For plastic materials, there are many safety things need to be considered since we daily use the plastics.
Among the most prevalent plastics in day-to-day usage, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is, a matter of fact one and often seen together with food-related packaging like milk bottles, package pans or even bevvy containers.
HDPE is used everywhere and not only in home life this mineral plays an important role among industrial products. But there may be some trepidation of the safety aspects of HDPE among those who worry about plastics in general or have had issues with other plastics.
Is this material that is much more common, HDPE indeed safe? Well, to find out lets look at some of its chemistry, the production process, and how it performs in actual use.
What is HDPE Plastic?
Definition of HDPE
HDPE is the most common of five polyethylene subclasses. High-density polyethylene is favored because it displays more strength and endurance properties compared to other forms of polyethylenes due in large part to its high density.

Made of petroleum, this plastic has many advantages. Not only is HDPE very fluid and extrmely strong, it is also highly resistant to chemicals, heat and sunlight. It is stronger than plain polyethylene, does not soften at room temperature and water-resistant. They are also long lived because they resist insects and decay.
Properties of HDPE
Here is a table showcasing some key properties of HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) along with their typical values:
| Property | Typical Value |
| Density | 0.94–0.97 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 21–37 MPa |
| Melting Point | 120–130°C |
| Impact Strength | 31–60 kJ/m² |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 60–68 |
| Flexural Modulus | 0.8–1.5 GPa |
| Elongation at Break | 500–700% |
| Water Absorption | < 0.01% |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.44 W/m·K |
| Max Continuous Use Temp | 65–100°C |
| Flammability | UL 94 HB |
| Dielectric Strength | 24 MV/m |
What is HDPE Plastic Used For?
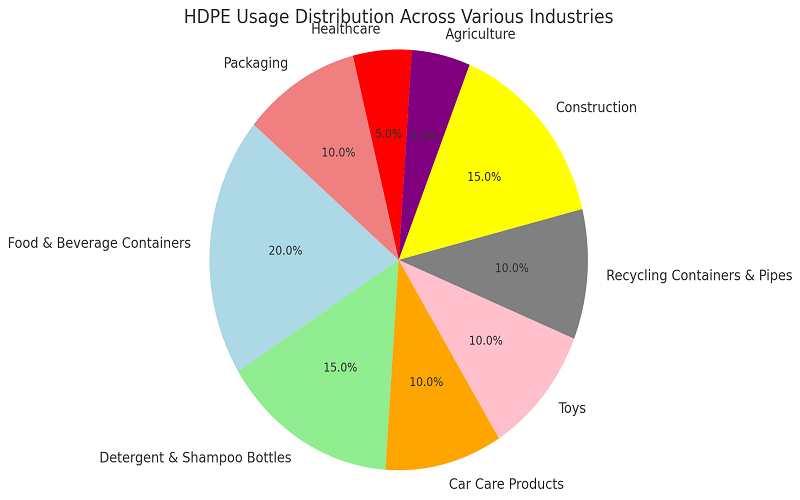
HDPE is commonly used for food and beverage containers because of its lightweight structure and strength. This is why milk and juice bottles are easy to manufacture, transport and fairly inexpensive.
HDPE is also used in detergent and shampoo bottles, oils and chemical treatments due to its fairly high corrosion resistance. It is also used in car care products, creams, lotions, soaps and paints/adhesives.
From a commercial point of view, the best thing about HDPE is that you can use special printing techniques to imprint any design on the bottle.
Recycling HDPE and reusing it also helps brands meet sustainability goals without major design changes. HDPE is not damaged by sunlight, which makes HDPE an ideal material for toys, and all toys made from HDPE will be weather resistant and will not fade, even when left outdoors.
Zero weathering, no mold, and no rotting make HDPE ideal for recycling containers and pipes.
Advantages of HDPE Material
HDPE is a widely used material due to its numerous benefits. The key advantages include:
- Durability: HDPE is exceptionally strong and resistant to wear, providing a long service life. As a result, it is commonly used in applications such as pipes, containers, and packaging.
- Chemical Resistance: HDPE remains stable when in contact with most chemicals, solvents, and acids, making it an ideal choice for storing corrosive substances.
- Non-absorbent: HDPE does not absorb moisture, remaining dry even when exposed to wet conditions.
- Heat Resistance: HDPE can endure higher temperatures compared to many other plastics, though there are some limitations.
- Recyclability: HDPE can be recycled, contributing to waste reduction and being friendlier to the environment.
- Food Safety: HDPE is free from harmful toxins and odors, rendering it safe for food packaging. This makes it a common material for food and beverage containers.
- UV Resistance: HDPE does not degrade under sunlight, making it suitable for outdoor applications.

