When should you use blow mold vs injection mold? This article will compare these two molding techniques, outlining their differences, advantages, and best use cases to help you decide which is suitable for your project.
Key Takeaways
- Blow molding is primarily used for creating hollow plastic parts through the extrusion of a parison, while injection molding is used for producing solid components by injecting molten plastic into molds.
- Blow molding offers advantages in efficiency and versatility for high production volumes of lightweight and thin-walled products, whereas injection molding provides high precision and intricate design capabilities essential for high-tech industries.
- Choosing between blow molding and injection molding depends on factors such as project complexity, production volume, budget, and quality requirements, with each method catering to different application needs.
Understanding Blow Molding

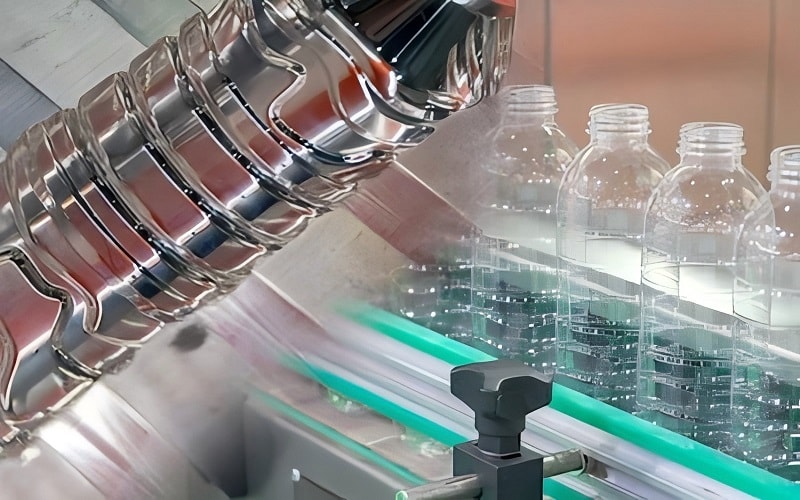
Blow molding is a fascinating blow molding process primarily used to produce blow molded hollow plastic parts and thin walled hollow parts, involving molding and blow techniques.
It involves heating raw thermoplastic materials until they soften, then extruding them into a tube known as a parison. This parison is placed into a mold, and compressed air is blown into it, causing the plastic to expand and take the shape of the mold.
After cooling, the final product is ejected and any excess material is trimmed off. This method is particularly effective for creating lightweight, thin-walled hollow products like bottles and containers.
Types of Blow Molding
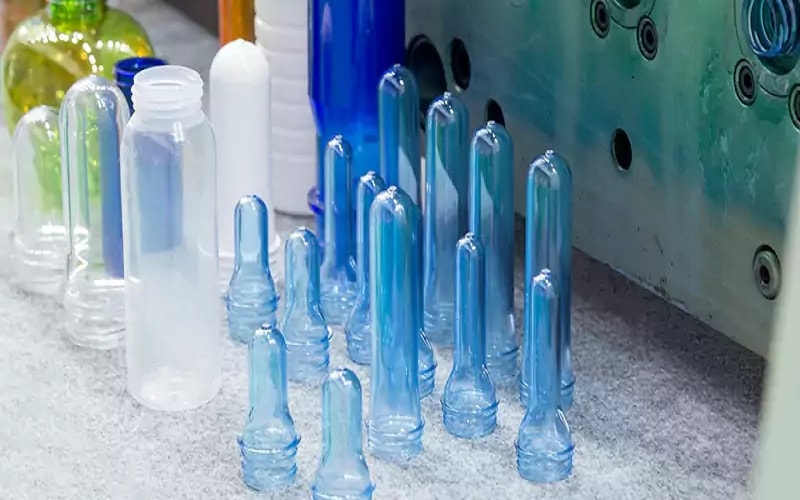
Blow molding comes in several varieties, each suited to different applications. The most prevalent type is extrusion blow molding, where a parison is formed by heating plastic and blowing air to create a hollow tube. This tube is then placed in a mold where it expands to fit the shape. This method is widely used for making bottles and containers from materials like HDPE and PET.
Another common method is injection blow molding, which begins with shaping a preform using a mold. The preform, usually test-tube-shaped, is then expanded into its final shape using pressurized air. This technique is favored for producing complex shapes with tighter tolerances through injection molding and blow.
Lastly, stretch blow molding combines the strengths of both methods, creating intricate design features, especially with PET materials.
Advantages of Blow Molding
Blow molding stands out for its efficiency and ability to produce lightweight products. The process allows for faster production cycles compared to other molding techniques, making it ideal for high production volume manufacturing.
