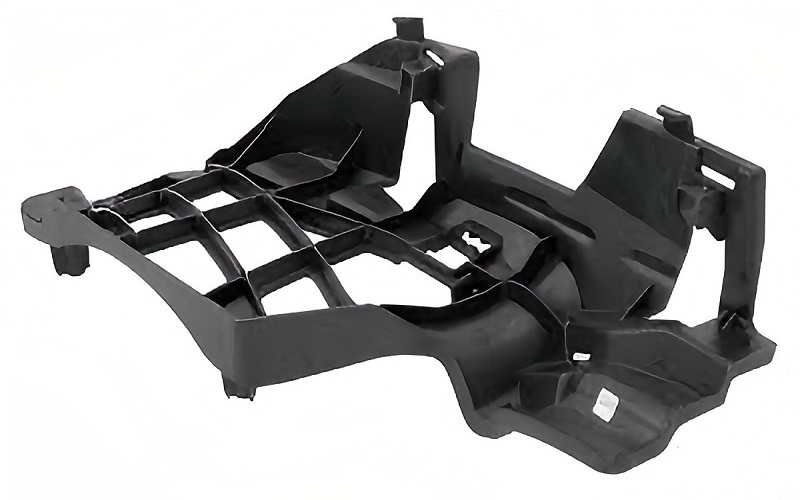
Automotive plastic injection molding is a key process for making car parts, from door handles to under the hood components.
It’s fast, precise, and perfect for creating high-quality plastic parts used in vehicles, including electric vehicles.
This guide breaks down the best practices for automotive injection molding, covering the process, materials, and tips to ensure top results.
Whether you’re new to the automotive industry or looking to improve your molding process, this article will explain everything in a simple, easy-to-follow way.
Understanding Automotive Injection Molding
Before diving into the best practices, it’s helpful to understand what automotive injection molding is and why it’s so important.
This process creates durable, precise plastic components for cars, supporting everything from fuel efficiency to sleek designs.
What is Automotive Plastic Injection Molding?
Automotive plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic, like polyvinyl chloride or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is injected into a mold cavity to form plastic parts.
These parts can be anything from interior trim to exterior components like headlight covers.
The injection molding process uses an injection molding machine to heat raw materials, push them into a mold, and cool them into molded parts.
It’s widely used by automotive injection molding companies because it’s great for mass production, creating identical parts with complex shapes quickly and consistently.
Why It Matters in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry relies on injection molding for its precision and efficiency.
Plastic injection molded parts are lightweight, which helps increase fuel efficiency in vehicles, including electric vehicles.
These parts are also durable, with chemical resistance to handle tough conditions under the hood or on exterior components.
From door panels to suspension bushings, injection molding produces high-quality parts that meet the strict standards of automotive OEMs (original equipment manufacturers).
Plus, it’s cost-effective for high-volume production, keeping production costs low while maintaining quality.
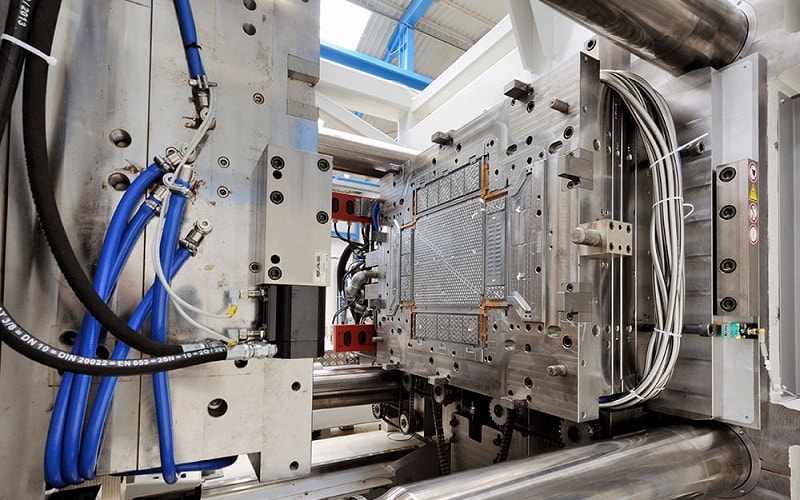
Key Steps in the Automotive Injection Molding Process
Getting the injection molding process right is crucial for producing reliable car parts. Let’s walk through the main steps and best practices to ensure success in automotive injection molding.
