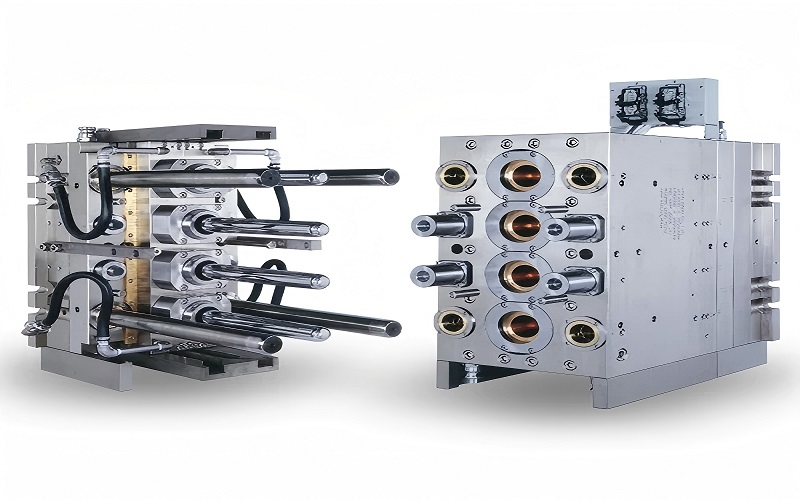
When should you use a hot runner mould instead of a cold runner mould? This article breaks down the key differences, benefits, and drawbacks of each type—hot runner mould and cold runner mould—to help you make the best choice for your project.
What is a Hot Runner Mould?
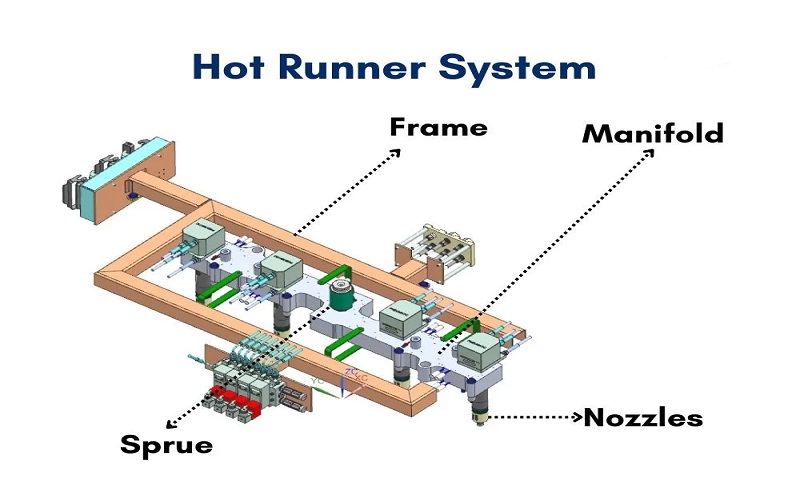
A hot runner system is an internally heated setup used in plastic injection molding to inject molten material directly into the part cavity. This system is the backbone of hot runner molds, ensuring that the temperature of the molten plastic is maintained consistently throughout the injection process.
This consistency is achieved through the use of multiple heating technologies, which significantly impact the heated runner molding process’s quality and efficiency. The hot runner mold plays a crucial role in this system, particularly in runner injection hot runner injection molding.
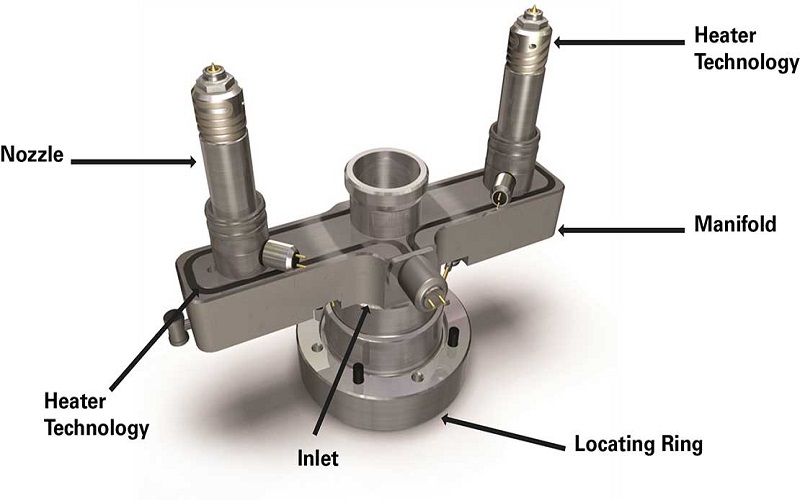
The hot runner system comprises various heated components, each individually controlled to maintain the optimal temperature. Temperature controllers manage these settings with precision, ensuring a stable molding environment. The system includes a heated manifold system, which directs the molten plastic from the inlet to various valve gate nozzles and injection points. These nozzles ensure the precise melt flow into the mold cavity plate, maintaining accurate temperature control in injection molded applications using an injection molding machine.
