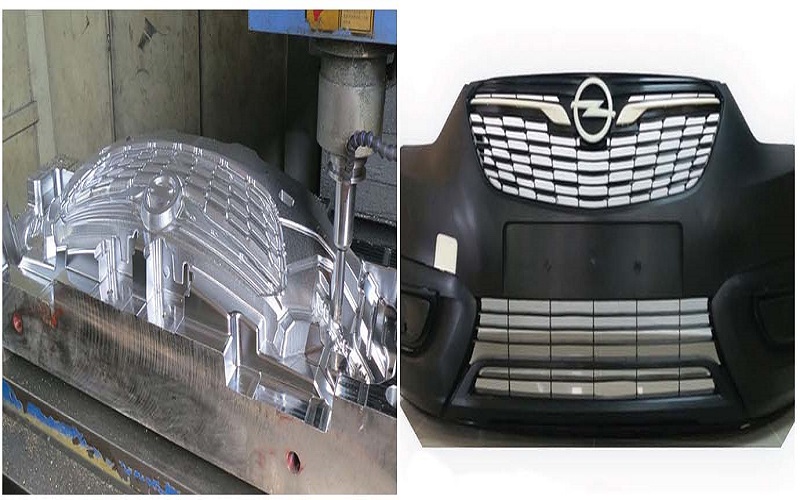
Automotive injection molding produces high-quality car parts efficiently. From dashboards to engine components, this process combines precision and cost-effectiveness. We’ll delve into how it works, its advantages, and its applications in the automotive industry.
Evolution of Automotive Injection Molding
The journey of automotive injection molding began in the 1940s with the introduction of thermoplastic materials suitable for the process. Initially, the technology was used to produce small and simple injection molded plastic parts, but its potential for transforming the automotive industry was quickly recognized.
During the 1950s and 1960s, injection molding gained widespread adoption in the automotive sector, enabling manufacturers to produce injection molding automotive parts more efficiently and precisely.
The 1970s and 1980s marked a significant shift as the automotive industry increasingly utilized plastic car parts to achieve lighter and more fuel-efficient vehicle designs.
During this period, gas-assisted injection molding (GAIM) was developed, enabling the creation of lighter injection molded plastic parts with hollow channels, which improved shape retention and further enhanced the benefits of using plastics in automotive manufacturing.
Today, multi-material injection molding technology permits the combination of different materials in a single injection molding automotive part, improving functionality and design complexity. This evolution has paved the way for innovative applications and has solidified injection molding as an essential process in the automotive industry.
Key Benefits of Automotive Injection Molding

Automotive injection molding offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred method in the industry. From high precision manufacturing to cost efficiency and material versatility, these benefits have revolutionized how automotive parts are produced.
Let’s delve into each of these key benefits to understand why injection molding is so highly valued.
High Precision Manufacturing
The precision capabilities of automotive injection molding are unparalleled. The process can achieve tolerances as fine as +/-0.0002 inches, ensuring that each plastic injection molded part, including body panels, meets exact specifications.
For automotive applications, achieving tight tolerances of +/-0.001 inches is critical for ensuring consistent production and high-quality performance. This level of precision is made possible through the use of robust metal molds, advanced injection molding machines, and techniques like metal injection molding for specific components.
Repeatability is another major advantage of injection molding. The ability to produce identical plastic injection molded parts consistently is crucial in the automotive industry, where safety and reliability are paramount.
The use of different plastic materials and surface textures also allows manufacturers to achieve the desired surface finish for each component, such as body panels, further enhancing the flexibility and precision of the manufacturing process.
Cost Efficiency in Large Scale Production
One of the standout benefits of automotive injection molding is its cost efficiency, particularly in large-scale production.
As production volumes increase, the cost per unit of automotive parts decreases significantly. This scalability makes injection molding a more economical choice for automotive manufacturers, allowing them to produce high-quality parts at lower long-term expenses.
High-speed injection molding technique has further enhanced production efficiency, resulting in shorter manufacturing cycles and timely delivery of quality products. However, it’s important to note that tooling costs can impact cost efficiency, especially for production levels below mass production.
