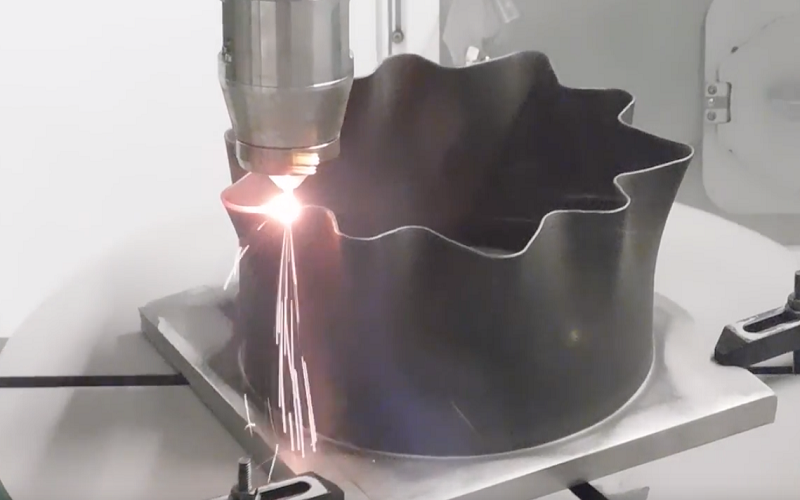
Metal 3D printing, a form of additive manufacturing technology, is transforming the creation of metal parts.
By using metal powder and advanced techniques like direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), this process builds objects layer by layer from CAD files.
Unlike traditional methods such as CNC machining or injection molding, it offers unique advantages for producing prototypes and production parts.
This article explores how metal 3D printing enhances mechanical properties, reduces manufacturing costs, and accelerates lead times.
Whether for aerospace components or custom parts, its benefits are reshaping industries.
With materials like titanium and aluminum, it delivers quality parts with complex geometries, making it a game-changer for engineers and manufacturers.
Understanding Metal 3D Printing Basics
Metal 3D printing is an innovative process that uses metal powder to create solid structures.
Techniques like selective laser melting (SLM) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) involve a laser fusing loose powder particles into precise shapes.
This additive manufacturing process starts with a digital model, allowing engineers to produce parts with high accuracy.
Unlike conventional processes, it builds layer by layer, offering flexibility for various applications.
Understanding these basics is key to leveraging the technology effectively in modern production.
How It Works?
The metal 3D printing process begins with uploading CAD files to a metal printer.
The machine then deposits the next layer of metal powder, which a laser fuses based on set process parameters.
For complex geometries, support structures are added and removed during post-processing.
This method ensures dimensional accuracy and is suitable for creating industrial-grade parts.
The use of metal laser sintering (DMLS) or metal binder jetting highlights its precision, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers.
Excellent Mechanical Properties
One of the standout benefits of metal 3D printing is its ability to produce parts with superior mechanical properties.
Materials like cobalt chrome, stainless steel, and titanium offer high tensile strength, hardness, and yield strength.
This makes them ideal for end-use parts in demanding environments.
The process allows for customization of metal alloys, enhancing corrosion resistance and performance.
Engineers can rely on these properties to create durable components for aerospace and automotive industries.
Material Versatility
The versatility of materials in metal 3D printing sets it apart.
With options like aluminum and steel, manufacturers can tailor metal powder particles to specific needs.
Adjusting process parameters further optimizes part volume and mechanical performance.
This flexibility supports the production of quality parts, from lightweight aerospace components to robust automotive pieces.
The ability to work with diverse metal alloys ensures that engineers have the tools to meet varied industrial requirements.
Durability in Harsh Conditions
The enhanced mechanical properties also ensure durability in harsh conditions.
Parts made with metal 3D printing, such as those using titanium, exhibit excellent corrosion resistance.
This durability is crucial for aerospace components exposed to extreme temperatures and pressures.
Similarly, automotive parts benefit from this resilience, extending their lifespan and reliability.
Cost Efficiency and Reduced Manufacturing Costs
Metal 3D printing significantly reduces manufacturing costs compared to traditional methods.
By using only the necessary metal powder, it minimizes waste, unlike casting or injection molding.
The elimination of extensive tooling for custom parts further lowers expenses.
This cost efficiency is a major advantage for producing functional prototypes and production parts, especially for small manufacturers.
The technology’s ability to streamline production makes it an economical choice across industries.
Shortened Lead Times
Another key benefit is the reduction in lead times. Metal 3D printing offers instant quotes and eliminates the lengthy setups of conventional processes.
