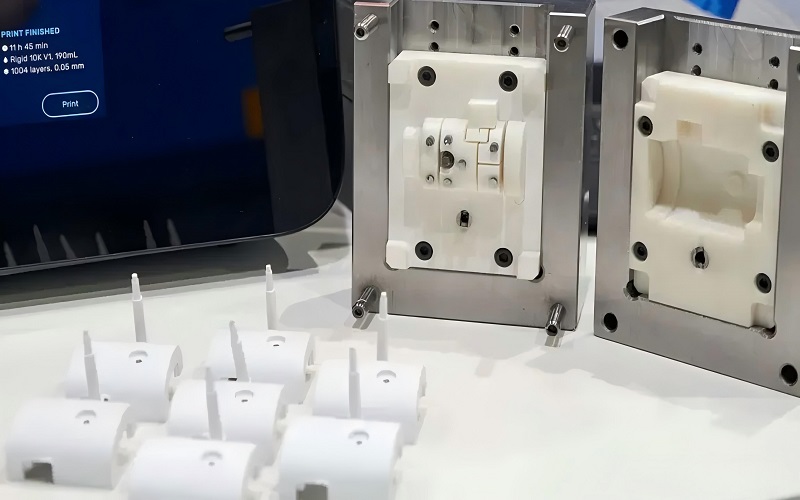
PVC injection molding allows manufacturers to produce complex, precise parts from Polyvinyl Chloride efficiently and cost-effectively. This article covers the techniques, benefits, applications, and challenges of PVC injection molding.
Understanding PVC Injection Molding
PVC injection molding is a revolutionary manufacturing process used to produce parts from Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). This versatile technique allows for the mass production of various components, such as machine housings, from a single mold, thanks to advanced tooling technologies.
The process has evolved significantly, becoming an economical choice for industries due to innovations in plastic polymers and injection mold technology, despite PVC’s low heat deflection temperature. The success of PVC injection molding hinges on having a well-thought-out, manufacturing-ready design, a skilled production partner, and considerations like optimal screw length in machinery.
In essence, PVC injection molding involves liquefying PVC material and injecting it under pressure into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. This method is not only efficient but also cost-effective, making it a go-to solution for producing complex and intricate designs, including machine housings, with high precision.
The ability to use both flexible and a rigid form of PVC, even with its low heat deflection temperature, further enhances its applicability across various industries. Grasping the intricacies of this process, including factors like screw length, is vital for anyone aiming to utilize PVC injection molding in their manufacturing operations.
What is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)?
Polyvinyl chloride, commonly known as PVC, is a robust industrial thermoplastic polymer that can be formulated into both flexible and rigid forms. This duality allows PVC to cater to a wide range of applications.
For instance, flexible PVC is often used in flooring and electrical wire insulation, while rigid PVC finds its place in plumbing pipes and vinyl siding. Its lightweight nature makes it easier to handle and transport, and its poor conductivity of electricity makes it suitable for electrical insulation applications. Additionally, vinyl chloride PVC plastic is known for its versatility in various industries.
One of the standout features of PVC is its fire-retardant nature, which helps slow the spread of flames when ignited. In the healthcare sector, PVC’s flexibility and biocompatibility make it indispensable for items like medical tubing and IV bags.
Its versatility extends to being molded into a variety of products, including other products, from soft toys to various rigid rubber structures, demonstrating its adaptability and access importance in modern manufacturing by the Goodrich Company, which offers many benefits.
Key Characteristics of PVC Material
PVC is renowned for its durability, often remaining functional for up to 40 years. This long-lasting nature is complemented by its resilience and resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and weathering, making it an ideal choice for various applications. Its chemical structure lends it exceptional resistance to many acids, bases, salts, fats, alcohols, and even diesel fuel. This robustness ensures that PVC can withstand harsh environments without degrading.
Another notable characteristic of PVC is its self-extinguishing property, which enhances its safety profile. Its resistance to environmental degradation and its resistant recyclability further add to its appeal, making it a cost-effective and sustainable material for manufacturing.
Whether used in construction, healthcare, or consumer goods, PVC’s numerous properties make it a versatile and reliable material.
