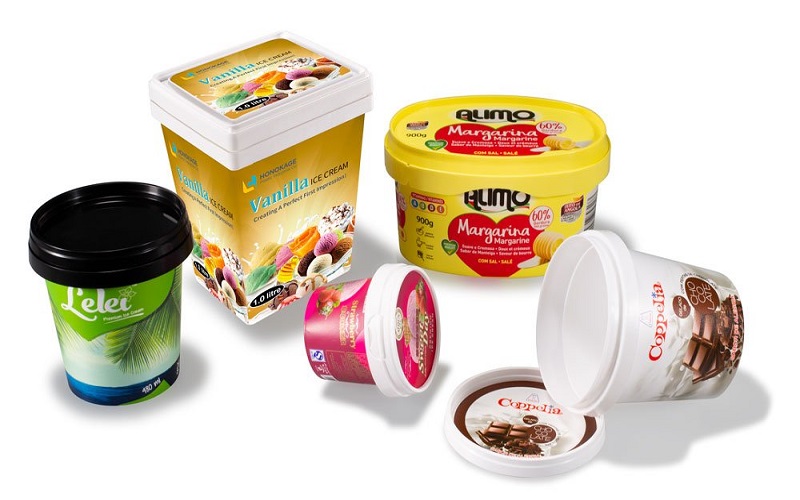
In today’s competitive market, businesses across various industries are constantly seeking efficient and reliable ways to package their products.
Injection molding packaging stands out as a versatile solution that combines precision, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Whether you’re in consumer electronics, cosmetics, or food storage, understanding how injection molding can meet your specific needs is crucial.
This article explores the best injection molding packaging solutions, delving into the processes, benefits, and applications to help you make informed decisions for your business.
What is Injection Molding?
This manufacturing technique has revolutionized the production of plastic parts and components, offering unparalleled efficiency for high-volume outputs.
Injection molding is a process where molten plastic material is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure to form a desired shape.
It begins with raw material, typically plastic resin in pellet form, which is heated in a barrel until it becomes molten.
This molten material is then forced into hardened steel molds or aluminium moulds using an injection unit equipped with a helical screw or reciprocating screw.
The injection moulding machine plays a pivotal role here, controlling parameters like injection pressure, injection speed, and the overall injection moulding cycle.
As the material cools and solidifies within the mold cavity, it takes on the precise geometry of the moulded parts.
This rapid cooling phase ensures tight tolerances and minimizes defects such as sink marks or trapped air, which can be mitigated through proper air vents and ejector pins.
The result is a final product that exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including wear resistance and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for packaging components like bottle caps or storage containers.
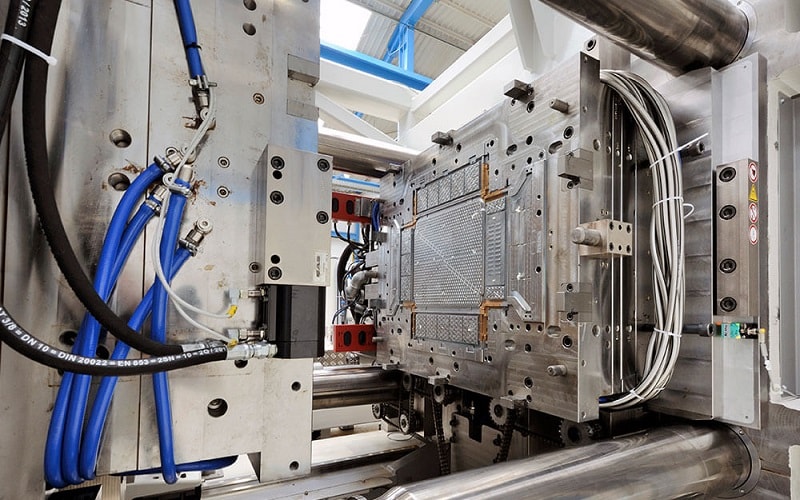
The Injection Molding Process in Detail
The injection molding process is a meticulously controlled sequence that ensures consistent, high-quality outputs, particularly suited for packaging applications.
Its precision and adaptability make it ideal for producing a wide range of packaging components.
Core Steps of Plastic Injection Molding
The process starts with the preparation of plastic materials, which are fed into a heated barrel. Here, a reciprocating screw or helical screw pushes the raw material forward, melting it into molten polymer or molten plastic.
This injecting molten material is then propelled into the mould cavity at high pressure, filling multiple cavities if the design allows for it.
The injection moulding process demands precise control over variables like material shrinkage, which can affect the final dimensions of the product.