Manufacturers can fine-tune fill times in hot runner systems by adjusting mold cavity or nozzle temperatures. This level of flow control reduces defects such as sink marks, resulting in higher-quality molded parts. The overarching benefit of hot runner technology is its ability to produce consistent, high-quality parts with minimal waste.
What is a Cold Runner Mould?
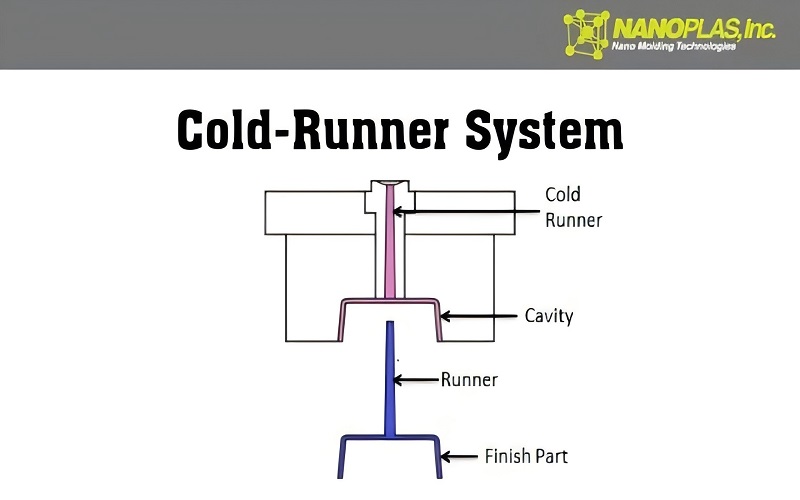
Cold runner molds represent a more straightforward approach to injection molds. Unlike hot runner systems, cold runner molds operate using unheated channels that allow the plastic to flow through at the same temperature as the mold cavity. This method is less expensive and more accessible than hot runner molds, making it a popular choice for many manufacturers. Additionally, cold runner mold systems provide efficient production capabilities, especially when using plastic injection molds. Cold runner injection molding is favored for its cost-effectiveness. Cold runners are an essential aspect of this process.
However, cold runner molds generate solidified plastic flow channels that must be removed after molding. This process results in excess material considered scrap, which must be reprocessed or discarded. Despite the additional handling and potential waste, cold runner molds remain a viable option due to their simplicity and lower initial costs.
Types of Hot Runner Systems
Hot runner systems can vary significantly, with different gate type gating such as hot tip gating and valve gating each suited for specific applications. The choice between these systems depends on the material being used and the desired characteristics of the final product. For instance, externally heated hot runners are ideal for thermosensitive materials, while internally heated systems are better suited for general plastic polymers.
Additionally, nozzle designs in hot runner systems can include options like spring-loaded machine nozzle tips, which enhance performance for various resin processing characteristics. Manufacturing techniques such as gun drilling and two-piece brazing further contribute to the efficiency and precision of hot runner systems and manifold systems.
These variations allow manufacturers to tailor their hot runner systems to meet specific production needs effectively.
Types of Cold Runner Systems
Cold runner systems are typically designed with either two or three plates, which dictate their operational complexity and functionality. Two-plate molds are simpler and more cost-effective, but they require manual removal of the sprue from the final plastic parts. In these systems, the runner is part of the final product and must be manually removed after molding.