Material Versatility
The material versatility of automotive injection molding is another key benefit. This process can utilize both thermoplastics and thermosets, providing a broad range of material options for manufacturers.
This material flexibility enables the production of parts with diverse properties—strength, flexibility, and heat resistance—to meet the automotive industry’s varied needs through thermoplastic injection molding.
Applications of Injection Molded Parts in Vehicles
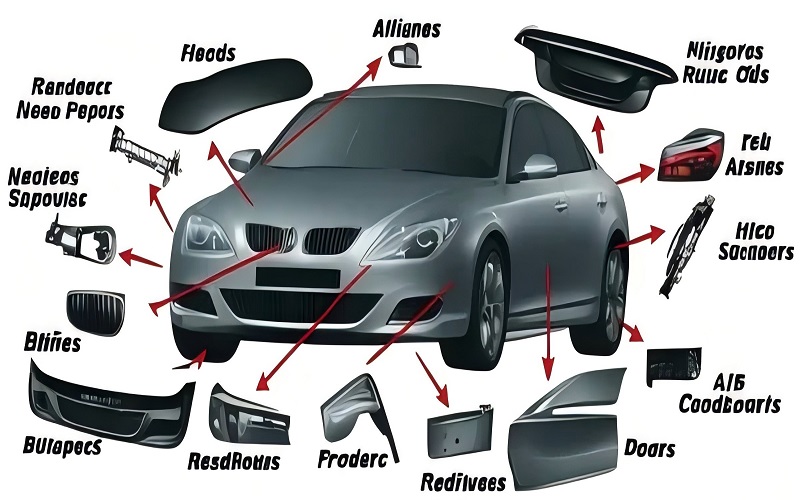
Injection molded parts are integral to various aspects of modern cars, including electric vehicles, from interior automotive components to exterior and under-the-hood parts.
This versatility allows automotive manufacturers to produce automotive components that are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing and durable, often complemented by CNC machining for precision finishing.
We can explore the specific applications of injection molded parts in vehicles.
Interior Components
The interior of a vehicle, including those in electric vehicles, is a complex assembly of various automotive components, many of which are produced using injection molding.
One of the most significant products of this process is the dashboard, which includes multiple functional elements and intricate shapes. The dashboard’s complexity and need for integration make injection molding, sometimes paired with CNC machining for refined details, an ideal manufacturing method for a car’s interior.
Besides dashboards, other interior automotive components such as door panels, instrument panels, air vents, and interior trim are also produced using injection molding.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is commonly used for these parts due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. This method ensures that each component meets high-quality standards and fits seamlessly into the car’s interior, including those in electric vehicles.
Exterior Components
Exterior components of vehicles also benefit greatly from injection molding. Parts like fenders, grilles, bumpers, headlight covers, and light housings are all produced using this method.
Injection molding enables the creation of aesthetically appealing and durable exterior components that enhance vehicle design and performance.
Under-the-Hood Components
Under-the-hood components are critical for the performance and reliability of vehicles. Injection molding is used to produce parts such as oil gauges, battery casings, and cylinder head coverings. Common materials like ABS, Nylon, and PET, along with alternatives like glass-filled nylon, are used to ensure that these plastic components can withstand high temperatures and chemical exposure.