Once filled, the cooling phase begins, where the thermoplastic materials or thermosetting plastics harden through a chemical reaction or simple temperature drop. Excess material is trimmed, and the part is ejected using ejector pins.
For more complex shapes, insert moulding can be incorporated, where additional components are placed into the mould before injection.
This moulding process is highly adaptable, supporting custom mould designs made from steel moulds or complex moulds to produce intricate packaging like cosmetic packaging with multiple materials.
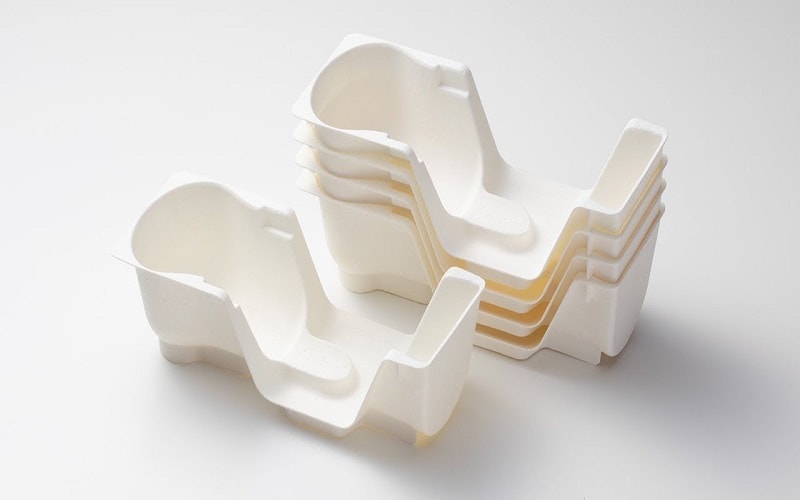
Sustainable Variation: Pulp Injection Molding
It’s worth noting that variations exist, such as pulp injection molding, which uses eco-friendly pulp materials instead of traditional plastic resin.
Unlike typical pulp forming processes, this method injects pulp under pressure into moulds, offering a sustainable alternative for packaging components.
However, for most applications, plastic injection molding remains the go-to due to its ability to handle high volume production with consistent quality.
With this process in mind, we can now explore the different types of injection molding tailored for packaging needs, ensuring your business selects the most suitable approach.

Types of Injection Molding for Packaging Solutions
One common type is standard plastic injection molding, where molten plastic is injected into a mould base to create uniform parts like plastic products for consumer electronics or bottle caps.
This method excels in producing vast arrays of items with tight tolerances, using most commonly used materials such as thermoplastics for their flexibility and recyclability.
For enhanced functionality, insert moulding integrates metal or other inserts into the plastic during the injection process.
This is particularly useful for packaging that requires reinforced mechanical properties, such as handles on storage containers or threaded caps. The process ensures the inserts bond seamlessly with the plastic, reducing assembly time and costs.
Another variant is overmolding, often confused with insert moulding but distinct in that it involves molding one material over another.
This is ideal for cosmetic packaging, where a soft-touch exterior can be added over a rigid core, improving grip and aesthetics.
High-pressure injection ensures the layers adhere without defects, and the use of multiple materials can enhance properties like thermal conductivity or chemical resistance.
In contrast, pulp injection molding represents a greener option, injecting pulp mixtures into moulds to form biodegradable packaging.
While it differs from conventional plastic case production, it shares similarities in the injection moulding cycle, including filling, cooling, and ejection stages.
For businesses requiring precision in complex shapes, CNC machining can complement injection molding by refining moulds or prototypes.
Aluminium moulds, being lighter and faster to produce, are often used for short runs, while hardened steel moulds suit high-volume needs due to their durability.
Benefits of Injection Molding Packaging
One primary benefit is cost-effectiveness, especially for high volume production. The ability to produce multiple cavities in a single cycle reduces per-unit costs, making it ideal for mass production of plastic parts like packaging components. Unlike other methods, the initial investment in custom moulds pays off quickly through efficient cycles and minimal waste from excess material.
Quality control is another standout feature. The controlled environment of the injection unit ensures consistent mechanical properties across batches, with parameters like injection speed and pressure fine-tuned to avoid issues such as sink marks or trapped air. This results in final products that meet tight tolerances, crucial for industries like cosmetics where aesthetic appeal is key.
Versatility across various industries is evident, from consumer electronics needing durable casings to the plastics industry producing everyday items like bottle caps. The process handles a range of plastic materials, including thermoplastic materials for flexibility and thermosetting plastics for heat resistance, allowing for tailored solutions.
