What makes polyurethane foam so essential across various industries? This material, available as flexible and rigid foam, is used for everything from insulation to cushioning.
In this article, discover the types of polyurethane foam and their key applications.
Types of Polyurethane Foams

Polyurethane foams are primarily divided into two types: flexible and rigid. Flexible polyurethane foam is known for its low density, softness, and compressibility, often enhanced by polyurethane coatings for added durability. Its ability to return to its original shape after compression greatly enhances its durability across various uses, particularly when combined with polyurethane elastomers for improved flexibility.
On the other hand, rigid polyurethane foam is known for its high density, offering superior strength and thermal insulation capabilities, sometimes augmented by polyurethane coatings for surface protection. This type of foam excels in applications where structural integrity and insulation are paramount, and polyurethane elastomers can enhance its toughness.
Flexible and rigid polyurethane foams, often paired with polyurethane coatings and polyurethane elastomers, possess distinct properties catering to different needs. Flexible foams are ideal for comfort and cushioning applications, while rigid foams excel in insulation and structural uses. This versatility makes polyurethane foams invaluable across numerous industries.
Flexible Polyurethane Foam Applications
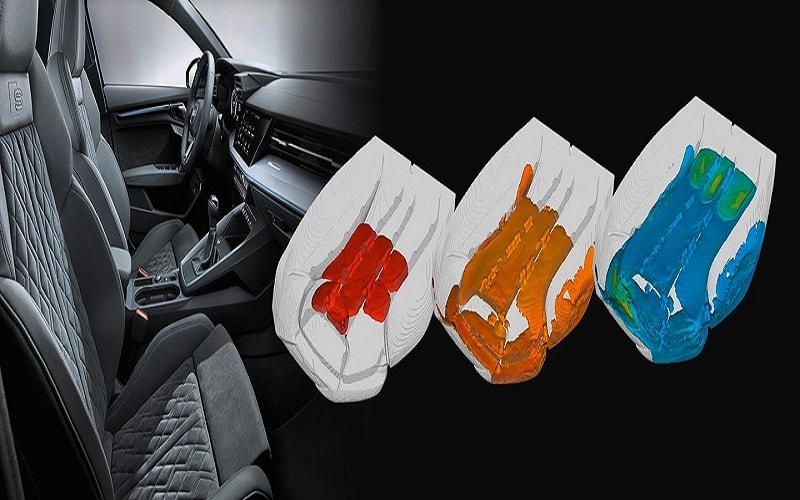

In the automotive industry, flexible polyurethane foam, including cured foam, is extensively used for car seats, headrests, and armrests due to its shock-absorbing qualities in automotive interiors and components like conveyor belt systems. The industry’s demand for lightweight materials that enhance fuel efficiency and comfort makes it the largest consumer of flexible polyurethane foam.
In the furniture sector, flexible polyurethane foam, often as cured foam, is frequently used in mattresses, pillows, carpet underlay, and upholstered furniture due to its comfort and support. High-density variants often create a durable outer skin, enhancing abrasion resistance and making them suitable for upholstery, carpet underlay, and footwear. Additionally, pu foams are known for their versatility in various applications, including cushioning material.
Flexible polyurethane foam, particularly cured foam, is also utilized in medical applications like prosthetics and wound care products. Its softness and flexibility offer essential comfort and support, showcasing the material’s versatility across various fields, including specialized uses like conveyor belt padding.
Manufacturing Processes of Flexible Polyurethane Foams
Flexible polyurethane foams are manufactured through various processes, each with unique benefits. One such melt processable process is the continuous or slabstock process, which:
- Produces large foam blocks
- Allows these blocks to be cut into various shapes
- Enables efficient production
- Provides customization to meet diverse industrial needs
Molded processes, on the other hand, create specific foam shapes and densities suitable for specialized uses. Molding polyurethane foams are particularly useful in other applications requiring strong support, such as automotive seats and specialty packaging.
These manufacturing techniques ensure that flexible polyurethane foams produced can meet diverse industry elastomer demands.
