As two prominent plastic materials widely utilized in the industrial and consumer goods sectors, ASA and PC each possess unique characteristics and serve diverse applications.
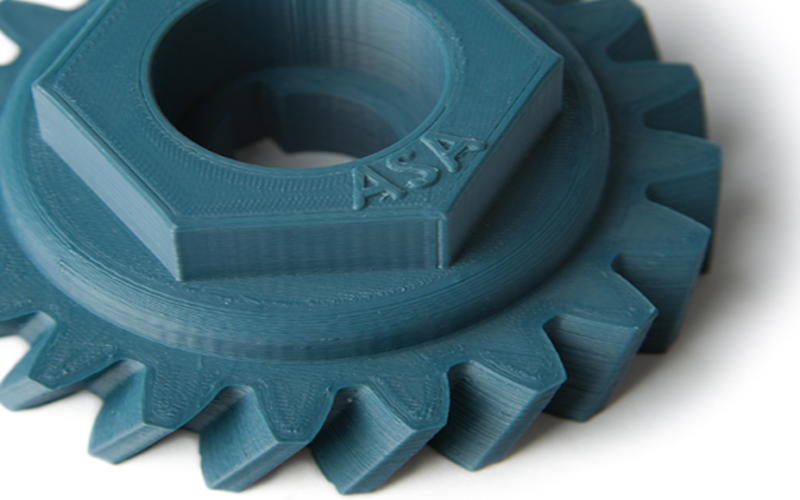
ASA is celebrated for its exceptional weather resistance and robust mechanical strength, positioning it as a top choice for outdoor uses such as automotive parts and garden furniture.
Conversely, PC is prized for its remarkable impact resistance and high transparency, making it a preferred option in the automotive and medical industries, including bulletproof windows and medical devices.
This article explores the theme of “ASA vs PC,” offering a thorough comparison of their differences to guide your material selection process.
What Is Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA)?
ASA, or Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate, is a thermoplastic polymer known for its impressive UV stability and weather resistance.
ASA’s weather resistance makes it an excellent choice for applications where durability and longevity are critical, especially in outdoor settings. Additionally, styrene acrylate ASA enhances the overall performance of the material.
ASA’s versatility extends to various industries, including automotive, where it is used for making durable and UV-resistant components.
It’s also popular in the production of outdoor furniture and fixtures, where its resistance to UV rays and weathering is a significant advantage.
The material composition of ASA, which includes a blend of acrylonitrile, styrene, and acrylate, contributes to its unique properties and makes it a reliable choice for demanding applications.

What Is Polycarbonate (PC)?
Polycarbonate (PC) is another powerhouse in the world of 3D printing filaments.
Known for its exceptional strength and impact resistance, PC is often the go-to material for applications requiring robustness and durability.
Its transparency and ability to withstand high temperatures further enhance its appeal, making it a versatile choice for various demanding projects.
PC finds its applications in a wide range of industries. However, due to its sensitivity to printing conditions, PC is prone to warping and layer separation if not processed correctly, requiring controlled air environments during production to maintain quality and performance.
The material composition and manufacturing process of PC contribute to its unique properties and materials, making it a reliable choice for high-performance applications.
ASA vs PC: Key Properties Comparison
Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA) and Polycarbonate (PC) are two widely used thermoplastic polymers, each with distinct properties that make them suitable for various applications.
This section compares their key properties to provide a clear understanding of their strengths and limitations.
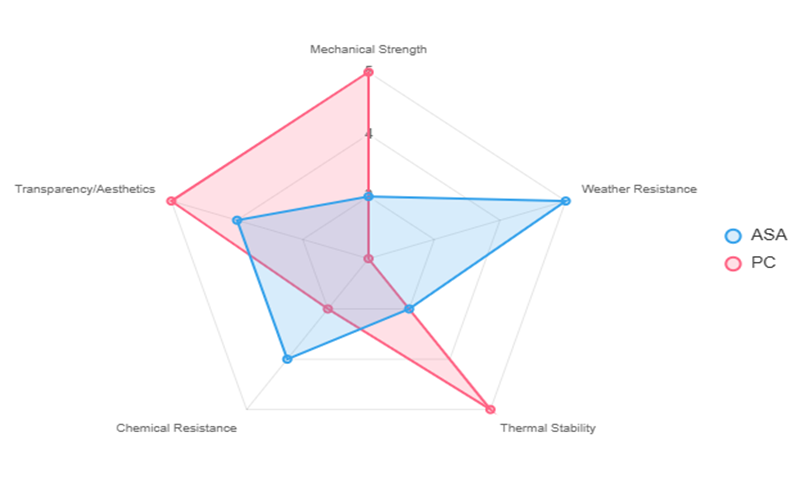
Mechanical Strength
ASA offers good tensile strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for many outdoor applications where durability is important.