The PVC Injection Molding Process
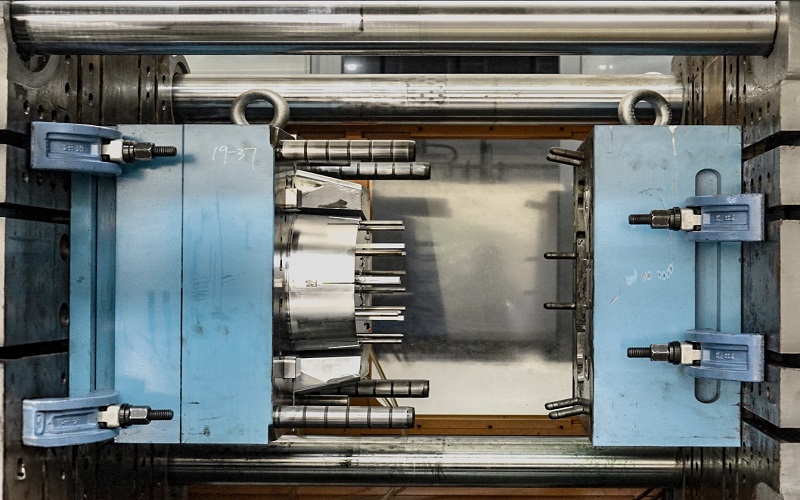

The PVC injection molding process is a meticulous procedure that involves several critical steps:
- Initially, PVC material is liquefied through heating.
- The liquefied PVC is then injected under pressure into a custom mold.
- Once inside the mold, the PVC cools and solidifies, taking on the desired shape.
To achieve optimal results, several factors must be carefully managed:
- Mold design
- Temperature
- Injection speed
- Pressure
Each of these aspects plays a vital role in ensuring the quality and efficiency of the PVC injection molding process.
Material Preparation
Material preparation is a crucial first step in the PVC injection molding process. Before PVC can be injected, it must be appropriately dried to eliminate moisture, which can adversely affect the quality of molded products.
The recommended drying time and temperature for PVC are 1.5 to 2.5 hours at 75 to 90°C, ensuring that the material is in the best possible condition for molding. This step is critical to prevent defects and ensure the consistency of the final products.
In addition to drying, various different additives or plasticizers are incorporated into PVC to enhance its heat stability during the injection molding process. These processing aids help in achieving the desired chemical properties and making the material suitable for producing complex parts.
Proper material preparation ensures a smooth and efficient molding process, ultimately enhancing the quality of the final products through post processing.
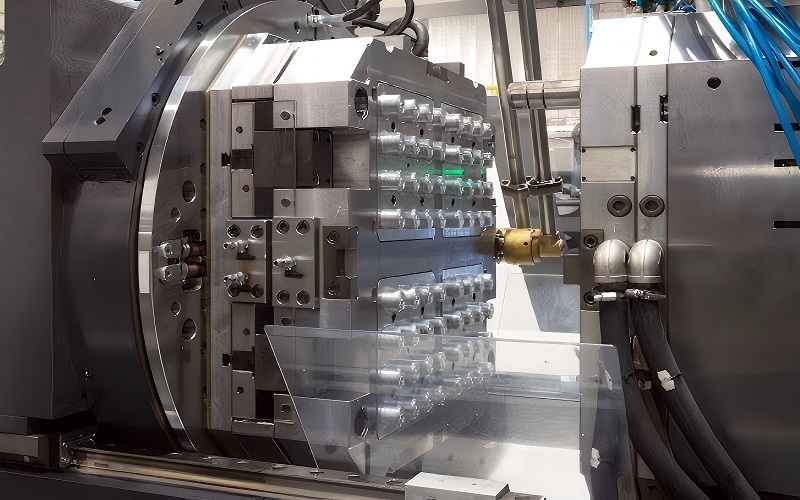
Injection Molding Machine Settings
The settings of the injection molding machine are pivotal in the PVC injection molding process. Typically, a screw-type injection molding machine is used for PVC. One of the key settings is the injection pressure, which should be above 90 MPa to ensure proper filling of the mold, with the maximum packing pressure reaching up to 100 MPa.
Additionally, the screw speed should be maintained between 50-70 rpm to avoid overheating the PVC, with an optimal rotation speed of 35-50 rpm.
