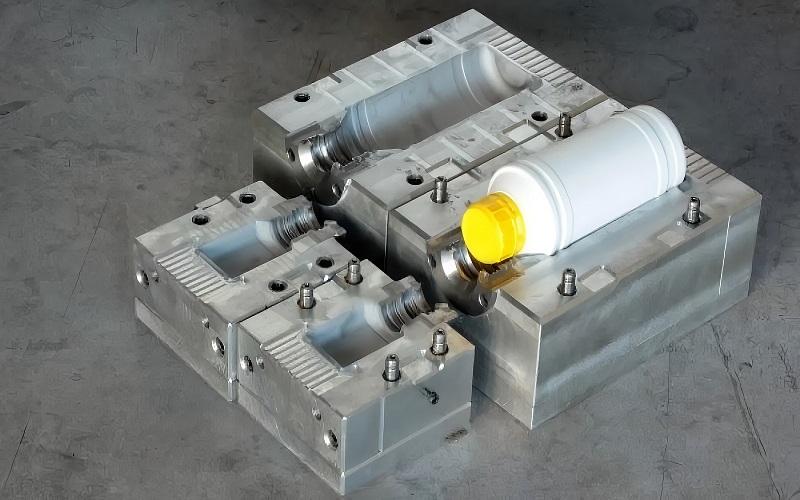
Need to produce a small batch of high-quality plastic parts? Injection molding low volume production can help. This method is ideal for creating 1,000 to 10,000 units efficiently and cost-effectively. In this article, we’ll cover its benefits, key design considerations, and the process itself.
Understanding Low Volume Injection Molding
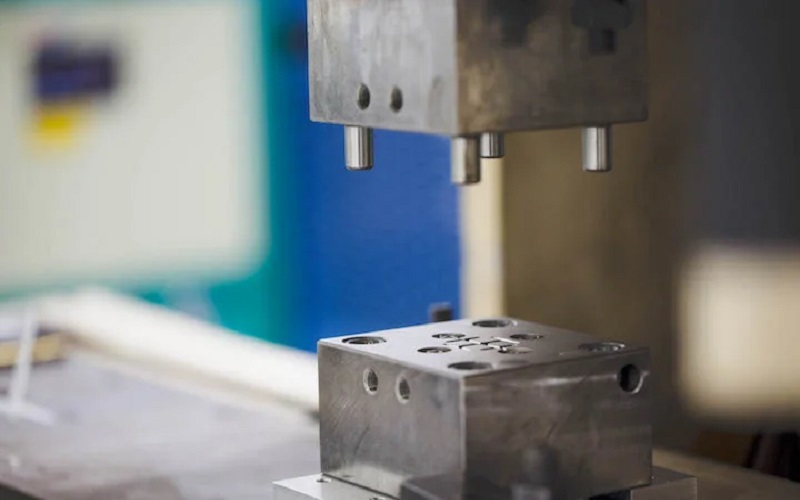

Low volume injection molding is a specialized process used to create small quantities of injection molded parts with consistent characteristics. Typically, the volume range for this type of low volume manufacturing falls between 1,000 to 10,000 parts, making it ideal for small batch orders and rapid prototyping.
Unlike high-volume equipment, the machinery used in low volume injection molding is smaller and designed for faster changeovers, ensuring quick production times and cost efficiency, while optimizing mold cavity surfaces for precision.
The cost-effectiveness of low volume molds stems from the lower tooling costs spread across several thousand parts. Compared to 3D-printed molds, steel molds used in low volume manufacturing offer longer durability and better accuracy in part design.
This makes low volume injection molding a go-to option for those needing high-quality, precise injection molded parts without the commitment of large-scale production.
