When it comes to selecting the right piping materials for your plumbing projects, ABS vs PVC are two of the most popular and widely used plastic pipes options available.
Understanding the key differences between these materials—including their specific characteristics, installation methods, and performance in various environments—can save you time, money, and potential headaches.
In this article, we’ll explore the difference between ABS and PVC, their unique properties, benefits, and ideal use cases to help you make an informed decision on whether to choose PVC or ABS for your next plumbing job, while also considering local building codes and regulations that may influence your choice.
What Is ABS ?
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a tough and durable thermoplastic widely used in many different applications, including plumbing projects such as drainage, wastewater, and vent piping.
These pipes are known for their high impact resistance, lighter weight, and excellent performance in extreme cold conditions (usable from -40°C to 80°C).
Such pipes are an ideal choice for underground and outdoor plumbing applications where exposure to direct sunlight is minimal, as ABS can degrade under UV light.
Additionally, ABS has a relatively low melt point, making it important to avoid high-temperature environments.

What Is PVC?
Polyvinyl Chloride, or PVC, is a versatile thermoplastic polymer produced from vinyl chloride monomers. It is one of the most widely used plastic pipes in indoor plumbing and commercial plumbing due to its excellent chemical resistance and durability.
PVC pipes have a rigid structure and are commonly used in pressurized systems such as potable water supply lines, irrigation, and pool plumbing.
PVC is more resistant to UV light than ABS, but prolonged exposure can still cause degradation. It is typically white or light-colored, making it easy to distinguish from black ABS pipes.

ABS vs PVC: Key Property Differences
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), as two common engineering plastics, have significant differences in performance.
Mechanical Properties
Strength And Toughness
ABS: has high toughness and impact strength and is suitable for applications that need to withstand impact or dynamic loads. Its butadiene component gives good flexibility.
PVC: Divided into rigid PVC and soft PVC. rigid PVC is rigid but has low toughness and is prone to brittleness; soft PVC improves flexibility through the addition of plasticizers, but has lower strength than ABS.
Impact Resistance
ABS: Excellent impact resistance and toughness even at lower temperatures, suitable for durable consumer products.
PVC: Rigid PVC has poorer impact resistance and is susceptible to low temperatures and becomes brittle; soft PVC has slightly better impact resistance but is still not as good as ABS.
Hardness And Rigidity
ABS: Moderate hardness, both rigidity and toughness, with good surface resistance to scratches.
PVC: Rigid PVC has high rigidity and hardness and is suitable for structural applications ; soft PVC is soft and less hard.
| Physical Property | ABS | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.04–1.06 lighter weight, easy to handle | 1.38–1.40 denser, more rigid structure |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 40–50 moderate strength, suitable for non-pressurized applications | 50–60 higher strength, suitable for pressurized piping |
| Impact Resistance | High (7–8/10) resists cracking at low temperatures | Moderate (4–5/10) more brittle, may require additives |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m· K) | 0.15–0.25 good insulation properties | 0.16–0.19 slightly better insulation than ABS |
| Flexibility | Good (6–7/10) slightly elastic, easy to cut and install | Low (3–4/10) rigid, requires precise processing |
Thermal Properties
Heat Resistance And Heat Distortion Temperature
ABS: Heat Distortion Temperature (HDT) is usually between 80-100°C. Heat resistance is moderate and suitable for general indoor applications, but may soften at high temperatures.
PVC: The heat resistance of rigid PVC is slightly lower than that of ABS (HDT about 60-80°C), and it is easy to be deformed under high temperature; the heat resistance of soft PVC is even lower due to the influence of plasticizers.
Flame Retardant
ABS: itself does not have flame retardant, need to add flame retardant to meet the fire requirements, increasing the cost.
PVC: Due to the chlorine content, PVC has a natural flame retardant, the gas released during combustion can suppress the flame, and is widely used in occasions where fire protection is required.
Chemical Performance
Chemical Resistance
ABS: It has some resistance to acids, alkalis and oils, but is sensitive to certain organic solvents and is prone to swelling or cracking.
PVC: excellent chemical resistance, especially rigid PVC, strong resistance to acid, alkali, salt and water, widely used in chemical industry and piping system.
Weathering And UV resistance
ABS: Weathering resistance is poor, long-term exposure to ultraviolet light will turn yellow and brittle, need to add anti-UV agent or surface coating.
PVC: Rigid PVC has better weathering resistance, but also needs UV resistance treatment; soft PVC has slightly less weathering resistance due to possible volatilization of plasticizers.
Processing Performance
Forming And Processing Difficulty
ABS: easy to injection molding, extrusion and thermoforming, excellent processing performance, the surface can be plated, painted and other treatments, suitable for complex shapes of products.
PVC: Slightly more difficult to process, especially rigid PVC, because of its poor thermal stability, the process requires strict temperature control to avoid decomposition. Soft PVC is more flexible but requires the addition of plasticizers.
Surface Treatment
ABS: High surface gloss, easy to color, plating or bonding, suitable for products with high demands on appearance.
PVC: Slightly inferior surface treatment performance, the surface of hard PVC is smoother but the bonding is general, soft PVC surface treatment is limited.
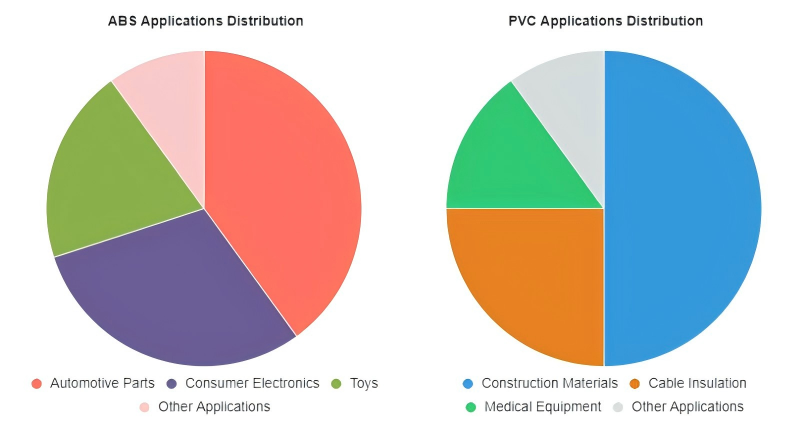
In conclusion, ABS is suitable for applications requiring high toughness, attractive surfaces and moderate heat resistance, such as automotive parts, electronics housings and toys.
PVC is better suited for cost-sensitive, corrosion-resistant or flame-retardant scenarios, such as construction piping, cable insulation and medical equipment.
Understanding these key differences and examples of their applications helps plumbers, contractors, and DIY enthusiasts choose the right piping materials for specific residential and commercial plumbing projects, ensuring compliance with local building codes and optimal system performance.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of PVC Materials
Advantages
- Excellent Chemical Resistance: Highly resistant to acids, bases, and salts, making it perfect for chemical drainage systems.
- High Tensile Strength: Suitable for pressurized systems like hot water supply lines (with certification).
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: Ensures long-term durability in harsh environments.
- Versatile Applications: Used widely in residential and commercial plumbing, irrigation, and pool systems.
- Better Sound Insulation: PVC pipes help reduce noise from running water, ideal for indoor plumbing.