This speed allows engineers to quickly produce parts, from initial prototypes to final components.
Shortened lead times are particularly valuable in industries like aerospace, where rapid development is critical.
By integrating this technology, manufacturers can enhance their production schedules and respond faster to market demands.
Economic Benefits for Small Businesses
The cost efficiency extends to small businesses, which can now afford to manufacture without large-scale investments.
By leveraging metal 3D printing, these companies can produce industrial-grade parts at a fraction of the cost.
This economic advantage fosters innovation and competitiveness, allowing smaller players to thrive in the market.
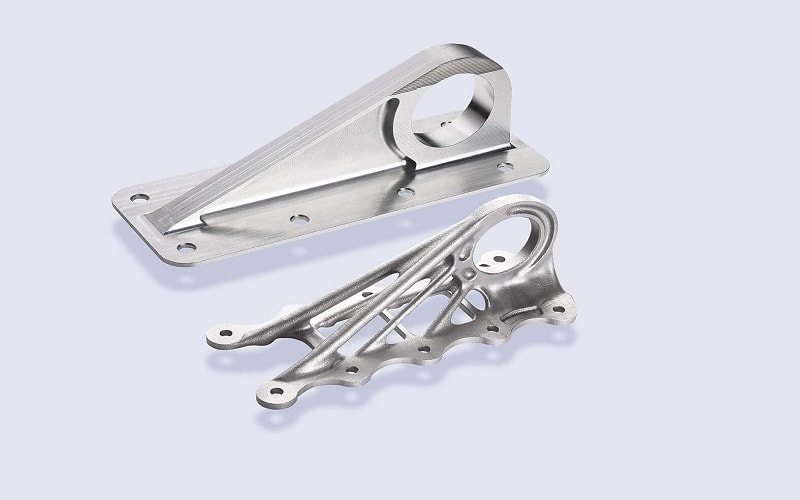
Design Freedom with Complex Geometries
Metal 3D printing excels in creating complex geometries that traditional machining struggles to achieve.
Techniques like metal binder jetting and selective laser melting allow for internal channels and intricate designs.
This design freedom reduces weight and improves functionality, especially for custom parts.
The ability to produce such shapes without limitations opens new possibilities for innovative engineering solutions.
The design flexibility of metal 3D printing is particularly beneficial in aerospace and automotive sectors.
Engineers can create lightweight aerospace components with optimized build finishes, improving fuel efficiency.
Similarly, automotive parts benefit from reduced weight and enhanced performance.
This technology supports the production of high-quality, complex structures, making it a vital tool for these industries.

High Precision and Dimensional Accuracy
Precision is a hallmark of metal 3D printing, ensuring dimensional accuracy in every part.
The layer-by-layer approach, guided by advanced laser technology, produces components with tight tolerances. This precision is essential for quality parts used in critical applications.
The process consistently delivers reliable end-use parts, meeting the strict standards of modern manufacturing.
Metal 3D printing reduces the need for extensive post-processing compared to conventional methods.
After printing, parts often require minimal finishing, saving time and resources.
This efficiency allows manufacturers to produce ready-to-use components with excellent surface quality.
The minimized post-processing enhances the overall production workflow, making it more cost-effective.
Sustainability and Material Efficiency
Sustainability is a growing concern, and metal 3D printing addresses it effectively.
By using only the required metal powder, the process generates less waste than subtractive manufacturing.
Recycling loose powder further boosts material efficiency, supporting eco-friendly practices.
This approach aligns with the goals of green manufacturing across various industries.
The adoption of metal 3D printing supports green manufacturing initiatives.
Its efficient use of materials like titanium and steel reduces environmental impact.
Manufacturers can produce components with a lower carbon footprint, contributing to sustainable production.
This benefit is increasingly important as industries prioritize eco-conscious solutions.
Accessibility for Small Manufacturers
Metal 3D printing is now more accessible, helping small manufacturers create high-quality parts without large facilities.
With metal printers, they can make custom parts, boosting innovation and competitiveness even with limited resources.
Partnering with 3D printing services adds value, offering techniques like metal laser sintering (DMLS) and binder jetting.
This allows them to produce industrial-grade parts and compete with bigger companies.

Conclusion
Metal 3D printing brings key benefits for prototypes and mass-produced parts, with strong mechanical properties and lower costs.
Its design flexibility and precision benefit industries like aerospace and automotive.
As the technology grows, its uses will expand.
Manufacturers can use it to make custom, high-quality parts quickly, keeping them competitive in today’s market.