Disadvantages of HDPE Material
While HDPE boasts numerous advantages, it also presents a few drawbacks.
- Opaque: HDPE is nearly opaque, making it unsuitable for applications requiring a clear view of the contents. If you need transparent containers, HDPE may not be the best option.
- Manufacturing Challenges: The production of HDPE can be complex. The high temperatures and pressures needed for its creation can lead to unexpected bending or shrinkage.
- Brittleness at Low Temperatures: In extremely cold environments, HDPE can become brittle and prone to damage.
- UV Degradation: Although HDPE offers some resistance to UV radiation, prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause it to weaken or discolor.
- Limited Flexibility: When compared to other plastics (such as LDPE), HDPE has lower flexibility. It is strong but not easily bendable.
- Chemical Emission: Certain chemicals involved in the production of HDPE can be released when the plastic is heated, potentially causing issues when used at high temperatures.
These issues can affect the use of HDPE, so these disadvantages should be considered on a case-by-case basis when choosing to use HDPE.

Manufacturing Safety of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is produced through processes like blow molding, injection molding, and extrusion. While HDPE is generally considered safe, manufacturing can pose certain risks.
For instance, some additives and catalysts utilized in production may contain chromium or titanium, which can be hazardous to health if mishandled. Additionally, heating HDPE can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), potentially endangering workers in poorly ventilated areas or where safety measures are inadequate.
To ensure safety, factories must implement specific measures. These may include using filters to manage emissions, opting for safer materials, and mandating the use of protective gear for workers. Such practices help mitigate environmental impact and enhance safety in the production process.
Is HDPE Safe for Food?
When handled appropriately, HDPE is typically safe for food contact. It is a highly stable material, making it well-suited for food packaging.
Additionally, it performs effectively in demanding conditions, preventing moisture and gas infiltration to maintain food freshness. Importantly, it does not alter the taste, smell, or nutritional value of the food.
However, issues may arise if HDPE is subjected to high temperatures. Chemicals from the manufacturing process can leach into food when heated in a microwave or exposed to sunlight.
For safety, it is advisable to avoid heating HDPE containers or placing them in direct sunlight. We recommend using containers that have a food safety certification to mitigate potential risks.

Is HDPE Recycled Material Safe?
If HDPE passes all the tests of the “CSD” and meets one of the many specification grades, then to a certain extent sorted and shredded HDPE is not a problem. However, the recycling process can lead to problems such as material deterioration and residual contamination, which can compromise safety, especially in food contact applications.
The safety of recycled HDPE is related to a number of factors such as the method of recycling, the application and how international standards are adopted.
Food packaging made from food-grade recycled HDPE must pass a series of tests and certifications before it can be considered suitable for use.


Is Polyethylene Harmful To Human Health?
In most cases, HDPE is safe. It never breaks down chemically and it does not release any harmful chemicals. It is used to manufacture food and beverage containers, medical devices, automotive exterior parts as well many other products. This helps to eliminate the possibility of contaminants because HDPE does not leach or mix with whatever it holds – whether oil, ink, water (especially if saltwater) and more.
But HDPE has a limitations from which it can not be used in long-term storage of oils and alcohol. Importantly, in this instance toxic chemicals can be released from the plastic.
HDPE is non-irritating and does not cause allergiesIt can be safely touched.
HDPE is considered safe for food by the FDA so it’s widely used in consumer products. Overall, HDPE is suitable for everyday use and may but it’s better to avoid using it for storing oils or similar substances for long periods.

Conclusion
HDPE is a safe and flexible material used in many things. It’s made by breaking down oil and turning it into plastic with metal catalysts. HDPE is strong, resists chemicals and impacts, and can be recycled.
You’ll find HDPE in products like food containers, medical devices, and 3D printer filaments. It handles tough conditions well and is durable and low-friction, which makes it popular for different uses.
HDPE is also safe for food contact. It meets strict FDA standards, so it won’t leak harmful substances into food or drinks. While HDPE production requires controlling dust and fumes, the plastic itself is safe.
Overall, HDPE is reliable and adaptable, making it a great choice for many applications.

