties make them highly versatile.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Polyurethane resins are engineered to provide superior flexibility, allowing them to bend significantly without cracking. This flexibility is complemented by high impact resistance, making these resins more suitable than ABS-like materials for applications requiring these properties, particularly when enhanced with biocompatibility certifications castable resins for medical or dental applications.
Flexible 3D printing resins possess the ability to bend and compress without deformation, allowing parts to recover their initial shape after being compressed.
This characteristic ensures a long life expectancy and the ability to withstand constant use without breaking, making them ideal for applications such as ball joints and other parts requiring consistent flexible resins.
Chemical and Abrasion Resistance
Polyurethane resins are renowned for their robust chemical resistance, making them suitable for use in harsh environments. This chemical resistance enables the parts to maintain functionality even when exposed to aggressive substances, thereby prolonging their longevity and enhancing performance over time. Additionally, the use of resistant resin further contributes to their durability.
The abrasion resistance of polyurethane resins further adds to their durability, allowing them to be used effectively in multiple demanding applications. This combination of chemical and abrasion resistance ensures that parts made from polyurethane resins remain reliable and durable, even in the most challenging conditions.
Types of Polyurethane Resins for SLA 3D Printing

Polyurethane resins are versatile materials that can be customized for various applications, ranging from soft elastomers to rigid thermoplastics. These liquid resins can be processed in multiple forms, including liquids used in stereolithography and thermoplastic materials for fused filament fabrication.
SLA 3D printing can utilize various types of polyurethane resins such as standard, tough, flexible, and specialty resins, each fulfilling specific needs in production and leading to successful outcomes in diverse projects.
Standard Polyurethane Resins
Standard polyurethane resins are recommended for prototypes in SLA 3D printing due to their suitability for rapid prototyping. These resins are commonly used for decorative objects, prototyping, and figurines, providing a cost-effective solution for creating detailed and intricate parts.
However, a notable drawback is their fragility, as they can break or crack under stress. Additionally, standard sla resin, sla resins, common sla materials, and other sla resins can also be considered for various applications.
Despite this limitation, standard polyurethane resins remain popular for rapid prototyping because they do not require specialized equipment and are less expensive. This makes them an accessible option for various users looking to create prototypes quickly and efficiently.
Flexible Polyurethane Resins
Flexible polyurethane resins are ideal for applications that require soft-touch surfaces and ergonomic designs. These resins typically have a shore hardness of around 80A, making them soft yet durable and well-suited for creating products that need to be comfortable and user-friendly.
While flexible polyurethane resins offer many advantages, they have some limitations, including the lack of true rubber properties and degradation over time with UV exposure. Nevertheless, their properties make them exceptionally suited for ergonomic designs, contributing to comfort and usability in final products.
High-Performance Polyurethane Resins
High-performance polyurethane resins are engineered for demanding applications, offering superior properties compared to standard resins. These durable resin exhibit enhanced toughness, enabling them to withstand high impact without breaking. This makes them suitable for various industrial environments where durability and resilience are critical, including applications that utilize engineering resins.
In addition to their toughness, high-performance polyurethane resins demonstrate excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for use in harsh and demanding environments. Their ability to maintain performance under extreme conditions, including high temperatures, makes them a preferred choice for high-stakes applications, including tough resins, tough and durable resins, heat resistant resins, and high temperature resistance.
Applications of Polyurethane Resins in 3D Printing
Polyurethane resins are widely utilized in industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer products due to their versatility and performance characteristics. These resins can be tailored for specific applications, enhancing their utility in 3D printing and ensuring successful outcomes across various sectors.
Automotive and Aerospace Industries
In the automotive sector, automotive parts made with polyurethane resins can be designed to meet stringent performance and durability standards. The durability and precision required in the design and manufacturing of automotive and electrical components make polyurethane resins an excellent choice for these industries.
Medical and Dental Applications
Biocompatible polyurethane resins are crucial in creating custom medical equipment that must adhere to safety and health regulations. Class I biocompatible resins and medical resins, including medical sla resins, are used for custom medical equipment like surgical guides and can withstand sterilization through autoclaving, making them ideal for surgical aids.
Class IIa biocompatible resins, suitable for short-term use devices, provide high accuracy, resistance to fracture and wear, making them ideal for custom hard splints and retainers. These dental resins can stay in contact with the human body for up to one year, ensuring safety and reliability for dental applications.
Consumer Goods and Electronics
Polyurethane resins enable the production of aesthetically pleasing components for consumer electronics, enhancing both functionality and design. Their excellent abrasion resistance further ensures the longevity of parts in wear-intensive applications, making them ideal for consumer goods.
Watertight SLA prints are particularly important in consumer products to ensure durability and functionality, contributing to the overall quality and performance of the final products.
Comparing Polyurethane Resins to Other SLA Materials
Polyurethane resins offer strength and durability comparable to ABS-like materials, making them suitable for applications that require structural integrity. However, their flexibility and impact resistance set them apart, making them more suitable for designs requiring stretchy and durable features.
The following subsections will provide a detailed comparison with ABS-like and epoxy resins.
Polyurethane vs. ABS-like Resins
Polyurethane resins generally offer superior flexibility compared to rigid ABS-like resins, making them more suitable for applications requiring elasticity. While polyurethane resins are tough and durable, ABS-like resins tend to have higher stiffness but are more brittle and have lower impact strength.
This comparison highlights the specific applications for each material, with ABS-like resins being preferred for parts needing high stiffness and strength, while the right material, polyurethane resins, are favored for their resilience, flexibility, and different material properties.