The Injection Molding Process for Automotive Parts
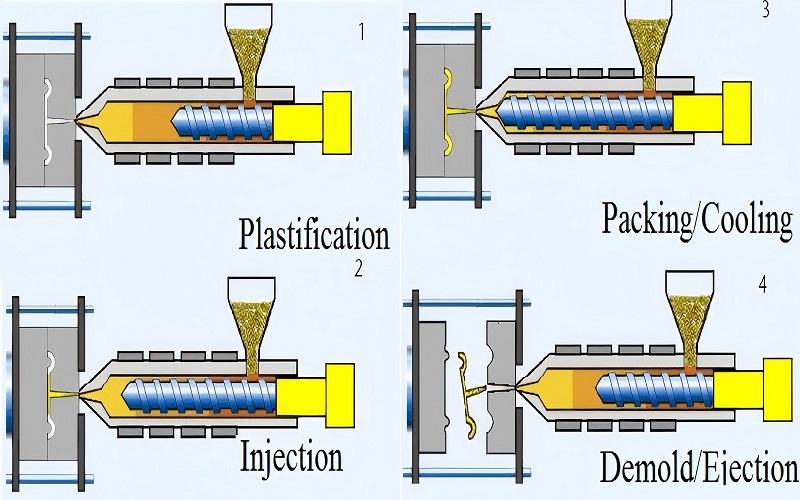
The injection molding process is essential for manufacturing high-quality automotive parts. This automotive injection molding process involves injecting melted rubber plastics into a mold under high pressure, cooling the plastic to maintain its shape, and then ejecting the finished part, such as door handles, for automotive OEMs in the automobile sector. The use of lightweight rubber plastics helps reduce vehicle weight, contributing to increase fuel efficiency.
Proper tooling design, guided by an injection molding design guide, and scientific molding are essential for effective complex plastic part production, ensuring properties like chemical resistance for durability.
Tooling Design and Development
Precision molds, as outlined in the injection molding design guide, are critical for achieving consistent quality and efficiency in automotive parts manufacturing, including door handles with chemical resistance. These molds ensure that parts meet stringent quality standards, enhancing overall vehicle performance, vehicle weight reduction, and consumer satisfaction for automotive OEMs in the automobile sector.
3D printed molds have facilitated rapid design changes and reduced production lead times for rubber plastics components, supporting efforts to increase fuel efficiency.
Injection Molding Cycle
The injection molding cycle involves several key steps: melting rubber plastics resin, injecting it under high pressure into a mold, cooling the plastic to maintain the shape, and then ejecting the part, such as door handles, using the plastic injection molding procedure. This process is crucial for efficient plastic injection for automotive OEMs.
Strong metal molds and consistent quality checks during production ensure the manufacturing of high-quality parts.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is integral to the injection molding process, ensuring that automotive parts, including those made from rubber plastics, meet industry standards and maintain their integrity and reliability through consistent checks, as recommended by the injection molding design guide.
Advanced Materials for Automotive Injection Molding
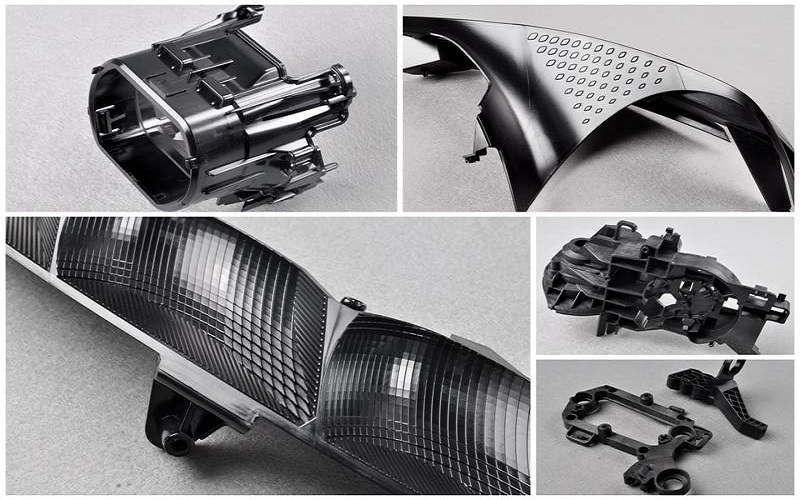

Advanced materials play a crucial role in automotive injection molding, providing specific properties tailored for different applications. From common thermoplastics to reinforced composites, these automotive plastics injection molding materials enhance the performance and durability of automotive parts.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is frequently chosen for automotive applications due to its lightweight nature and impressive resistance to chemicals and UV radiation. This material is ideal for parts like bumpers, offering moisture resistance and fatigue strength, making it suitable for various automotive environments.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a hard and shiny material that is suitable for parts like plastic wheel covers. It is known for its ability to withstand varying temperatures while maintaining its structural integrity, making it an excellent choice for automotive interiors.
