Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) are the two most widely used types of polyethylene plastic.
You may not expect these two plastics to be used in a wide range of applications, from shopping bags to bulletproof clothing. Although both LDPE and HDPE are made from ethylene, different production methods result in different molecular structures, as well as different properties and uses.
HDPE is suitable for applications that require durability, such as pipes, containers, and industrial equipment. LDPE’s low density and high flexibility make it ideal for products that require softness and impact resistance, such as plastic bags and film packaging.
Understanding the differences between LDPE and HDPE can help you choose the plastic that best suits your needs.
What is LDPE?
LDPE is a very soft, versatile plastic made from ethylene. LDPE is less dense and more flexible than HDPE, it is particularly resistant to water and chemicals, which makes it ideal for things like plastic bags, shrink wrap, and squeeze bottles. Because LDPE can be easily shaped, it is a good choice for products that need to be flexible and adaptable.

What is HDPE?
HDPE is a high-density plastic made from petroleum. HDPE is stronger and denser than LDPE, making it very durable. You’ll often see HDPE used in areas such as pipes, containers, and plastic lumber because it resists chemicals and weather conditions very well.

Chemical Properties of LDPE vs HDPE
LDPE and HDPE have different chemical structures that give them unique properties.
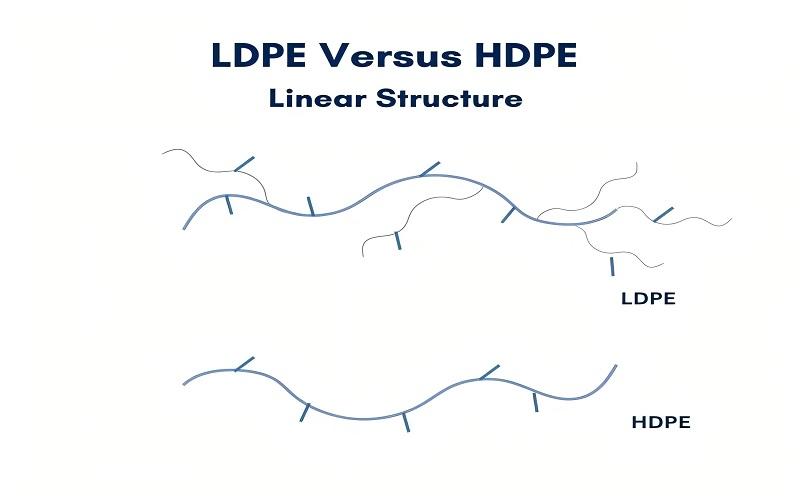
LDPE features side branches in its polymer chains. Picture a straight line representing a molecular chain, with additional chains branching off in various directions. These side branches disrupt the orderly arrangement of the polymer molecules, resulting in a less crystalline structure. This irregularity makes LDPE less dense and reduces the attraction between its polymer molecules.
On the other hand, HDPE has a more orderly molecular arrangement. Imagine an army marching in tight formation, with molecules packed closely together in rows and columns. This orderly, crystalline structure makes HDPE denser and stronger. With fewer side branches, the polymer chains in HDPE fit tightly together during crystallization, leading to a material that is more rigid and elastic compared to LDPE.
| LDPE | HDPE | |
| Melting point | 105 – 115°C / 221 – 239°F | 135°C / 275°F |
| Tensile strength | 1,400 psi / 9.65 MPa | 4,000 psi / 27.47 MPa |
| Tensile elongation | 500 psi / 3.44 MPa | 600 psi / 4.13 MPa |
| Flexural modulus | 30,000 psi / 206.84 Mpa | 200,000 psi / 1378.59 MPa |
| Water Absorption rate | 0.10% over 24-hour immersion | 0.10% over 24-hour immersion |
| Density | 0.910–0.940 g/cm3 / 910-940 Kg/m3 | 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3 or 970 kg/m3 |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.12 – 0.70 | 0.200 – 0.280 |
LDPE vs HDPE: Applications
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) both come from ethylene, so they do have similarities in some of their uses. However, they each have some unique applications as well.
Common Applications:
- 1. Packaging materials:
– Plastic bags: LDPE is commonly used for supermarket shopping bags and lightweight packaging bags, while HDPE is used for garbage bags and sturdier shopping bags.
– Containers and bottles: Both LDPE and HDPE can be used to make plastic bottles and containers. HDPE is usually used for hard bottles (such as milk bottles), while LDPE is used for squeeze bottles (such as detergent bottles).
- 2. Packaging film: LDPE is used to make soft, transparent packaging film, while HDPE is made into stronger films suitable for places that require better puncture resistance.
- 3.Low-pressure pipes: Both LDPE and HDPE can be used to make low-pressure pipes, but HDPE is usually used to make more durable piping systems because it is stronger.
Different Applications:
LDPE’s Unique Uses:
- Cling film: LDPE’s flexibility and transparency make it ideal for food cling film.
- Agricultural film: Its soft properties make LDPE suitable for agricultural mulch.
- Cable insulation: LDPE is often used in the insulation layer of wires and cables because it has good insulation properties.