This efficiency translates into cost savings, especially for larger production runs. Additionally, the products made through blow molding are lightweight, which is a significant advantage for industries like packaging and transportation where weight reduction is crucial.
Another significant benefit is the design flexibility that blow molding offers. It can produce a variety of shapes and sizes that are not easily achievable with other molding processes.
This flexibility makes it a preferred choice for manufacturing diverse hollow plastic products, from simple bottles to complex automotive components.
Common Applications of Blow Molding
Blow molding finds extensive applications in various industries, primarily due to its ability to create hollow plastic products efficiently.
The packaging industry, for instance, relies heavily on blow molding to produce bottles and containers of various shapes and sizes. These products are not only lightweight but also durable, making them ideal for storing liquids and other goods.
In the automotive sector, blow molding is used to manufacture components like tanks and ducting, which require precise shapes and durability. The process’s versatility allows for the efficient production of these components, ensuring they meet the stringent requirements of the automotive industry.
Overall, the ability to produce a wide range of hollow products makes blow molding a valuable technique across multiple sectors.
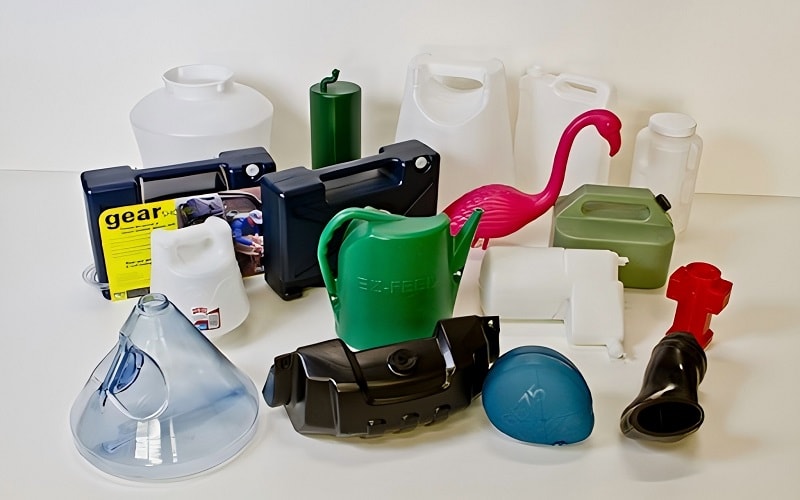

Understanding Injection Molding
Injection molding is another critical process in the manufacturing of plastic parts, primarily used to create solid plastic parts components.
It involves melting plastic and injecting it into a precision mold under high pressure, resulting in injection molded products using an injection molding machine and molding machines to manufacture solid plastic parts.
The process consists of several steps:
- Clamping
- Injection
- Dwelling
- Cooling
- Mold opening
- Product removal
Once the molten plastic cools and hardens, the mold opens, and the solid part is ejected. This method is known for its ability to produce high-precision and intricate designs, making it indispensable in industries like electronics and medical devices.
Types of Injection Molding
Various types of injection molding cater to different manufacturing needs. Injection stretch blow molding, for example, combines injection and blow molding processes.
It starts with creating a solid preform using injection molding, which is then heated and expanded into its final shape using air. This method is particularly effective for creating complex shapes with intricate design features, especially using PET material.
Injection blow molding is another technique that begins with the formation of a preform. This preform is then placed in a blow mold where it is expanded into the final product shape using air.
This method is favored for its ability to produce complex shapes and achieve tighter tolerances in the final products.
Advantages of Injection Molding
One of the standout advantages of injection molding is its precision. The process is ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances and high accuracy.
This precision allows for the creation of highly intricate designs and high-strength parts, which are essential in sectors like consumer electronics and medical devices.
Moreover, the ability to produce parts with intricate designs due to its precise manufacturing capabilities makes injection molding a preferred choice for many industries. The detailed construction of injection molds ensures that the flow of molten plastic is accurately maintained, resulting in high-quality products with minimal defects.