Reinforced Composites
Reinforced composites significantly enhance the mechanical properties of automotive parts, offering improved strength-to-weight ratios. Techniques like insert molding, which integrates metal components into carbon fiber reinforced plastics and plastic parts, further boost the durability and strength of these components. This is why reinforced composites manufacturers are increasingly sought after in the industry.
Innovations in Automotive Injection Molding Techniques
Innovations in injection molding techniques have significantly improved the efficiency and effectiveness of automotive part manufacturing. These advancements include the use of softer or semi-hardened steel molds, which accelerate production time by allowing for quicker mold fabrication and easier modifications.
Overmolding
Overmolding is a technique that molds one material over another to enhance properties and reduce costs. This process allows for the creation of parts from two or more polymers, improving production efficiency and aesthetic appeal.
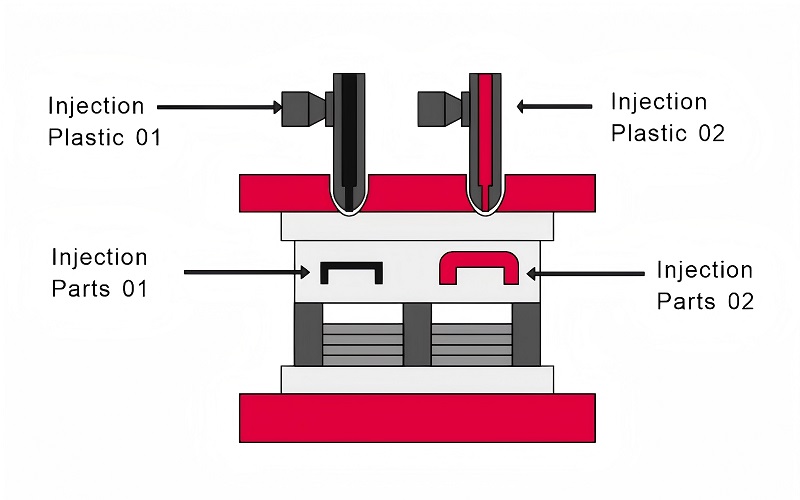
Insert Molding
Insert molding combines metal parts with plastic parts to produce components that are stronger and more durable. By placing metal inserts into the mold and injecting molten plastic around them, this process enhances the strength and resilience of the final product for automotive companies.
Rapid Prototyping with Injection Molding
Rapid prototyping with injection molding enables faster turnaround for short runs of prototype molded components. Automotive companies use low-cost aluminum molds for rapid prototyping, allowing for the quick and cost-effective development of new parts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of automotive injection molding is a growing concern, leading to a focus on sustainable practices. Recent trends include using recycled and bio-based plastics, as well as biodegradable polymers, to reduce the environmental footprint.
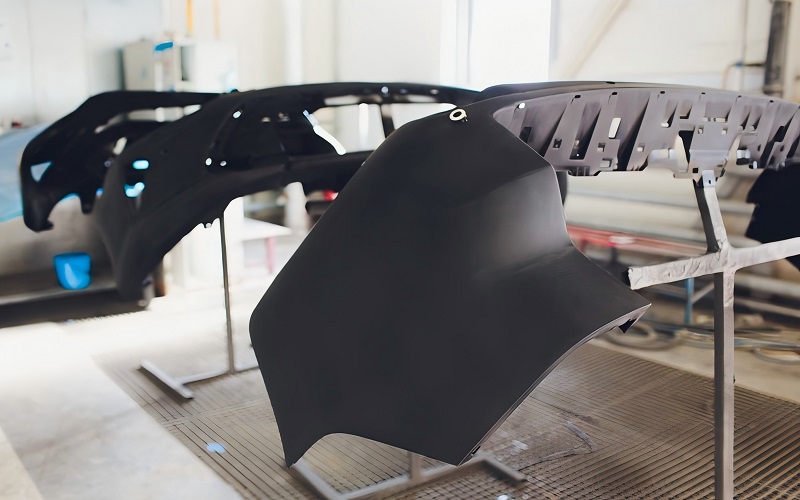

Recycling of Thermoplastic Materials
Recycling thermoplastic materials such as:
- polypropylene
- polycarbonate
- ABS
- acrylic
- nylon
is a key aspect of sustainable automotive manufacturing. The use of mixed plastic waste in automobiles further supports environmental sustainability.