Disadvantages
- Brittle in Cold Temperatures: Can crack below freezing without additives, limiting use in extreme cold climates.
- Higher Cost: Slightly more expensive than ABS, which can impact large-scale plumbing projects.
- Rigid Structure: Less flexible, requiring precise cutting and fitting, making it less DIY-friendly.
- Installation Requires Primer: The two-step process can be time-consuming compared to ABS.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of ABS Plastics
Advantages
- High Impact Resistance: Especially effective at low temperatures, ideal for cold water and outdoor drainage applications.
- Lighter Weight: Easier to handle and install, contributing to faster project completion.
- Cost Effective Choice: Generally cheaper than PVC, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects.
- Simple Installation: Uses a one-step process with special cement for quick joining without primer or glue.
Disadvantages
- Limited Chemical Resistance: Less resistant to certain solvents compared to PVC.
- Not Suitable for Pressurized Systems: Not recommended for hot water lines or potable water supply.
- UV Sensitivity: Degrades under direct sunlight unless UV-stabilized.

Applications Of ABS And PVC
Applications Of ABS
Automotive Parts
ABS is widely used in automotive manufacturing due to its toughness and resistance to impact, making it ideal for durable interior components.
Consumer Electronics
The lightweight and sturdy nature of ABS makes it a popular choice for protective casings and electronic housings.
Toys & Lego Bricks
ABS’s excellent impact resistance and ease of molding contribute to its extensive use in manufacturing toys and building blocks that withstand rough handling.
ABS Pipes
ABS’s durability and resistance to corrosion make it an excellent choice for manufacturing pipes that ensure reliable performance in plumbing and drainage systems.
Applications Of PVC
Construction Materials
Valued for their durability and versatility in building projects.
Electrical Insulation
Providing reliable protection for wiring in residential and commercial plumbing systems.
Medical Devices
Where the biocompatibility and chemical resistance of PVC make it an ideal material choice.
PVC Pipes
PVC’s durability and resistance to chemical corrosion make it a preferred material for manufacturing pipes used in reliable and long-lasting plumbing and drainage systems.
How To Choose, ABS Or PVC?
When deciding between ABS vs PVC for your plumbing projects, consider the specific requirements of your application.
ABS is better suited for cold water drainage, underground use, and extreme cold climates due to its high impact resistance and durability in low temperatures. On the other hand, PVC is preferred for hot water supply, pressurized systems, and environments requiring excellent chemical resistance.
Installation preferences also play a role: ABS offers a simpler, one-step bonding process using special cement, which can save time and labor costs. PVC requires a two-step process involving priming and gluing, which, while more complex, provides strong, reliable joints suitable for pressurized systems.
Compliance with local building codes and regulations is essential to ensure your project meets legal requirements. Always check local codes as they may dictate the use of either ABS or PVC for certain applications.
Environmental exposure factors such as direct sunlight and temperature extremes should influence your choice. ABS is sensitive to UV light and should be protected from prolonged sun exposure, whereas PVC offers better UV stability but can become brittle in very cold conditions.
Budget and project scale are practical considerations; ABS is generally a more cost-effective choice, making it ideal for large-scale or budget-conscious projects.
When joining ABS pipes, use special cement and appropriate fittings to ensure secure, leak-proof connections. If you need to connect ABS and PVC pipes, mechanical couplings or rubber sleeves with metal clamps are recommended instead of glue due to chemical incompatibility.
Ultimately, whether you opt for ABS or PVC, both materials have proven their worth in many different applications across residential and commercial plumbing. Understanding their strengths and limitations will help you make an informed decision tailored to your plumbing job’s unique needs.
Remember, not all plastic pipes are created equal, so choosing the right one for your specific project is key to success.