Benefits of Low Volume Plastic Injection Molding
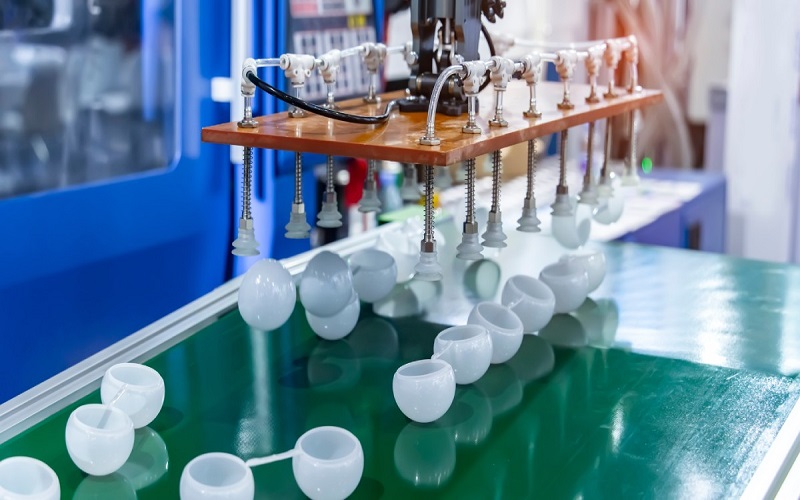

Low volume plastic injection molding offers a plethora of benefits that make it an attractive option for various industries. From cost efficiency to design flexibility and shorter lead times, this method addresses many of the challenges faced by manufacturers today, including optimizing the supply chain for small batch production.
Let’s delve into these benefits in more detail, such as how avoiding sharp corners in part design can reduce stress and improve durability, or how ejector pins push the finished parts out of the mold efficiently, minimizing production delays.
Cost Efficiency
One of the standout benefits of low volume plastic injection molding is its cost efficiency. Eliminating minimum order requirements allows businesses to produce parts based on actual demand, reducing storage costs and minimizing large inventories of unnecessary products, even when working with molten material that requires precise handling.
This approach is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized businesses operating in unpredictable industries, offering a cost-effective solution for short run production, especially for materials that are naturally transparent like polycarbonate, where careful design is needed to avoid defects that create stress in the final parts.
Design Flexibility
Design flexibility is another major advantage of low volume injection molding. This process allows for quick adjustments and strategic enhancements in product design, enabling manufacturers to fine-tune products and processes to better meet market demands.
The ability to iterate quickly and test designs before mass production ensures that the final product is optimized for performance and consumer satisfaction.
Shorter Lead Times
Shorter lead times are crucial for a product’s success in today’s fast-paced market. Low volume injection molding significantly reduces lead times by simplifying the mold manufacturing process and allowing for quicker production in a shorter period.
Functional parts can be produced within days, enhancing responsiveness to market needs and enabling on-demand manufacturing.
This agility is crucial for staying competitive and meeting consumer expectations.
Key Considerations for Low Volume Injection Mold Design
Design is critical in low volume injection molding as it ensures that parts meet project needs and allows for accurate, high-quality molding. Key design considerations include material selection, wall thickness, and draft angles, each playing a vital role in the overall success of the molding process, especially when using family molds to produce multiple parts in one cycle.
These factors must be meticulously planned to avoid defects like tool marks on the part surface, ensure a straight pull for easy ejection, and guarantee that the final product meets all functional, aesthetic requirements, and design considerations.
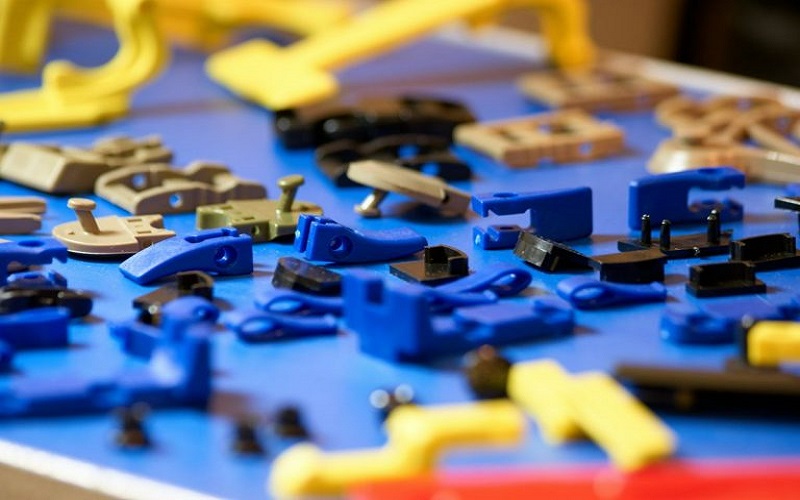

Material Selection
Material selection is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process, influencing the durability, heat resistance, and flexibility of the final product.