Sustainability aspects shouldn’t be overlooked. Modern injection molding incorporates recycled plastic resin, reducing environmental impact. Pulp injection molding further advances this by using renewable resources, aligning with eco-conscious business strategies.
Moreover, the rapid cooling and ejection phases enable quick turnaround times, supporting just-in-time manufacturing. This efficiency is bolstered by the moulding process’s ability to create complex shapes without additional assembly, saving labor and time.
Choosing the Right Injection Molding Packaging Solution
To select the optimal injection molding solution for your packaging needs, evaluate key factors such as material options, production scale, and manufacturer expertise to align with your business objectives. Begin by defining your packaging requirements.
For durability, choose materials with high wear resistance, suited for hardened steel moulds. Consider the complexity of the desired shape—intricate designs require complex moulds, while simpler moulds work for basic storage containers.
Production scale is crucial: steel moulds are ideal for high volume production due to their durability, whereas aluminium moulds suit prototypes or smaller runs. Ensure the injection moulding machine can deliver the required force and pressure without compromising quality.
Material choice is equally important—thermoplastics offer recyclability, thermosetting plastics provide heat stability, and pulp injection molding supports eco-friendly initiatives as an alternative to traditional plastic injection.
Collaborate with trusted manufacturers prioritizing quality control, from raw material selection to final product inspection. Seek those with CNC machining capabilities for precise mould creation and expertise in managing the entire production process, including cooling phases and ejector pin systems.
Budget considerations matter—custom moulds involve higher upfront costs but deliver long-term savings through efficient cycles. Choose providers skilled in controlling variables like injection speed and material shrinkage to reduce defects.
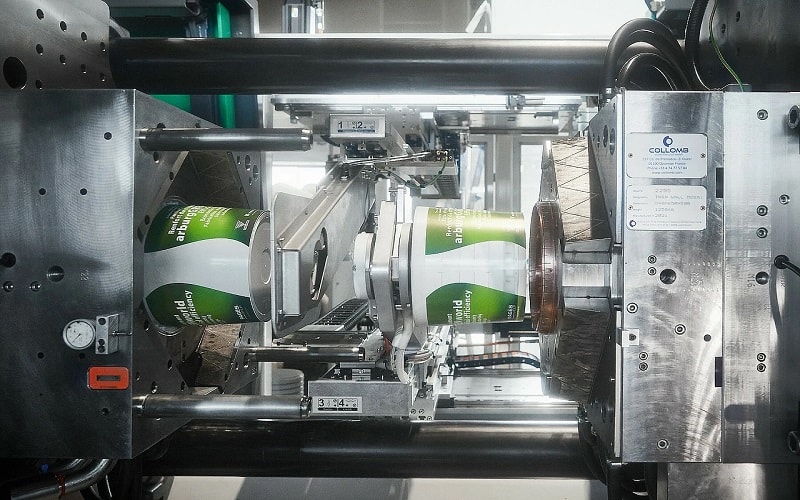

Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Drawing from the selection criteria, examining practical examples highlights how injection molding packaging drives success across sectors.
In the cosmetic packaging industry, a leading brand utilized insert moulding to create multi-layered compacts with embedded mirrors. The high-pressure injection ensured seamless integration, enhancing the product’s mechanical properties and aesthetic appeal. This resulted in a 30% increase in production efficiency and reduced assembly costs.
For consumer electronics, a company producing protective cases employed plastic injection molding with multiple cavities. Using molten polymer injected into steel moulds, they achieved tight tolerances and rapid cooling, enabling high-volume output of 10,000 units daily. The process minimized sink marks through optimized air vents, leading to fewer rejects and higher customer satisfaction.
In sustainable packaging, a food company adopted pulp injection molding for eco-friendly trays. Unlike typical pulp forming processes, this method used injection pressure to form complex shapes, replacing conventional plastic cases. The result was biodegradable storage containers that maintained quality while appealing to environmentally aware consumers.
Another example from the plastics industry involves bottle caps made via the standard injection moulding process. By controlling the injection moulding cycle and using thermosetting plastics, the manufacturer ensured chemical resistance and cost-effective mass production, serving various industries with reliable products.
These applications underscore the versatility and effectiveness of injection molding, paving the way for future innovations.
Conclusion
Injection molding is a great way for businesses to make awesome packaging that fits their needs.
It’s super precise, saves money, and can churn out tons of products, whether for cosmetics, electronics, or other industries.
By knowing the different types, their perks, and how to choose the right one, you can make smart moves for your business.
Plus, cool new options like eco-friendly pulp molding are worth checking out.
Team up with pros who know their stuff, and you’ll get top-quality packaging that makes your brand stand out.