Sustainability Initiatives in Flexible Polyurethane Foams
Sustainability is increasingly important in the production of flexible polyurethane foams and raw materials, including additives, used in applications like fuel tanks and cushioning effect products. Manufacturers are reducing the toxicity of production processes by using safer chemicals to minimize environmental impact, making greener practices essential for the industry’s future while maintaining cost effective solutions.
Furthermore, initiatives to lower emissions during foam production, particularly for fuel tanks and cushioning effect applications, contribute to overall sustainability goals. Enhanced recycled recycling methods are being developed to promote circular economy practices, making flexible polyurethane foams more eco-friendly and cost effective.
Tightening environmental regulations are increasing scrutiny over VOC emissions and sustainability practices in the production of foams for fuel tanks and cushioning effect uses. This regulatory pressure drives the industry to adopt more sustainable and cost effective production methods and materials, ensuring flexible polyurethane foams remain a viable and responsible choice, pu.
Rigid Polyurethane Foam Applications
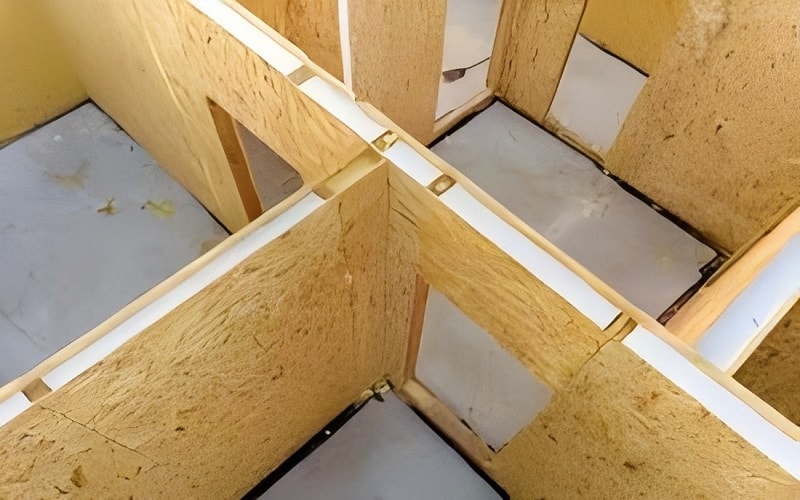

Rigid polyurethane foam is mainly used in building insulation due to its excellent thermal resistance. Its thermal conductivity ranges between 0.022 and 0.028 W/m/k, making it highly effective for maintaining energy efficiency in buildings.
Additionally, rigid polyurethane foam is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for environments with common water exposure. This property ensures the foam’s longevity and reliability in applications such as roofs and wall insulation.
Production methods for rigid polyurethane foams allow for varying densities, affecting their mechanical strength and insulation capabilities. This adaptability ensures that rigid polyurethane foams can meet the specific needs of various construction projects.
Production Techniques for Rigid Polyurethane Foams
Key techniques for producing rigid polyurethane foams include cavity-filling and spray methods. Each method affects the foam’s density and thermal performance, enabling customized applications based on structural needs.
Cavity-filling involves injecting foam into a mold or cavity where it expands and hardens. Spray foam is applied directly to surfaces, creating an insulating barrier that conforms to the shape of the substrate. These techniques offer flexibility and precision in manufacturing rigid polyurethane foams.
Challenges and Innovations in Rigid Polyurethane Foams
The rigid polyurethane foam industry faces challenges, particularly in transitioning to eco-friendly blowing agents. These new alternatives often exhibit lower thermal efficiency, posing a challenge for maintaining heat transfer performance standards and temperature stability.
However, recent innovations are addressing these issues by improving moisture resistance and enhancing the longevity of rigid polyurethane foams and other materials, including coatings, to combat corrosion. These advancements ensure the material remains reliable in various applications.
Optimizing formulations to meet strict environmental regulations while maintaining performance is also a key focus. Innovations in this area are crucial for the industry’s future, ensuring that rigid polyurethane foams continue to meet both performance and environmental standards in form.