Another important aspect is the screw cushion, which refers to the residue of PVC in the barrel that cannot pass into the mold after filling. The recommended cushion value is 2-3 mm, which may increase for larger machines.
Back pressure should be controlled around 1 MPa, ideally within a range of 0.4 to 0.7 MPa, to prevent excessive shear force and overheating. Adjusting these settings optimally is key to ensuring the production of high-quality PVC parts.
Temperature Control
Controlling temperature is a pivotal aspect of the PVC injection molding process. The molding temperature range for PVC is typically between 160-190°C, with a maximum limit of 200°C to prevent degradation. The mold temperature should be kept below 40°C and not exceed 60°C, using cooling water to achieve this. The temperature of the ejector side of the mold should be 10-20°F less than the inlet water temperature.
Barrel temperature settings are equally important, with specific ranges for different zones: Feed (30-60°C), Rear (160-180°C), Middle (150-170°C), and Front (140-160°C). The nozzle temperature should be maintained 10-20°C lower than the temperature at the end of the barrel.
Proper temperature maintenance ensures thermal stability and prevents the release of harmful gases during the injection molding process.
Injection Speed and Pressure
Controlling injection speed and pressure is essential for producing high-quality PVC parts. Injection speed should be adjusted based on the complexity of the product to prevent defects. A medium to lower injection rate is generally advisable to ensure consistent quality.
Fast injection rates can lead to poor venting, increased frictional heat, and potential defects such as burning plastic or color changes.
Higher injection speeds can help reduce temperature fluctuations, minimize shrinkage marks, and improve weld lines. However, for full-scale production, it is often necessary to increase the injection speed to meet production demands efficiently.
Properly managing these variables ensures the successful molding of complex PVC components with minimal defects.
Design Considerations for PVC Molds
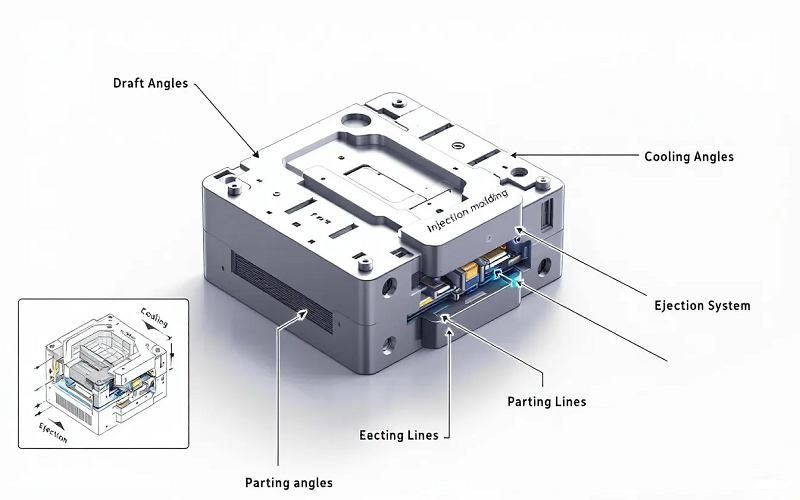
Designing molds for PVC injection molding requires careful consideration to ensure high-quality production. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
- Integrating cooling systems into mold designs can reduce cycle times and improve part quality.
- A circular nozzle design optimizes material flow and enhances the efficiency of the molding process.
- Draft angles of 1-2 degrees are suggested for the smooth ejection of PVC parts from molds.
By focusing on these aspects, you can achieve better results in your PVC injection molding projects.
Uniform wall thickness is crucial to avoid warping and achieve consistent quality in PVC parts. Vent holes should be strategically placed to allow air escape and prevent defects during the injection process. Rib designs should maintain a maximum thickness of 75% compared to adjacent walls.
Incorporating proper radii in designs enhances both aesthetics and structural integrity of the molded parts. These design considerations play a critical role in achieving high-quality PVC parts with minimal defects.
Industrial Applications of PVC Injection Molding

PVC injection molding has a wide range of industrial applications, thanks to its versatility, durability, and chemical resistance. In the construction industry, PVC is widely used for products such as pipes, window frames, and roofing elements due to its strength and weather resistance. Its lightweight and durable nature make it a popular substitute for traditional materials in various applications.