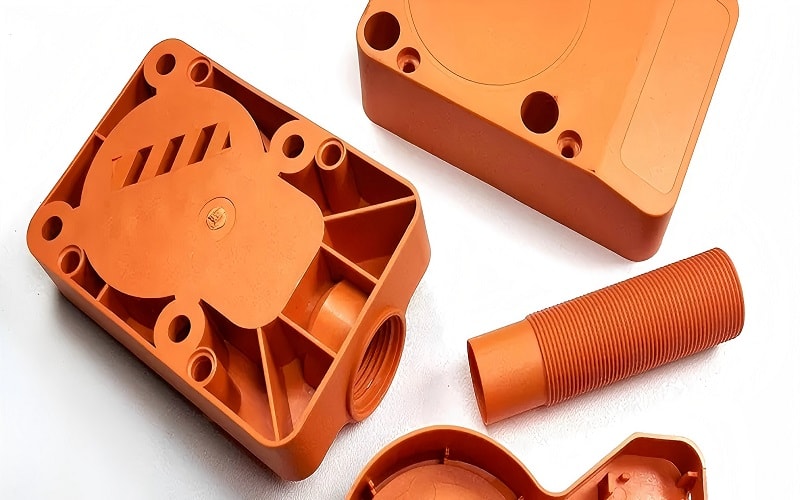

Common Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding is widely used in various industries due to its ability to produce high-precision parts. The consumer electronics industry, for instance, relies on injection molding to create complex components with tight tolerances, ensuring the functionality and reliability of the final products. Similarly, the automotive sector uses injection molding to manufacture intricate parts that require high strength and durability.
The medical device industry also benefits significantly from injection molding. The process allows for the production of complex, high-precision components that are crucial for medical equipment and devices.
This versatility and precision make injection molding an essential technique across multiple high-tech industries.
Key Differences Between Blow Molding and Injection Molding
Understanding the key differences between blow molding and injection molding is essential for selecting the right manufacturing technique for your project.
Blow molding specializes in creating hollow parts like bottles and containers, whereas injection molding is preferred for solid, intricate components found in consumer electronics and medical devices.
These differences influence the choice between the two methods, depending on the project requirements and desired product characteristics.
Molding Process Comparison
The primary distinction between blow molding and injection molding lies in their respective processes. Blow molding focuses on creating hollow parts by expanding a hollow tube of plastic, known as a parison, into a mold using compressed air.
This process is efficient for producing lightweight, thin-walled items that are ideal for packaging and automotive applications.
In contrast, injection molding is used to manufacture solid components. The process involves melting plastic and injecting it into a precision mold under high pressure. This method allows for the creation of highly detailed and intricate designs, making it suitable for high-precision applications.
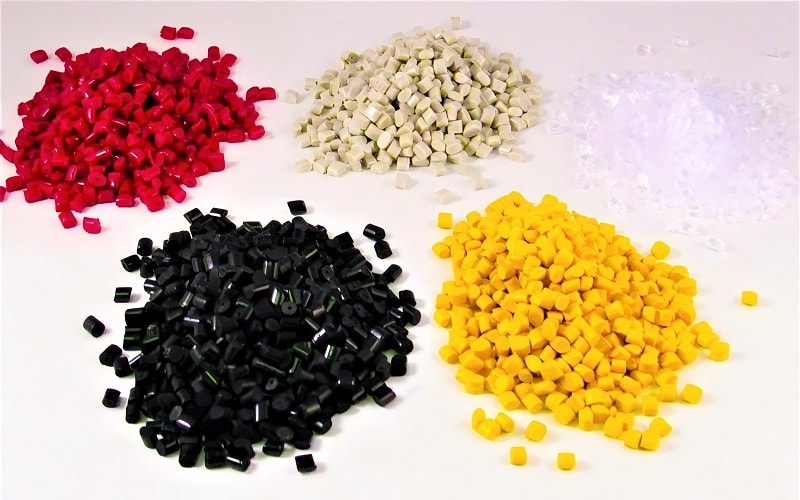
Material and Design Flexibility
Material and design flexibility are crucial factors in choosing between blow molding and injection molding. Blow molding typically uses softer and more flexible plastics like ABS, HDPE, LDPE, and PP, which allow for varying wall thicknesses and complex shapes.
This flexibility makes blow molding suitable for producing a wide range of hollow products, from simple bottles to more complex automotive components.
On the other hand, injection molding is preferred for high-precision applications that require intricate details and tight tolerances. This method is ideal for manufacturing solid components with complex designs, such as those found in consumer electronics and medical devices.
The choice of material and design flexibility should align with the specific requirements of the project to ensure optimal results.

Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Cost and efficiency are critical considerations when choosing between blow molding and injection molding. Blow molding generally has lower setup costs compared to injection molding, making it a more budget-friendly option for certain production runs.
This method is particularly cost-effective for producing large quantities of simpler products, such as packaging materials and automotive components.
In contrast, injection molding tends to have higher upfront costs due to the complexity of the molds and the high-pressure mechanisms involved. However, this method is more suitable for high-precision applications that require intricate designs and tight tolerances, highlighting the injection molding differences.
The choice between the two methods should consider the specific cost and efficiency requirements of the project.