Mold Making and Design
The process starts with mold making, where a mold maker creates a high-quality mold to shape the plastic.
The mold cavity is designed to match the exact shape of the part, whether it’s a wheel flare or an instrument panel.
Use precision engineering to ensure the mold is accurate, as even small errors can affect the final product.
Work with reliable automotive injection molding companies to design molds that support complex shapes and tight tolerances. Rapid prototyping can help test mold designs before full production, saving time and materials.
Material Selection
Choosing the right injection molding materials is critical. Thermoplastic materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are popular for their strength and flexibility.
Thermoplastic elastomers are great for parts like seals or suspension bushings that need to bend without breaking.
Consider the part’s purpose—interior components like air vents need a smooth finish, while under the hood components require heat and chemical resistance.
Always match the material to the automotive application to ensure durability and performance.
Injection Molding Process
The injection molding process involves several steps.
First, raw materials are heated in an injection molding machine until they become molten plastic.
This liquid is then injected into the mold cavity under high clamping force to fill every detail. After cooling, the mold opens, and the molded parts are ejected.
For automotive parts like body panels or door handles, maintain consistent temperature and pressure to avoid defects.
Regular maintenance of the injection molder ensures smooth operation and high-quality parts.
Post-Molding Operations
After molding, post-molding operations like trimming, painting, or assembly may be needed.
For example, interior trim or splash guards might be painted for a polished look, while structural components could be assembled with metal parts.
Quality control is key here—inspect each part for defects like warping or uneven surfaces.
Continuous improvement practices, like analyzing production data, help refine the process and reduce errors over time.
Best Practices for Automotive Injection Molding
To get the best results from automotive injection molding, follow these practical tips.
They’ll help you produce high-quality plastic components while keeping costs and errors low.
Optimize Mold Design
Work closely with a mold maker to create high-quality molds that match your part’s needs.
Use computer-aided design (CAD) tools to ensure precision and test designs with rapid prototyping.
For complex shapes like headlight covers or floor rails, incorporate features like cooling channels in the mold to speed up production.
A well-designed mold reduces defects and supports high-volume production.
Choose the Right Materials
Select thermoplastic materials based on the part’s function.
For exterior components like wheel flares, use materials with UV and chemical resistance.
For interior components like instrument panels, prioritize a smooth texture and durability. Thermoplastic elastomers work well for flexible parts like seals.
Always source high-quality raw materials from trusted suppliers to ensure consistent results.
Maintain Equipment
Keep the injection molding machine in top shape with regular cleaning and calibration.
Check the clamping force and temperature settings to avoid issues like incomplete fills or burn marks on molded parts.
A well-maintained injection molder ensures reliable production and reduces downtime, which is critical for automotive manufacturers aiming for mass production.
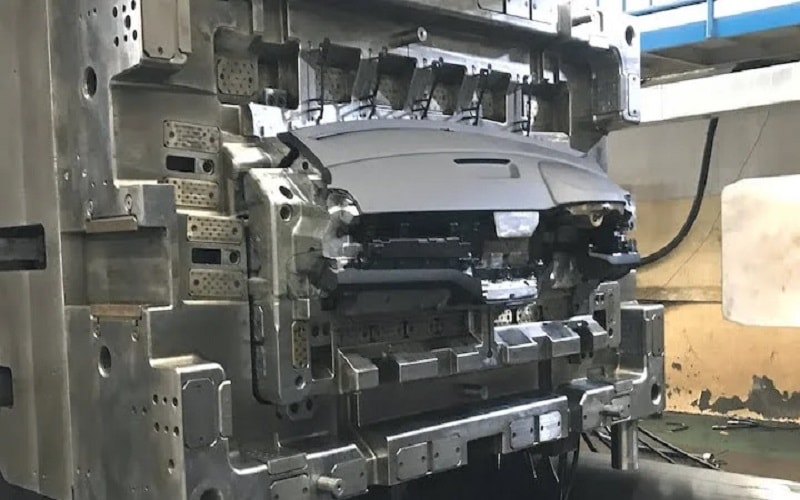

Focus on Quality Control
Implement strict quality control at every stage.