Its toughness is reliable for typical use but is generally lower than that of PC when subjected to very high-stress conditions or heavy mechanical loads.
This makes ASA a strong candidate for parts that require weather resistance and moderate mechanical performance.
On the other hand, polycarbonate (PC), exhibits exceptional impact strength and is often described as “virtually unbreakable.”
This outstanding toughness makes PC ideal for high-impact environments such as safety equipment, automotive components, and other mechanical parts that must withstand significant force or sudden shocks.
Its superior mechanical properties, including rigidity and dimensional stability under stress, set it apart for demanding applications where strength and durability are critical.
Temperature Resistance
ASA excels in UV resistance and maintains its color and gloss even after prolonged outdoor exposure, making it a preferred choice for exterior applications such as automotive trim and building materials.
Its excellent weatherability ensures that parts remain durable and visually appealing when exposed to harsh environmental conditions over time.
In contrast, Polycarbonate (PC) is more susceptible to UV degradation, which can lead to yellowing and a reduction in mechanical properties unless UV stabilizers are incorporated into the material.
While PC offers superior heat resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, its vulnerability to UV exposure makes it less ideal for prolonged outdoor use without additional protective measures.
Thermal Stability
ASA has a heat deflection temperature of around 85–100°C, making it suitable for environments with moderate heat but less effective under very high temperatures.
In contrast, PC offers superior thermal stability with a heat deflection temperature between 130–140°C, which makes it better suited for applications that require resistance to elevated temperatures and high heat.
Chemical Resistance
ASA exhibits good chemical resistance to water, salts, and certain acids, making it suitable for many outdoor and industrial applications.
However, it can degrade when exposed to some organic solvents, which limits its use in environments with harsh chemicals.
Polycarbonate (PC), on the other hand, demonstrates moderate chemical resistance but is more sensitive to stress cracking when in contact with specific chemicals such as hydrocarbons and alkalis.
This sensitivity requires careful consideration when selecting PC for applications involving chemical exposure to ensure durability and longevity.
Transparency And Aesthetics
ASA is typically opaque and is known for its excellent color retention and smooth surface finish.
These qualities make it an ideal choice for applications where long-term aesthetic appeal is critical, especially in outdoor environments where exposure to sunlight and weather can cause fading or degradation in other materials.
The material’s ability to maintain its appearance over time contributes significantly to its popularity in outdoor furniture, automotive trim, and architectural elements.
In contrast, PC (Polycarbonate) is naturally transparent, offering high clarity that is essential for applications such as lenses, windows, and protective covers.
This transparency allows for versatile uses where visual clarity is important, including in eyewear and electronic device screens.
Additionally, PC can be tinted or made opaque to meet specific design requirements, providing flexibility in aesthetics without compromising its mechanical strength or impact resistance.
PC vs ASA: Application
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) and PC (Polycarbonate) are two robust plastics with distinct properties, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
ASA is commonly used in a variety of outdoor applications due to its exceptional ASA’s weather resistance makes and UV stability.
For example, ASA is ideal for producing outdoor furniture, fixtures, and automotive components that need to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight and harsh weather conditions.
Its dimensional stability and durability make it a reliable choice for parts that need to maintain their shape and performance over time.

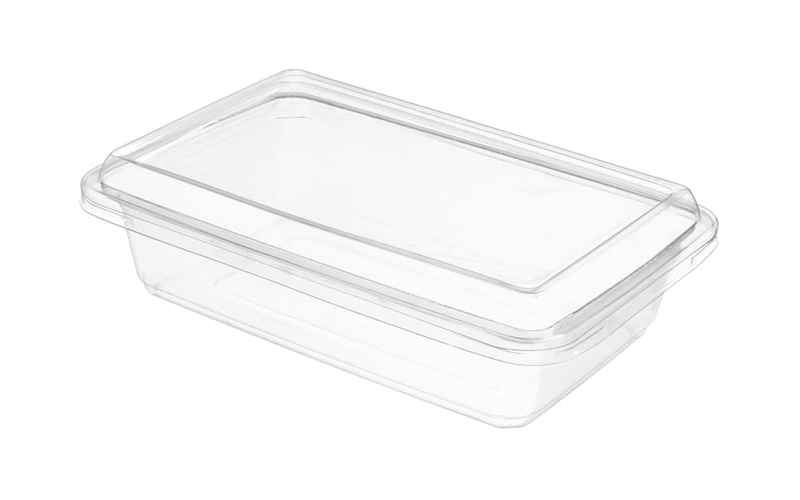
PC, on the other hand, excels in applications that require high strength and impact resistance and hardness.