In the consumer goods sector, PVC is used to create durable household items like garden hoses and appliance handles. The electronics industry leverages PVC for its effective electrical insulation properties, using it in electrical wires, cable insulation, and protective enclosures.
The packaging industry also employs PVC for its malleability, producing items such as bottles and blister packs. These diverse applications highlight the significance of PVC injection molding across various sectors.
Advantages of PVC Injection Molding

PVC injection molding offers numerous important advantages, making it a preferred choice in the manufacturing industry. One of the key benefits is its cost-effectiveness, enabling both small-scale and mass production without high expenses. PVC is less expensive than specialty plastics, further enhancing its appeal. The process is highly efficient, allowing for the production of complex parts with high precision.
PVC injection molding achieves precision as tight as +/-0.000015, enabling the creation of durable injection molded plastic parts with intricate designs using a pvc injection molding machine. This level of precision is essential for producing complex geometrical structures with tight tolerances.
PVC’s flexibility allows it to be molded into various forms, accommodating a range of application requirements. Strong impact resistance and weather durability make it suitable for outdoor applications. In summary, PVC injection molding is a cost-effective, efficient, and durable manufacturing process that includes PVC molding.
Challenges and Solutions in PVC Injection Molding
Despite its advantages, PVC injection molding presents several challenges. Excessively high processing temperatures can cause accelerated degradation of PVC, releasing harmful gases and corroding machine parts. Controlling temperature during the injection heating process is vital to mitigate these risks. Lowering the temperature of the injection material can help prevent heat-related defects.
Warping is another common issue that can occur when parts cool at different rates, leading to shape distortions. A consistent cooling rate prevents uneven stresses that may result in warping. Symmetrical mold designs can also minimize the likelihood of warping during the cooling phase.
Materials with low shrinkage during cooling can help minimize warping risks. Addressing these challenges with practical solutions ensures the production of high-quality PVC parts and enhances the efficiency of the injection molding process.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability of PVC
The environmental impact of PVC is a significant concern, as its lifecycle involves the release of harmful chemicals.
Here are some key issues associated with PVC:
- Dioxins produced during the disposal of PVC are highly toxic and can accumulate in living organisms, causing serious health risks.
- Phthalates, commonly used as plasticizers in PVC, can leach into the environment and have been linked to reproductive and developmental issues.
- Microplastics from PVC can accumulate in aquatic environments, posing risks to marine life and entering the food chain.
However, PVC’s recyclability is an important feature that promotes sustainable manufacturing. Effective recycling methods are crucial for reducing PVC’s environmental footprint, as it is challenging to break down and often ends up in landfills. Reusing PVC without significant quality loss promotes sustainable practices and mitigates some environmental concerns associated with its use.
Summary
In conclusion, mastering PVC injection molding involves understanding the material’s characteristics, preparing it properly, adjusting machine settings, and designing molds effectively.
The process offers numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, precision, and versatility, making it a preferred choice in various industries.
However, it also presents challenges that require careful management to ensure high-quality production. By addressing these challenges and considering the environmental impact, manufacturers can leverage PVC injection molding to its full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main advantages of PVC injection molding?
The main advantages of PVC injection molding are its cost-effectiveness, precision, efficiency, and capacity to produce complex parts that exhibit high durability and impact resistance. These benefits make it a favorable choice for various manufacturing applications.
What are the common applications of PVC injection molding?
PVC injection molding is widely applied in construction for pipes and window frames, in consumer goods for items like garden hoses, in electronics for cable insulation, and in packaging for products such as bottles and blister packs. This versatility highlights its crucial role across multiple sectors.
How does temperature control affect the PVC injection molding process?
Temperature control is essential in the PVC injection molding process as it prevents degradation and the release of harmful gases. Maintaining a temperature range of 160-190°C ensures thermal stability and optimal product quality.
What challenges are associated with PVC injection molding?
PVC injection molding presents challenges such as degradation at high temperatures, warping from uneven cooling, and potential release of harmful gases. Addressing these issues requires ensuring consistent cooling rates, employing symmetrical mold designs, and using proper temperature settings.
Is PVC environmentally friendly?
PVC is not considered environmentally friendly due to its significant environmental impacts, such as the release of harmful chemicals and microplastics; however, its recyclability can help mitigate some of these concerns if managed properly.