Inspect raw materials for consistency, monitor the molding process for defects, and test finished parts for strength and fit.
For automotive applications like under the hood components, use precision testing to ensure parts meet OEM standards.
Continuous improvement through data analysis helps identify and fix issues early, ensuring high-quality parts.
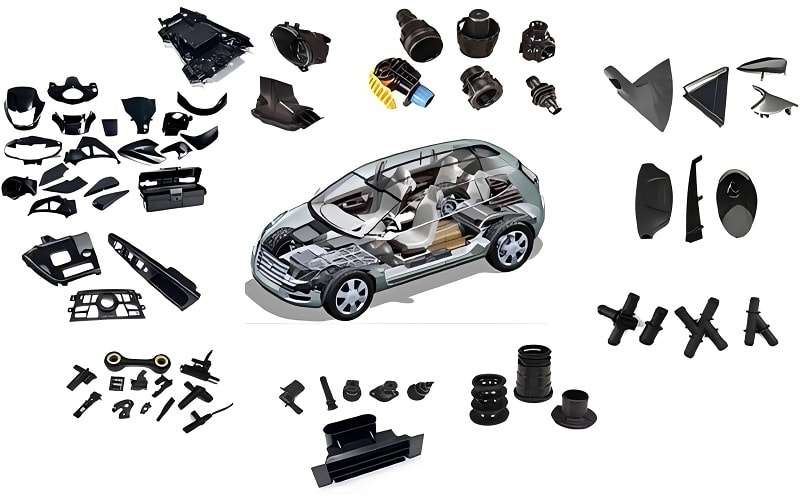
Applications of Automotive Plastic Injection Molding
Automotive injection molding is used to create a broad range of car parts. Here’s a look at how it’s applied across different areas of a vehicle.
Interior Components
Plastic injection molding produces interior components like door panels, air vents, and instrument panels.
These parts need a smooth finish and precise fit to enhance the vehicle’s look and feel.
Injection molded parts are lightweight and durable, making them ideal for interior trim that drivers and passengers interact with daily.
Exterior Components
Exterior components, such as body panels, headlight covers, and wheel flares, benefit from injection molding’s ability to create complex shapes.
These parts are made with materials that resist weathering and impacts, ensuring they last in tough conditions.
The process also supports high-volume production, keeping costs low for automotive OEMs.
Under the Hood Components
Under the hood components, like fuel system parts or suspension bushings, require heat and chemical resistance.
Injection molded rubber or thermoplastics are often used for these parts to handle high temperatures and exposure to oils.
The precision of automotive injection molding ensures these components fit perfectly and perform reliably.
Electric Vehicle Parts
Electric vehicles rely on injection molding for lightweight parts that improve fuel efficiency.
Components like battery housings or structural supports are made with high-strength plastics to reduce vehicle weight.
Injection molding companies use advanced materials and techniques to meet the unique demands of electric vehicle production.

Advantages of Automotive Injection Molding
Compared to traditional manufacturing methods like metal stamping or additive manufacturing, automotive plastic injection molding offers many benefits.
It’s faster and more cost-effective for high-volume production, producing identical parts with tight tolerances.
The process supports complex shapes, allowing for creative designs like curved body panels.
Lightweight plastic components improve fuel efficiency, and materials like PVC provide chemical resistance and durability.
Plus, injection molding reduces waste by using precise amounts of raw materials.
Conclusion
Automotive plastic injection molding is a powerful process for creating high-quality car parts, from interior trim to under the hood components.
By focusing on mold making, material selection, equipment maintenance, and quality control, manufacturers can produce durable, precise plastic parts that meet the automotive industry’s standards.
Whether for traditional vehicles or electric vehicles, injection molding supports mass production of complex shapes while keeping costs low.
Use these best practices to streamline your automotive injection molding process and deliver reliable, high-quality parts for any automotive application.