Common materials for low volume production include ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene, nylon, and thermoplastic resins, each offering unique advantages for specific applications. Factors such as mechanical properties, resistance to chemicals, and impact resistance are crucial considerations when choosing a resin.
Additives like glass and carbon fibers can also be incorporated to enhance performance properties.
Wall Thickness
Ensuring appropriate wall thickness is vital to prevent defects such as sinking and warping in molded items. Walls that are too thick or too thin should be avoided, and the selected injection molding material will determine the range of scale wall thickness that can be used effectively, often requiring designers to solve corners by incorporating tapered edges.
Proper temperature and pressure management during the molding process are also essential for maintaining quality and consistency, while using rounded edges can further reduce stress concentrations and improve the overall durability of the molded parts.
Draft Angles
Draft angles are essential as they simplify the removal of parts from the mold, reducing the risk of damage during ejection. Draft angles of 1 to 2 degrees are commonly used to facilitate easier part removal and enhance overall moldability.
This consideration ensures that the final molded parts are free from defects and maintain their structural integrity.
The Low Volume Injection Molding Process
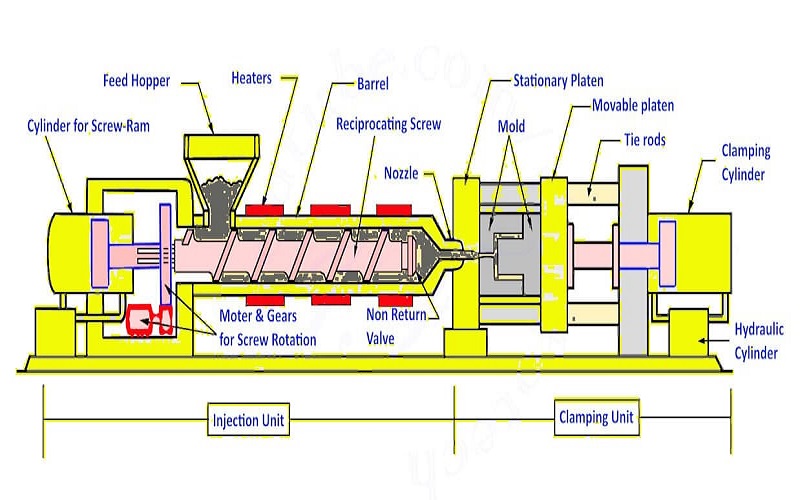
The low volume injection molding process involves several key steps, starting with loading resin pellets into the injection molding machine. The plastic is then melted, compressed, and injected into the mold, where it cools and solidifies before being ejected.
This process provides better design flexibility. It also enables immediate feedback, bridging the gap between prototyping and high-volume production.
Utilizing 3D printed molds can drastically lower production costs and time compared to traditional metal molds, making the process more economical for low volume production. This approach not only saves time but also allows for rapid iterations and design adjustments to produce molds, ensuring that the final product meets all specifications and quality standards.
Tooling and Mold Design
The first step in low volume injection molding is identifying the final plastic parts specifications and choosing appropriate materials. Typical tooling for this process involves softer aluminum molds, which are more cost-effective and quicker to produce compared to traditional steel molds.
Additionally, an injection molded plastic injection mold can be used to enhance efficiency in production, including the use of injection molds.
These molds can be ready in about two weeks, significantly reducing lead times. Aluminum tooling also benefits from quicker heat-up times and eliminates the need for an extra annealing step during heat treatment.
Prototyping
Prototyping is a crucial stage in low volume injection molding, allowing for testing and correcting design flaws before final production. 3D printing is frequently employed to create rapid prototypes, enabling rapid iteration and design corrections.
Soft tooling methods like silicone and urethane are also often used for prototyping and small production runs, providing a flexible and cost-effective solution for quick turnarounds.
Injection Molding Machine Setup
The machinery for low volume injection molding is typically smaller and designed for quicker setup changes due to shorter production runs. During the setup, components such as ejectors and cooling systems are integrated to prepare for multi cavity production.