Polyurethane vs. Epoxy Resins
Polyurethane resins tend to outperform epoxy in flexibility and impact absorption, making them suitable for dynamic applications. Epoxy resins, on the other hand, are typically more rigid, ideal for structural applications needing strong, durable bonds.
Moreover, polyurethane has superior resistance to UV light compared to epoxy, which can yellow over time when exposed to sunlight. The curing time for polyurethane can be as short as 48 hours, while epoxy may take up to a week to fully cure, offering a faster production cycle for polyurethane parts.
Tips for Successful 3D Printing with Polyurethane Resins
To achieve the best results with polyurethane resins, consider a few essential tips for successful 3D printing. These tips include proper curing and post-processing, thoughtful design considerations, and adequate storage and handling.
Curing and Post-Processing
Post-curing with UV light and uv laser can enhance the strength and dimensional stability of parts made from polyurethane resins. Optimizing the curing process can significantly improve the mechanical properties of polyurethane parts, making them more durable and reliable.
Incorporating support structures in designs can minimize post-processing time and improve print quality. Cleaning with isopropyl alcohol is required for post-treatment of resin 3D printed parts, ensuring a smooth surface finish and optimal mechanical properties.

Design Considerations
Designing parts with rounded edges helps reduce stress concentrations during printing. Thoughtful design considerations are crucial to ensure successful 3D printing outcomes when working with polyurethane resins, enhancing both the quality and durability of the final parts.
Storage and Handling
Polyurethane resins should be stored in a cool, dark place to prevent degradation from light exposure. Proper ventilation is crucial when handling these resins to prevent inhalation of harmful fumes.
Resins must be tightly sealed in their containers to avoid moisture absorption and contamination, ensuring they maintain their quality and performance with clear resins, gray resin, and white resin.
Summary
In summary, polyurethane resins offer a range of properties that make them ideal for SLA 3D printing. Their toughness, durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance set them apart from other materials, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Whether you’re creating prototypes, custom medical devices, or consumer goods, polyurethane resins provide the performance and versatility needed for successful 3D printing projects.
The potential of polyurethane resins in 3D printing is vast, and understanding their properties and applications can help you make informed decisions for your projects. Embrace the capabilities of these resins and explore the endless possibilities they offer in the world of 3D printing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is polyurethane resin an adhesive?
Polyurethane resin is indeed an adhesive, known for its durability and ability to form strong bonds. It exhibits excellent performance in various conditions, making it a reliable choice for both industrial and consumer applications.
Is polyurethane resin the same as epoxy resin?
Polyurethane resin is not the same as epoxy resin; they differ primarily in flexibility, with polyurethanes being more elastic and epoxies typically rigid. Both types of resin can be tailored for strength and UV resistance.
What is polyurethane resin used for?
Polyurethane resin is utilized across multiple industries for applications such as construction insulation, automotive components, and as coatings for wood and floors due to its durability, flexibility, and resistance to water and chemicals. This versatility makes it an essential material for enhancing both structural and aesthetic qualities.
What makes polyurethane resins suitable for SLA 3D printing?
Polyurethane resins are suitable for SLA 3D printing due to their exceptional accuracy, resolution, and ability to create high-detail parts with tight tolerances and intricate geometries. These properties ensure high-quality and precise results in 3D printed components.
How do polyurethane resins compare to ABS-like resins?
Polyurethane resins provide greater flexibility and impact strength, making them preferable for applications that require elasticity, unlike the rigidity of ABS-like resins. Therefore, for projects necessitating durability and flexibility, polyurethane resins are the better choice.