Reducing Waste in Production
Implementing zero-waste goals in production encourages continuous improvement and innovative solutions to minimize waste. Reducing waste not only benefits the environment but also enhances brand reputation and reduces costs in the long run, making processes more energy efficient.
Choosing the Right Injection Molding Partner
Choosing the right injection molding partner is crucial for ensuring high-quality and efficient production in automotive projects. Look for partners with design and manufacturing expertise, relevant certifications, and effective supply chain management.
Working with a vetted global network of partners can also ensure reliable and capable suppliers.
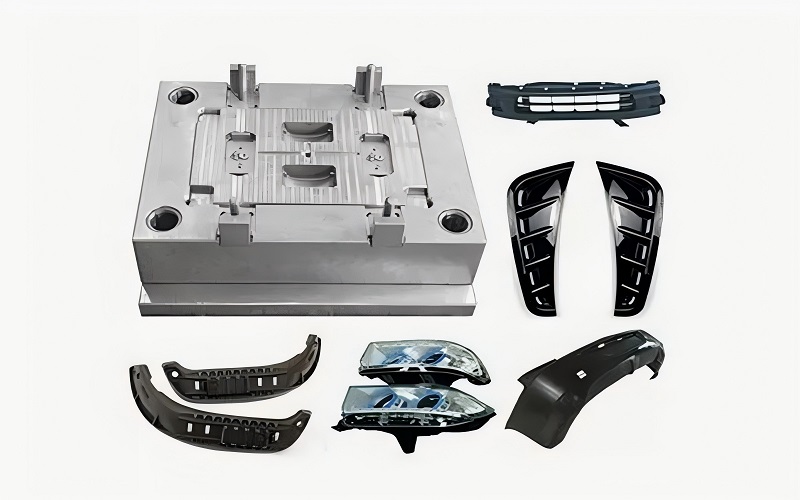

Summary
In conclusion, automotive injection molding has significantly advanced the automotive industry by providing high precision, cost efficiency, and material versatility.
From the historical development to the latest innovations, this technology has proven indispensable in producing high-quality automotive parts. By utilizing advanced materials and adopting environmentally friendly practices, the industry continues to evolve toward a more sustainable future.
Choosing the right injection molding partner is crucial for achieving these benefits and ensuring the success of automotive projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main benefits of automotive injection molding?
The main benefits of automotive injection molding are high precision manufacturing, cost efficiency for large-scale production, and versatility in materials used. These advantages contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness and efficiency in the automotive industry.
What materials are commonly used in automotive injection molding?
Automotive injection molding commonly utilizes polypropylene (PP), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), and reinforced composites like carbon fiber-reinforced plastics. These materials are favored for their durability and performance characteristics in vehicle components.
What are some applications of injection molded parts in vehicles?
Injection molded parts are crucial in vehicles, utilized for interior components like dashboards and door panels, exterior parts such as bumpers and light housings, as well as under-the-hood components including battery casings and oil gauges. These applications highlight their versatility and importance in automotive manufacturing.
How does injection molding contribute to environmental sustainability?
Injection molding enhances environmental sustainability through the use of recyclable thermoplastic materials, the implementation of zero-waste production goals, and the application of biodegradable polymers. These practices significantly reduce waste and promote material reuse in manufacturing processes.
What should be considered when choosing an injection molding partner?
When choosing an injection molding partner, crucial factors to consider include their design and manufacturing expertise, relevant certifications, quality assurance processes, supply chain management capabilities, and proficiency in integrating multiple materials. Prioritizing these aspects will significantly enhance the success of your project.