The ejector system is a crucial component installed into the mold to ensure smooth removal of the molded parts, including ejector pins.
Quality Control in Low Volume Injection Molding
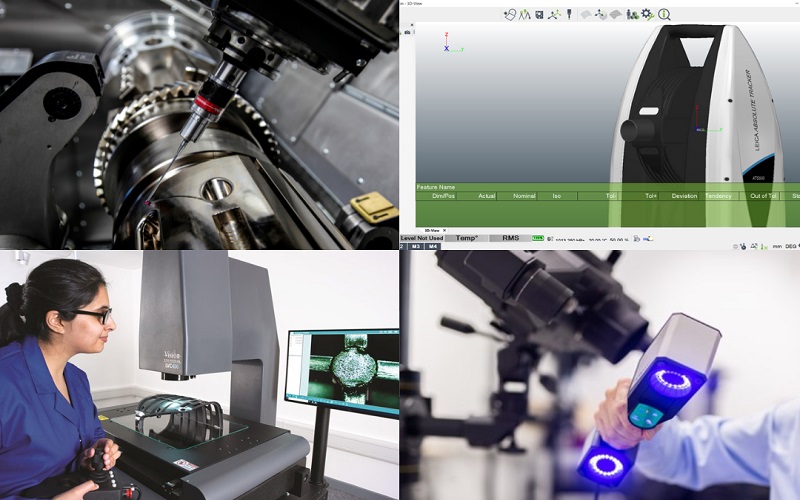
Quality control is vital in low volume injection molding to ensure that the final products meet all specifications and standards. Precise temperature control is crucial for maintaining molding quality and achieving part-to-part consistency.
Inspection procedures during production runs help identify any defects that may arise, ensuring that only high-quality components are produced.
Inspection Procedures
The quality control process involves inspecting quality parts for defects and ensuring compliance with quality standards. After the first three shots of molding, a three-part First Article Inspection (FAI) report and a 30-part Process Capability Report are provided to assess the quality of parts produced.
The Inspection Statement of Work (ISOW) alerts manufacturers to issues with tolerances and the moldability of specified features. Adhering to Critical-to-Quality (CTQ) features specified in the design is essential for ensuring that the final parts meet their functional requirements.
Post-Processing
Post-processing activities, including trimming molded parts and surface finish operations, are crucial for improving the aesthetic and functional quality of the final products. Finishing methods such as diamond buff, 600 gritstone, or bead blasting can be alternatives to hand-polishing for surface finishing, offering a smoother finish and enhancing the product’s overall appeal.
Applications of Low Volume Injection Molding
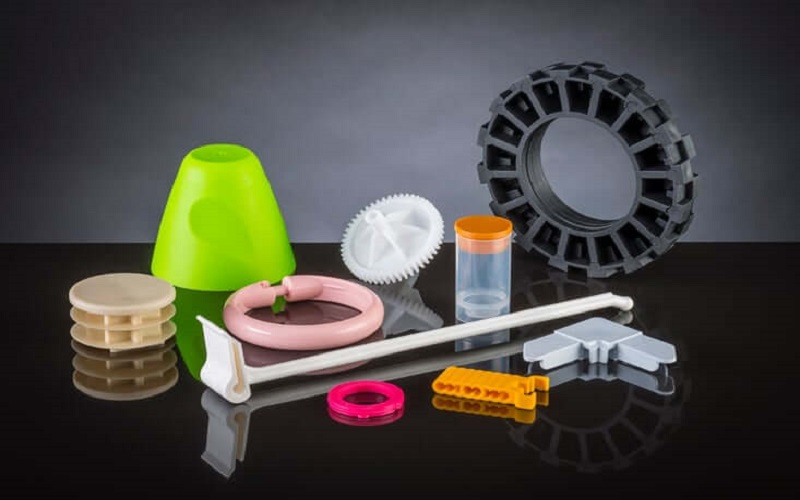

Low volume injection molding is a rapid and efficient method for producing plastic components ranging from 100 to 10,000 units, serving as a bridge between prototyping and mass production. This production type is utilized in various industries, including automotive manufacturing and consumer electronics, to create specialized components and prototype parts.