HDPE’s Unique Uses:
- Water and gas pipelines: HDPE is widely used in water and gas pipelines due to its strength and chemical resistance.
- Heavy industrial containers: Suitable for making corrosion-resistant chemical storage tanks and large industrial barrels.
- Building materials: HDPE is used in building waterproof membranes, floor tiles and wall panels, etc., and is suitable for construction and industrial fields.
- Automobile fuel tanks: Its chemical corrosion resistance and impact resistance make HDPE an ideal material for making automobile fuel tanks.
Although LDPE and HDPE have overlapping applications in some areas, their physical properties and molecular structures give them advantages in specific uses. LDPE is more suitable for applications that require flexibility and transparency, while HDPE is suitable for areas that require greater durability and chemical resistance due to its high strength and durability.

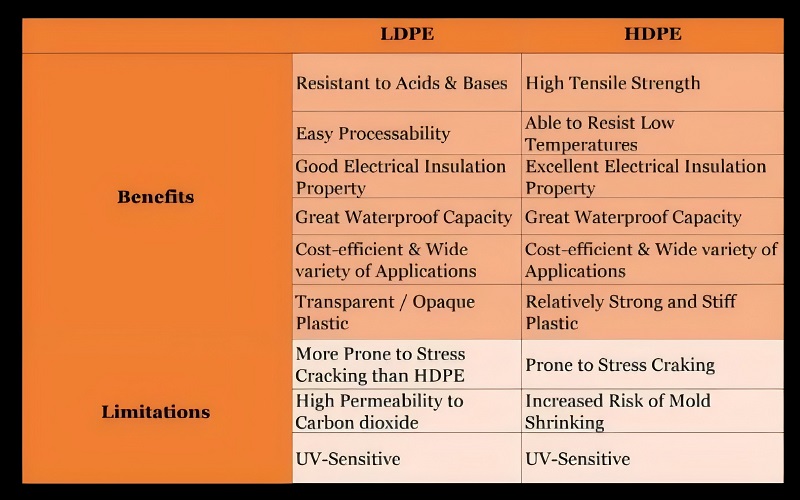
LDPE vs HDPE:Benefits and Limitations
Both materials have various benefits but they also have some limitations. The table below depicts the benefits and limitations of using LDPE and HDPE:
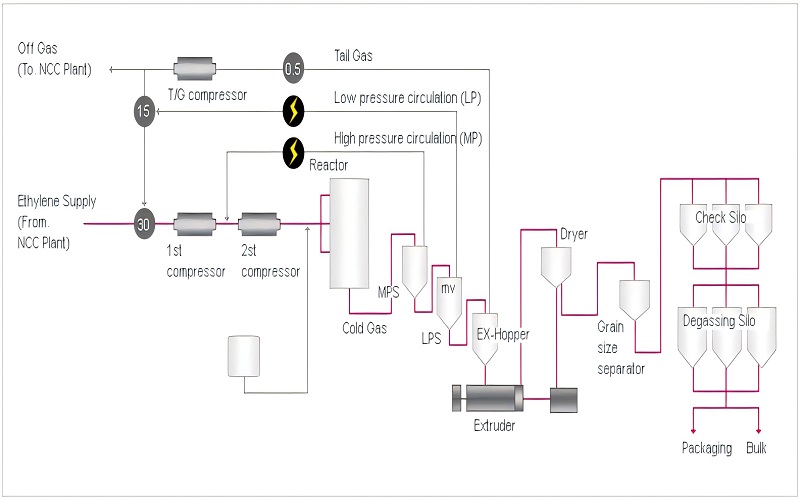
Detailed Overview of Production Processes: LDPE vs. HDPE
Both low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) can usually be processed by technologies such as injection molding and additive manufacturing. However, the most suitable production processing method for each material is different.
LDPE’s softness makes it better suited for production through free-radical polymerization at high pressures and for easy contouring during injection molding.
In contrast, HDPE, due to its higher density and rigidity, is better suited for production by suspension polymerization or gas phase polymerization, and allows for greater precision and tight tolerance control in CNC machining.
LDPE Production
LDPE is manufactured under high pressure, typically ranging from 1000 to 3000 bar, and at temperatures between 80 and 300°C using a free radical polymerization method.
The production process for LDPE generally involves either a stirred autoclave or a tubular reactor. This includes compressing ethylene gas, polymerizing the material with an initiator, and then separating the gas.
HDPE Production
HDPE can be produced using either slurry polymerization or gas-phase polymerization methods. The production process begins with polymerizing ethylene monomers, followed by steps to separate and dry the resulting material. The manufacturing of HDPE involves a three-step process:
HDPE can be produced by suspension polymerization or gas phase polymerization. The manufacturing process begins with the conversion of ethylene monomer into HDPE and involves several critical steps:
1.Initial conversion: First, the petroleum is heated and broken down into ethylene monomers. These ethylene monomers are then collected and used to produce high-density polyethylene.
2.Polymerization: Next, the gaseous ethylene is mixed with some metal catalysts (such as titanium chloride and diethylaluminum chloride). These catalysts help the ethylene become polyethylene slurry.
3.Extraction and purification: Finally, the slurry is filtered and dried to obtain high-density polyethylene. After that, the material can be washed and used for various commercial purposes.
Differences Between LDPE vs HDPE in Recyclability
Recycling Codes
The recycling methods of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) are different:
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE): The recycling code is “4”. It is mainly used for plastic bags and packaging materials. The recycling process includes collection, sorting, cleaning and reprocessing. Due to its low density, recycling requires more energy, the recycling rate is low, and the economic efficiency is poor.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE): The recycling code is “2”. It is used for bottles, containers and pipes. The recycling process includes collection, cleaning, crushing, melting and reprocessing. Due to its high density, it is easier to handle, the recycling efficiency is higher, and the cost is lower.
In general, HDPE has a higher recycling efficiency, while LDPE is more difficult to recycle.