This filament is commonly used in the production of engineering parts, protective gear, and items that need to endure high stress and impact, such as sunglass lenses, water bottles, and various surfaces.
PC’s transparency and ability to withstand high temperatures make it a versatile choice for various demanding projects, adding an extra layer separation of functionality to the surface. Additionally, it is temperature resistant.

ASA vs PC: Advantages And Disadvantages
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) and PC (Polycarbonate) are two versatile plastics, each with unique strengths and limitations.
Advantages Of ASA
ASA excels in outdoor applications due to its superior weather resistance and UV stability, maintaining color and durability under prolonged sunlight exposure.
It is also easy to process and offers good impact resistance and chemical resistance, making it a cost-effective and reliable choice for automotive parts, garden furniture, roofing panels, and other applications requiring excellent weatherability.
Additionally, ASA’s excellent dimensional stability ensures that printed parts retain their shape and mechanical properties even under varying temperature and moisture conditions, further enhancing its suitability for outdoor use.
Disadvantages Of ASA
However, ASA has a lower melting point and heat resistance compared to PC, which limits its use in high-temperature environments or applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
Additionally, ASA is typically opaque and lacks transparency, restricting its use in applications where clear or translucent materials are needed.
Recycling ASA can also be more challenging due to limited recycling infrastructure, which may impact its sustainability and environmental footprint compared to other thermoplastics.
Despite its good impact resistance, ASA is less rigid and generally less impact resistant than PC, making it more prone to break under extreme mechanical stress or high-impact conditions.
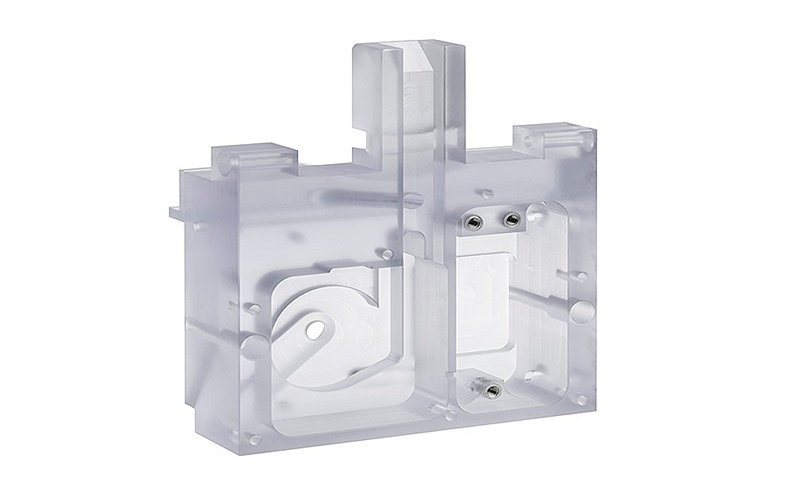
Advantages Of PC
Polycarbonate stands out for its exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for bulletproof windows, eyewear lenses, food containers, and electronic device covers.
Its high heat resistance and durability further enhance its suitability for demanding applications that require sustained performance under high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Additionally, PC offers excellent dimensional stability and can be manufactured in different types and grades to meet specific industry requirements, making it a versatile resin choice for engineering parts, automotive components, and other high-impact mechanical parts.
Disadvantages Of PC
On the downside, PC is more expensive and prone to scratching unless coated, which can increase costs.
Additionally, it is not UV-stable, requiring protective treatments for outdoor use, and its production has a higher environmental footprint due to petroleum-based origins.
Moreover, PC can be sensitive to stress cracking when exposed to certain chemicals, which limits its chemical resistance in some industrial environments.

Choosing Between ASA And PC For Your Project
Choosing between ASA and PC for your project hinges on a careful assessment of your specific needs, blending performance with practicality.
ASA is the ideal choice for outdoor applications, offering excellent weather resistance, UV stability, and durability for automotive parts, garden furniture, and other parts, though its lower heat resistance may limit high-temperature uses.
Conversely, PC shines in projects requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as bulletproof windows, eyewear lenses, and electronic covers, but its higher cost and susceptibility to UV degradation necessitate protective measures.
By aligning these material properties with your project’s environmental conditions, safety requirements, and budget, you can select the optimal plastic to achieve superior results and sustainability.