Rapid Prototyping
Low volume injection molding enables the testing of new concepts in various industries before mass production. This process allows for the rapid creation of multiple iterations of a prototype, offering faster feedback loops for design teams.
The benefits include speed, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to iterate quickly, ensuring that the final product meets all design specifications.
Small Batch Production
Low volume injection molding offers a cost-effective solution for small batch production, ideal for product developers, OEMs, and tier suppliers. It supports small run production, helping businesses with capital limitations reduce costs while still meeting their production requirements.
Choosing the Right Partner for Low Volume Injection Molding Services
Choosing the right partner for low volume injection molding services is crucial in ensuring efficiency and maintaining high-quality standards. Look for partners who offer comprehensive prototyping services, including mold flow analysis and responsive manufacturing.
Experienced service providers with a track record in low volume injection molding can help startups minimize investment in large-scale production.

Expertise and Specialization
Experience in low volume injection molding is crucial as it helps startups minimize investment in large-scale production. Companies with low to moderate production capacity can offer prototypes quickly for testing, ensuring the product meets the required standards before full production.
Compliance and Quality Standards
Compliance with specifications prevents compromises that might affect product quality. Choosing a partner with certifications can indicate a commitment to maintaining quality and compliance, ensuring the production of high-quality components with tighter tolerances.
Alternatives to Low Volume Injection Molding
Various methods exist as alternatives to low volume injection molding, including 3D printing, CNC machining, and urethane casting. Each of these alternatives offers unique advantages and can be more suitable depending on specific project requirements and constraints.
Let’s explore these options in more detail.
3D Printing
3D printing is considered an alternative manufacturing process to quick turn molding. It allows for rapid prototyping and eliminates the need for mold costs, making it a flexible option for small batch manufacturing processes.
This method is particularly beneficial for creating complex geometries and iterating designs quickly, providing significant flexibility in the manufacturing process, including sharp internal corners.

CNC Machining
CNC machining is a reliable method for small quantity plastic manufacturing. Known for its accuracy and reliability, CNC machining can produce high-quality molds, patterns, or dies. This method is ideal for creating precise and intricate parts with tight tolerances, making it a preferred choice for many high-quality component manufacturers.
Urethane Casting
Urethane casting involves pouring liquid polyurethane into a mold to create high-quality plastic parts. This method is particularly well-suited for low volume production, allowing the creation of multiple product copies from a single mold. Urethane casting offers low upfront costs and quick lead times, making it ideal for prototypes and limited runs.
Industries such as automotive and aerospace leverage urethane casting for creating durable components, thanks to its flexibility and ease of modification during the development process.
Summary
Low volume injection molding offers a versatile and cost-effective solution for producing high-quality plastic parts in small quantities.
From its benefits of cost efficiency, design flexibility, and shorter lead times to the key considerations in mold design and quality control, this process addresses many challenges faced by manufacturers today.
Whether you’re looking to prototype new designs or produce small batches, understanding the nuances of low volume injection molding can significantly impact your project’s success. Embrace this innovative approach to stay agile and competitive in the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is low volume injection molding?
Low volume injection molding is a manufacturing process designed for producing small quantities of plastic parts, typically between 1,000 to 10,000 units, while ensuring consistent quality and accuracy. This method is ideal for projects that require precision without the need for large-scale production.
What are the benefits of low volume injection molding?
Low volume injection molding offers cost efficiency, design flexibility, and shorter lead times, making it particularly suitable for small batch orders and rapid prototyping.
How important is material selection in low volume injection molding?
Material selection is critical in low volume injection molding, as it directly affects the durability, heat resistance, and flexibility of the final product. Choosing the appropriate material, such as ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene, or nylon, ensures optimal performance and quality.
What are common applications of low volume injection molding?
Low volume injection molding is commonly applied in rapid prototyping and small batch production, particularly in the automotive and consumer electronics industries. These applications enable efficient development and testing of products with reduced lead times.
What are some alternatives to low volume injection molding?
3D printing, CNC machining, and urethane casting are viable alternatives to low volume injection molding, each with distinct benefits tailored to various project needs. Consider these options to enhance your production process effectively.