Plastic materials have become an indispensable part of our daily lives.
Among them, polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) is favored for its excellent transparency, impact resistance, and easy processing.
With these characteristics, PETG is widely used in food packaging, medical equipment, and consumer goods manufacturing.
This article will explore the safety of PETG in depth and help readers better understand PETG and make wise decisions about its use by analyzing its material properties, production process, and potential risks.
Overview of PETG
PETG (Polyethylene terephthalate) is a transparent plastic that belongs to the PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) family.
Compared with traditional PET, PETG has ethylene glycol added to the molecule, which makes it better in processing and performance.
PETG is not only very transparent but also has strong impact resistance and good flexibility, and is also very convenient to use.

Applications of PETG
PETG is widely used in many industries due to its versatility.
- Packaging: The most common use of PETG is in food and beverage packaging. It is transparent enough for consumers to see the contents clearly, making it particularly suitable for transparent containers, bottles, and flip-top packaging.
- Medical: PETG’s low toxicity and chemical resistance make it popular in medical devices and pharmaceutical packaging. Syringes, medicine bottles, and medical trays are all made of PETG to ensure safety and hygiene.
- Consumer products: PETG is particularly popular in cosmetic packaging, electronic product housings, and display stands and signs because it is durable and looks good.
- 3D printing: PETG is also a popular material for 3D printing enthusiasts. It is easy to process and has strong toughness, making it particularly suitable for durable models and parts.
- Industrial applications: Because it is impact-resistant and not easy to break, PETG is also useful in industry. It is often used for safety shields, industrial parts, and other things that require strength and stability.
Properties of PETG
PETG is known for:
- Heat Resistance: While PETG cannot withstand extremely high temperatures, it remains stable in moderate heat. This stability is valuable for items that may be exposed to warm environments, like food packaging.
- Impact Resistance: PETG’s durability is one of its standout qualities. It can handle heavy impacts without cracking, which is critical in applications requiring sturdy material, such as medical and electronic products.
- Transparency: The high clarity of PETG makes it ideal for applications where visibility is necessary. Its transparency also adds an aesthetic appeal, particularly in packaging.
- Chemical resistance: PETG can resist a variety of acids, alkalis and common solvents, so it is stable in different environments, not easy to degrade, and suitable for medical and food contact.
- Water absorption: PETG has low water absorption and is not easy to absorb water, which can maintain chemical properties, prevent bacterial growth, and ensure the integrity of the material.
| Property | PETG |
| Tensile Strength | ~50 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 25% |
| Young’s Modulus | 2.1 GPa |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm³ |
| Melting Temperature | 220-260°C |
| Glass Transition Temp | 80°C |
| Impact Resistance | High (better flexibility, less brittle) |
| Print Temperature | 220-260°C |
| Bed Temperature | 70-90°C |
| UV Resistance | Moderate to High (better than PLA) |
| Water Resistance | High |
| Biodegradability | Low (recyclable, not biodegradable) |
Production and Processing Techniques of PETG
There are several different processing methods for making PETG, each with its own advantages.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is the most common method. In this process, PETG pellets are heated and melted, then injected into a mold to make things like containers, caps, and casings. This method is particularly suitable for high-volume production and can produce products with very accurate shapes and durability.

Extrusion
Extrusion is another method, in which the PETG is melted and pushed into a mold to form a continuous sheet or tube. This extruded PETG sheet is often used for packaging and protective materials. This method provides good control over the thickness and surface of the sheet, making it ideal for transparent packaging.
3D Printing
3D printing has also become more popular recently. PETG is particularly suitable for making flexible and resilient items because it combines the strength and heat resistance of ABS with the ease of printing of PLA. However, the temperature must be controlled during printing, otherwise it may deform.
Each manufacturing method will affect the properties of PETG. For example, injection molding generally produces stronger products, while 3D printing, while being able to customize shapes, may lack strength and consistency.
Safety Analysis of PETG
Overall, PETG is considered safe, especially under normal conditions of use.
During daily use, PETG presents a low risk because it does not release harmful substances. Studies have shown that PETG will not leach toxic substances at room temperature or slightly higher. It is suitable for food packaging and medical devices.
However, if PETG is exposed to extremely high temperatures or a hostile environment, there may be a risk of slight degradation with the release of traces of chemicals. This phenomenon is rare but is probably more likely to occur in an industrial environment when used at high temperatures for extended periods of time.
Overall, experts believe that these risks have little impact on the average consumer, so in most cases, PETG is a safe choice.
Compliance Analysis of PETG Food Contact Materials
PETG is a safe food plastic that meets U.S. food and drug administration (FDA) standards.
This means that under normal conditions PETG does not put food in contact with harmful chemicals, so many packaging materials, such as food containers and beverage bottles, use it.
However, although PETG is safe in itself, its safety also depends on the materials and environment used in the manufacturing process. Problems can arise if bad colorants or additives are used during manufacture or if the production environment is not clean.
If you are using PETG 3D to print food contact objects, you should pay close attention to the printing process, as this can leave some small gaps in the surface where bacteria can hide.
For safety reasons, it is recommended to apply a food safety coating to these PETG-printed items or to ensure that the food-grade PETG material is used in a clean environment.
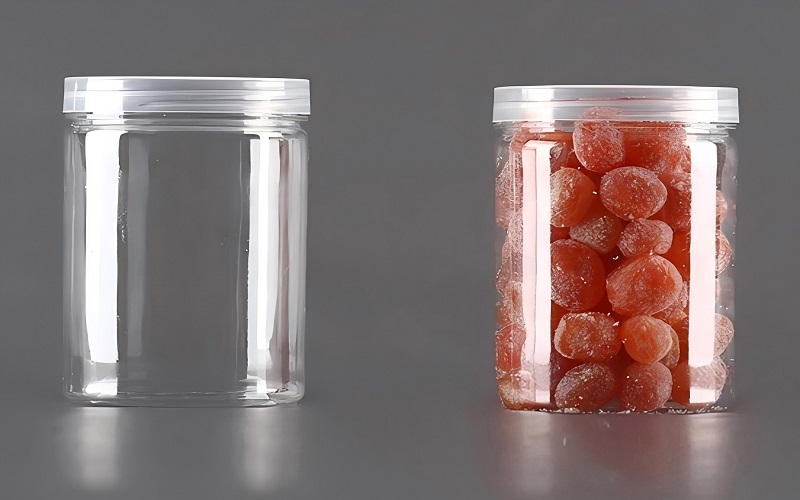