On the other hand, three-plate molds offer the advantage of automatically ejecting the runner, reducing the need for manual processing. This system includes an additional plate for runners, allowing them to eject separately from the molded part. While three-plate systems reduce post-molding trimming, they often result in longer cycle times compared to two-plate systems. However, they provide more flexibility for gate placement, enhancing design options with mold plates and enabling precise control over the molding process.
Comparing Hot Runner and Cold Runner Moulds
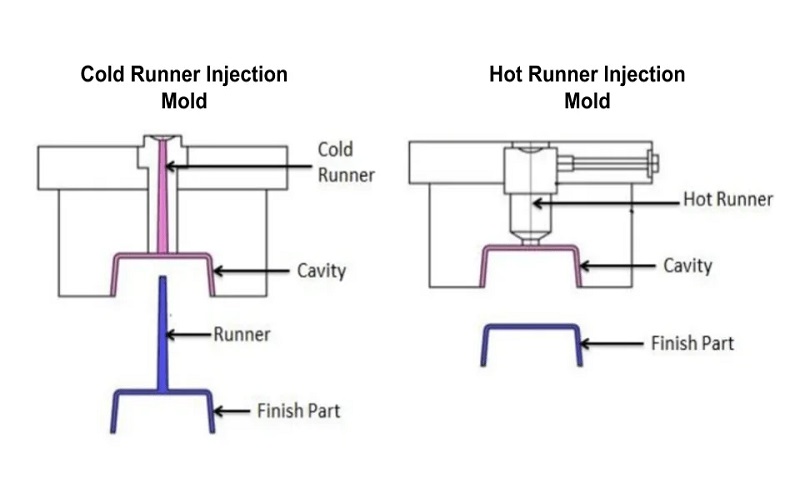
When comparing hot runner vs cold runner molds, several factors must be considered, including initial cost, maintenance requirements, cycle times, and part quality.
Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in determining which system is best suited for your specific needs.
Initial Cost
One of the most significant differences between hot runner and cold runner molds is the initial cost. Hot runner molds have a higher initial setup cost due to their advanced technology and complex design, often tailored for low volume production. The cost injection molders face increased expenses due to the cost of hot runner components, such as the locating ring, and the need for specialized equipment like cnc machining for precision manufacturing, which contributes to this higher expense. For small production runs, this initial investment may not be justifiable.
In contrast, cold runner molds have lower setup and maintenance expenses. Their simpler design and fewer components make them more affordable upfront. However, converting to a hot runner system can lead to significant cost savings over time, especially when high production volumes are achieved.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance is another critical consideration. Hot runner molds often necessitate more elaborate cleaning routines, including the potential removal of components for thorough maintenance. This complexity can lead to higher maintenance cost and potential downtimes if not handled properly.
On the other hand, cold runner molds are designed for simpler upkeep, making them user-friendly in maintenance scenarios. Their straightforward mold design reduces the time and effort required for regular maintenance, making them an attractive option for manufacturers looking to minimize downtime, especially for mold masters.
Cycle Times
Cycle times are crucial for production efficiency. Hot runner molds enhance production efficiency by reducing the time needed for materials to cool before ejection. This reduction leads to faster cycle times, significantly improving the speed of the production cycle time.
In comparison, cold runner molds often extend production times due to the need for additional cooling and handling steps. The differences in cycle times between hot runner and cold runner molds can greatly influence overall productivity in the injection molding process.
Part Quality
Part quality is another area where hot runner molds excel. The placement of gates in hot runner systems contributes to greater control over surface quality by eliminating runner trimming and inconsistencies. The absence of runner attachment leads to cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing finishes on the final products, including injection molded parts.
In contrast, cold runner molds produce significantly more scrap and can result in visible imperfections from de-gating. However, part quality plays a crucial role in determining the success of manufactured items, making it essential to compare these aspects when choosing between hot runner and cold runner molds.
Advantages of Hot Runner Moulds

Hot runner molds offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for many manufacturers. One of the primary benefits is the minimization of material waste. By keeping the runner material heated and reusable, hot runner systems significantly reduce plastic waste. This advantage is particularly beneficial in molds with multiple cavities, where waste reduction can lead to substantial cost savings.