Environmental Impact
Although low-density polyethylene (LDPE) can be recycled, its recycling rate is usually lower and requires more energy, so it is not as environmentally friendly as high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
In contrast, the recycling process of high-density polyethylene is simpler, uses less energy, and is more environmentally friendly. Recycling HDPE not only helps reduce plastic waste, but also better protects our natural resources.

LDPE vs HDPE Frequently Asked Questions
Why do HDPE and LDPE Have Different Properties?
LDPE and HDPE have different characteristics due to their different molecular structures and production methods.
LDPE’s molecular chain is very curved, so it is soft and transparent, suitable for making light things, such as plastic bags.
HDPE’s molecular chain is relatively straight and arranged very compactly, which makes it strong and durable, suitable for making pipes and hard containers.
Because the two plastics have different structures, they also have great differences in their uses and physical properties.
Which Plastic Bag is Better, LDPE or HDPE?
LDPE and HDPE plastic bags each have their own advantages and are suitable for different uses. LDPE bags are softer and more transparent, and have strong tear and puncture resistance, making them suitable for heavy or sharp objects, such as garbage bags.
HDPE bags are stronger and more durable, making them suitable for rigid containers and heavy items. When it comes to recycling, HDPE bags are more recyclable and accepted by most recycling programs, while LDPE bags are more difficult to recycle and need to be sent to special recycling points.
Therefore, although LDPE performs well in softness and tear resistance, HDPE usually has more advantages in strength and recyclability.

Does HDPE Leach Into Water?
Independent research studies have identified that chemical contaminants do migrate from HDPE pipe materials to water, and can permeate certain plastic pipes when in contact with contaminated soil. However, these studies are inconclusive as to human health impacts of these contaminants.
How Do You Identify LDPE and HDPE?
Here are some key ways to distinguish between LDPE and HDPE plastics:
1. Touch:
-LDPE: Feels soft, flexible, and smooth when touched.
– HDPE: Feels rigid, difficult to bend, and has a textured surface.
2. Transparency:
– LDPE: Usually transparent.
– HDPE: Usually opaque.
3. Thickness and Strength:
– LDPE: Soft and tear-resistant.
– HDPE: Durable and tear-resistant, strong even when thin.
4. Recycling Symbol:
– LDPE: Marked with the “4” recycling symbol.
– HDPE: Marked with the “2” recycling symbol.
These characteristics can help you distinguish LDPE and HDPE plastics.
Conclusion
Whether to choose LDPE or HDPE depends mainly on your needs.
LDPE is softer and suitable for uses that require flexibility, such as plastic bags; HDPE is more durable and suitable for uses that require strength, such as pipes.
Understanding the differences between them can help you make better choices.