Environmental Impact of PETG
PETG is recyclable and can be reused and recycled. Through mechanical recycling, PETG can be melted into new products and reduce environmental pollution.
Compared with other plastics, PETG has less environmental harm. For example, PVC releases harmful substances, while PETG does not, so it is safer.
PETG is an environmentally friendly material that leaves only carbon dioxide and water after burning. Many developed countries are advocating its use and have obtained SGS, FDA, and MSDN certification.
PETG has become a preferred alternative to non-environmentally friendly materials such as PVC. It does not release harmful substances when used, nor does it release toxic gases when heated, and the potential environmental harm is minimal.
The methods for recycling PETG mainly include:
- Mechanical recycling: PETG is washed and crushed, then melted into particles, and new products are remade.
- Thermal recycling: PETG is converted into fuel or other chemical raw materials through high-temperature treatment.
- Chemical recycling: PETG is decomposed into monomers or other reusable chemicals and further processed into new materials.

Applications and Safety of PETG in the Medical Field
PETG’s non-toxic properties and chemical stability make it an important material for the medical industry.
Items like face masks, trays, and surgical tools are often made from medical-grade PETG, which has been tested for biocompatibility to ensure it is safe for use around the human body.
In addition, PETG’s impact resistance and easy sterilization properties provide additional safety.
For example, PETG face masks provide protection without being easily broken, making them ideal for high-contact environments.
Moreover, PETG’s transparency allows medical personnel to clearly see what is behind the mask, which is an essential feature of medical protective equipment.
Which Materials can be Used to Replace PETG?
PLA (polylactic acid): environmentally friendly and easy to print, but poor heat resistance, suitable for low temperature applications.
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene): high strength and heat resistance, but strong odor, good ventilation is required when printing.
PC (polycarbonate): very durable, high transparency, but difficult to process.
PVC (polyvinyl chloride): widely used in packaging and pipes, low cost, but its safety and environmental protection are controversial.
ASA (acrylonitrile stearate): has good weather resistance and UV resistance, suitable for outdoor use.
PP (polypropylene): light, strong chemical resistance, but low transparency, suitable for some specific packaging needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does PETG last?
Under the right conditions, PETG can maintain good performance and generally has a long service life, especially in low-temperature and dry environments.
Is PETG difficult to clean and maintain?
Cleaning PETG is relatively simple. Dirt can be easily removed by wiping with mild soapy water and a soft cloth. Avoid using strong acid or alkaline cleaners to avoid damaging the material.
Is PETG suitable for children’s products?
Because PETG is safe and harmless, it is generally suitable for children’s products, such as toys and food containers. However, it is still necessary to choose certified products to ensure safety.
How does PETG perform in outdoor environments?
PETG can be used outdoors, but if it is exposed to sunlight for a long time, it may cause the color to fade or become brittle. Therefore, it is best to have some shelter when using it outdoors.

Can PETG be reprocessed?
Yes, PETG can be reprocessed through methods such as thermoforming or cutting, which makes it very flexible in manufacturing and customization.
Conclusion
Overall, PETG offers a safe, durable, and versatile option for a variety of industries.
Its lack of harmful chemicals, high clarity, strong impact resistance, and chemical stability make it a popular material in the packaging, medical, and consumer goods sectors.
Although PETG is not biodegradable, it can be recycled with relatively low environmental impact.
As material science advances, the safety and role of PETG in environmentally friendly and innovative applications will likely continue to grow.