Another advantage is the faster cycle times achieved by hot runner systems. By hot runners eliminate the need for runner recycling processes, hot runners enhance production efficiency and output capability. Additionally, parts produced by hot runners tend to have a cleaner finish, as there is no need for mechanical removal of runners. These hot runner advantages contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness of the manufacturing process.
Hot runner systems also allow for better control of temperatures, reducing defects like burn marks on the final product. This precise temperature control contributes to higher quality parts and greater consistency in production. Moreover, hot runner systems contribute to sustainability by reducing plastic waste, energy consumption, and heat.
Advantages of Cold Runner Moulds
Cold runner molds also offer several advantages in the injection molding process. One of the most significant benefits is the lower initial cost compared to hot runner molds. The design of cold runner molds is simpler, making them easier to implement and maintain. This simplicity translates to lower setup and maintenance expenses.
Another key advantage is the ease of color changes. Cold runner molds allow for simpler tool changes without the risk of bleeding, making them ideal for projects that require frequent color adjustments. Additionally, the straightforward design of cold runner molds makes them user-friendly and accessible for a wide range of applications.
Disadvantages of Hot Runner Moulds
Despite their many advantages, hot runner molds have some drawbacks. One of the primary disadvantages is the higher costs associated with their complex design and added features. The initial setup and maintenance costs can be significant, making hot runner molds a considerable investment.
Additionally, the maintenance of hot runner molds can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and equipment. If not properly managed, hot runner systems can present potential thermal degradation issues, affecting the quality of the final product. These factors can lead to increased operational costs and costly secondary operations, as well as potential downtime.
Disadvantages of Cold Runner Moulds
Cold runner molds also come with their set of disadvantages, including cold runner limitations. One of the main drawbacks is the slower cycle times compared to hot runner molds. Cold runner systems require additional cooling and handling steps, which can extend production times.
Another disadvantage is the increased waste that can generate waste by cold runner molds. The solidified plastic flows channels that must be removed after molding result in significant scrap material. This waste can raise the overall cost of production, especially if the material cannot be recycled.
Additionally, cold runner molds can face cooling challenges, further affecting the efficiency and speed of the injection molding process.
Choosing Between Hot Runner and Cold Runner Moulds
Choosing between hot runner and cold runner molds involves considering several factors. Key project requirements include functionality, quality expectations, and compatibility with design specifications. Production volume also plays a crucial role; cold runner molds offer flexibility for rapid design adjustments, which is beneficial for lower volumes or prototype runs.
Budget considerations are also essential. While hot runner molds may have higher upfront costs, they can lead to lower operational costs due to reduced waste. Incorporating all these factors will lead to a more informed decision on whether to choose hot runner or cold runner systems.
Summary
In summary, both hot runner and cold runner molds have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Hot runner molds offer benefits like reduced waste, faster cycle times, and higher part quality, making them ideal for high-volume production. On the other hand, cold runner molds are more cost-effective initially and easier to maintain, making them suitable for lower volumes or projects with frequent design changes.
Ultimately, the choice between hot runner and cold runner molds depends on your specific project requirements, production volume, and budget. By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that optimizes your injection molding process and meets your production goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hot runner in mold?
A hot runner system is a component in plastic injection molding that uses heated elements to keep molten plastic flowing from the injection unit to the mold cavities, enhancing efficiency by reducing waste and ensuring consistent temperatures. This system typically comprises an injection unit and a clamping unit.
What is the difference between hot sprue and cold sprue?
The primary difference between hot sprue and cold sprue lies in temperature control; hot sprues involve heated channels that keep the material molten while being transferred, whereas cold sprues use unheated channels which can lead to solidification of the material before it reaches the mold. This distinction affects the efficiency and quality of the molding process.
What are the different types of runners in Mould?
The two main types of runners in molding are cold runners and hot runners. Cold runners are simple and consistent, solidifying during the molding process, while hot runners maintain the melt state to enhance flow and reduce waste.
What is the difference between hot and cold compression molding?
The primary difference between hot and cold compression molding lies in their processing temperatures; hot compression involves preheating the material before molding, while cold compression is conducted at room temperature, followed by curing if necessary. This distinction affects the characteristics and applications of the produced components.
Which system has a higher initial cost?
Hot runner molds have a higher initial cost owing to their advanced technology and complex design.