Key Properties of Polyurethane Foams
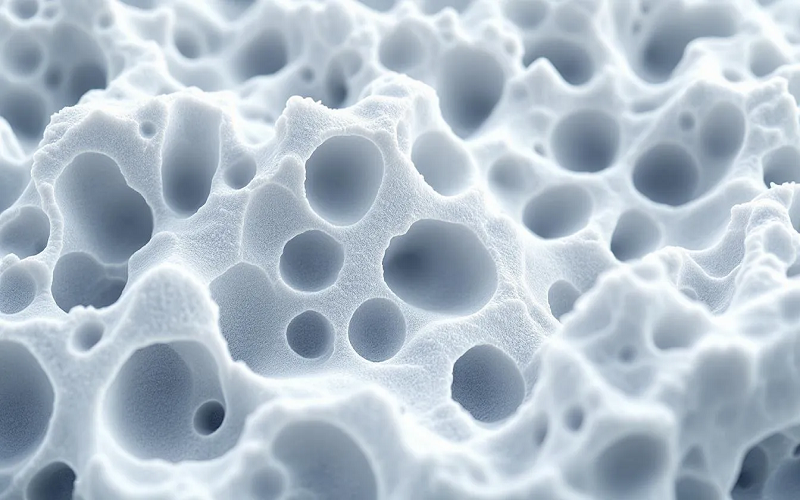
Polyurethane foams exhibit a range of foam properties that make them suitable for diverse applications:
- Open-cell foams are flexible.
- Closed-cell foams provide rigidity due to their distinct cellular structures.
- The stiffness of the polymer can vary, with higher density not always equating to greater stiffness.
These structural differences result in varying characteristics, making polyurethane foams adaptable to different needs. The cellular structure of polyurethane foams allows for this adaptability.
Moreover, polyurethane foams exhibit adhesion during formation, allowing for applications that do not require additional adhesives. Recent advancements focus on enhancing fire resistance and reducing toxic emissions, addressing safety concerns in construction applications involving flame retardants and polyurethanes.
Market Trends and Future Outlook for Polyurethane Foams

The flexible polyurethane foam market is projected to grow significantly, from $5.95 billion in 2024 to over $10.86 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.20%. This growth is driven by increasing demand across various industries, particularly automotive and construction.
Major manufacturers are focusing on mergers and collaborations to foster innovation and new technology development. These strategic moves are crucial for staying competitive and meeting the market’s evolving needs, combined with the need for adaptability.
Innovative applications, such as Smart Foam integrated with sensors for health monitoring, are emerging as key trends within the polyurethane foam market. North America is experiencing rapid growth, boosted by strict building codes and high comfort standards in the automotive sector.
Summary
Polyurethane foams, both flexible and rigid, offer unparalleled versatility and performance across various industries. From automotive interiors to building insulation, their unique properties make them indispensable.
Ongoing innovations and sustainability efforts are ensuring that polyurethane foams remain a vital material for the future. The industry’s focus on eco-friendly practices and advanced applications promises a bright and sustainable future for polyurethane foams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of polyurethane foams?
The main types of polyurethane foams are flexible and rigid. Flexible foams are soft and compressible, whereas rigid foams are dense and provide superior thermal insulation.
What are some common applications of flexible polyurethane foam?
Flexible polyurethane foam is widely utilized in automotive interiors, furniture, mattresses, and medical applications such as prosthetics and wound care products. Its versatility makes it an essential material across various industries.
How is flexible polyurethane foam manufactured?
Flexible polyurethane foam is manufactured primarily through the slabstock process, producing large blocks, or the molded process, which allows for the creation of specific shapes and densities. Both methods cater to diverse applications within the industry.
What challenges does the rigid polyurethane foam industry face?
The rigid polyurethane foam industry encounters challenges in adopting eco-friendly blowing agents that may compromise thermal efficiency. Additionally, ongoing innovations aim to enhance moisture resistance and comply with stringent environmental regulations.
What are the key properties of polyurethane foams?
The key properties of polyurethane foams are their flexibility or rigidity based on cellular structure, strong adhesion during formation, and improved fire resistance with reduced toxic emissions. These attributes make polyurethane foams versatile for various applications.