Choosing the Right Molding Method

Selecting the appropriate molding method depends on several factors, including project complexity, production volume, budget, and quality requirements. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring that the right technique is used for the task at hand, particularly when considering the molding definition and comparison, as well as the molding differences and comparison.
This section will delve into these considerations to help you make an informed decision.
Project Complexity and Volume
The complexity of a project often dictates whether blow molding or injection molding is more suitable.
Injection molding is typically chosen for projects involving solid parts with complex designs, as it offers high precision and the ability to create intricate details.
This method is ideal for high volume production of complex components, such as those found in consumer electronics and medical devices.
Blow molding, on the other hand, is better suited for producing large quantities of simpler, hollow products, including blow molded products.
This method is efficient for high production volume manufacturing, making it ideal for industries like packaging and automotive, where large quantities of lightweight, hollow parts are required.
Budget Considerations
Budget is a key factor in deciding between blow molding and injection molding. Real-time quotations and free DFM analysis from services like RapidDirect can provide critical insights into costs within 12 hours of uploading your design file.
These insights can help you evaluate the budget requirements and choose the most cost-effective method for your project.
Quality and Precision Needs
Quality and precision are paramount when selecting a molding method. Injection molding offers high precision and repeatability, making it suitable for products that require tight tolerances and intricate designs.
This method is ideal for industries where product performance and appeal are critical, such as consumer electronics and medical devices.
Blow molding, while primarily producing hollow parts, also offers quality advantages for specific applications. The method’s ability to produce hollow parts makes it suitable for packaging and automotive components.
Each molding method has its advantages in terms of material usage and design, influencing the decision based on specific product needs.
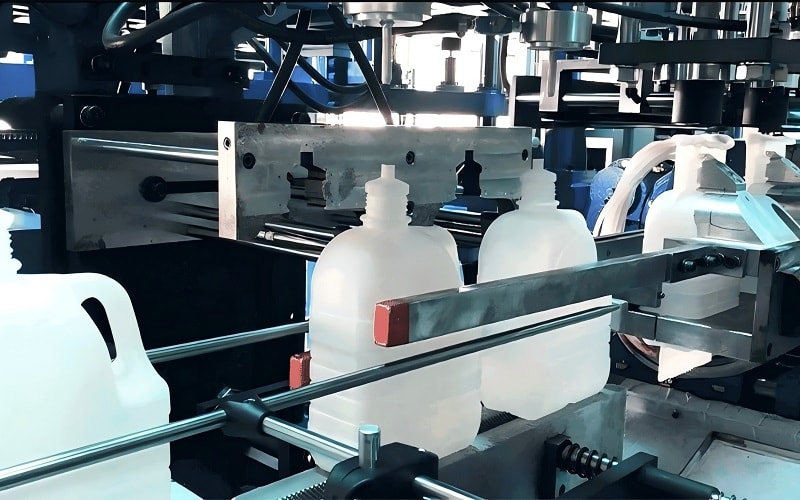

Summary
In summary, both blow molding and injection molding offer unique advantages and are suitable for different types of projects.
Blow molding is ideal for creating lightweight, hollow products like bottles and automotive components, thanks to its efficiency and design flexibility.
Injection molding, on the other hand, excels in producing high-precision, intricate designs required in industries like consumer electronics and medical devices.
Choosing the right molding method depends on various factors, including project complexity, production volume, budget, and quality requirements.
By understanding these differences and considering your specific needs, you can select the most appropriate technique for your manufacturing needs. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights to make informed decisions for your projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between blow molding and injection molding?
The primary distinction between blow molding and injection molding lies in their applications: blow molding manufactures hollow items like bottles, whereas injection molding produces solid parts with complex designs. This difference fundamentally influences the types of products each method is best suited for.
What types of materials are commonly used in blow molding?
Blow molding commonly utilizes materials such as ABS, HDPE, LDPE, and PP due to their flexibility and suitability for producing hollow products. These materials are essential for achieving quality results in the manufacturing process.
Which molding method is more cost-effective?
Blow molding is more cost-effective for producing large quantities of simpler products because it has lower setup costs and faster operation times, whereas injection molding is better suited for high-precision, intricate designs despite its higher upfront costs.
What are the common applications of injection molding?
Injection molding is commonly applied in consumer electronics, automotive components, and medical devices due to its precision and capability for intricate designs. This technique ensures efficient production in these critical industries.
How do I choose the right molding method for my project?
To choose the right molding method for your project, assess factors such as complexity, production volume, budget, and quality requirements. This evaluation will enable you to make a well-informed decision.