In factory processing, it is important to choose the right raw materials, especially in injection molding. PET and HDPE are two common plastic raw materials, each with unique properties and uses.
First, let’s talk about PET, a polyester plastic that has a number of uses. This is common in the production of textiles, food and beverage bottles. Especially in food packaging, PET can ensure food safety, which is very important for our health.
Then there is HDPE, a very hard plastic suitable for household chemicals and bottle caps. For example, this plastic is used for most washing-up liquid or laundry detergent bottles. It is strong and durable and the price is reasonable, making it very suitable for mass production.
Whether in industrial production or in everyday life, plastic is used a lot. PET and HDPE are the two most common types of plastic and are used for different purposes.
Next, we will discuss in detail the properties and uses of PET and HDPE, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each. We hope this article will give you a better understanding of these two types of plastic and help you make the right choice when the time comes.
What is PET Plastic?
PET plastic, short for polyethylene terephthalate, is a type of plastic that is used in a variety of places. For the production of PET plastic, ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid react to form small particles. These particles can be heated and shaped into different shapes as needed. The melting point of PET plastic is approximately 250℃.
PET plastic is very transparent and has a high gloss, making it ideal for food and beverage packaging. It is strong and can withstand high pressure without breaking or deforming. In addition, PET can effectively block gases and moisture, protect the contents of the package and extend the shelf life.
PET plastic is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals and is stable over a wide range of temperatures. PET helps reduce environmental pollution because it can be reused and recycled. It is widely used in the packaging of food, textiles, wrapping films, etc. and is important in modern industry and everyday life.

What is HDPE Plastic?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a very safe plastic used in a variety of applications. It is produced by harvesting ethane from ethylene gas, heating it, mixing it with benzene and reacting it with ultraviolet rays. After heat treatment to remove oxygen, it can be formed into sheets and finally made from high density polyethylene.
Although HDPE has a high melting point of about 71°C, it is easily shaped and deformed when melted and remains very strong even after cooling. It also has many advantages, such as long life, strong impact resistance, excellent water resistance and antibacterial properties. HDPE does not absorb water and can resist corrosion caused by salts, alkalis, acids and some chemicals.
Due to these excellent properties, HDPE is widely used in plastic containers, agricultural packaging and chemical containers. Due to its antibacterial properties, it is particularly safe in the production of products that come into direct contact with food, such as water bottles, kettles and food containers. In addition, HDPE is an environmentally friendly material that can be recycled and reused, which is good for the earth.

PET vs HDPE: Physical Properties
Below lists the physical properties comparison of PET vs HDPE:
| Characteristic | PET | HDPE |
| Density | 1.38 – 1.40 g/cm³ | 0.93 – 0.97 g/cm³ |
| Shrinkage | 0.2 – 0.5% | 1.5 – 4.0% |
| Water Absorption | < 0.5% | < 0.01% |
| Tensile Strength | 50 – 75 MPa | 20 – 40 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High | Very High |
| Transparency | High | Opaque to Translucent |
| Melting Point | 250 – 260°C | 130 – 137°C |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 60 – 80°C | 60 – 80°C |
PET vs HDPE: Temperature Range Comparison
| Temperature range | PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) |
| Melting Point | 250 – 260°C | 130 – 137°C |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 60 – 80°C | 50 – 80°C |
| Low Temperature Performance | as low as -70°C | as low as -100°C |
PET and HDPE are common plastics. Both have excellent heat resistance, but there are slight differences in melting point and cold resistance.
The melting point of PET is approximately 250°C, maintaining strength and stability even in high temperature environments. Therefore, PET is frequently used in general food and beverage packaging. HDPE has a relatively low melting point of 130°C, but performs better than PET at low temperatures.
HDPE can withstand temperatures up to -100°C, while PET can only withstand temperatures down to -70°C. Therefore, HDPE retains its flexibility and impact resistance even at low temperatures, making it well suited for the production of cooling pipes and cooling vessels.
Simply put, PET is suitable for high temperature environments such as hot fill packaging, while HDPE performs better in low temperature environments and is suitable for use in refrigeration equipment. The choice of material used depends on the specific requirements for use and environment.

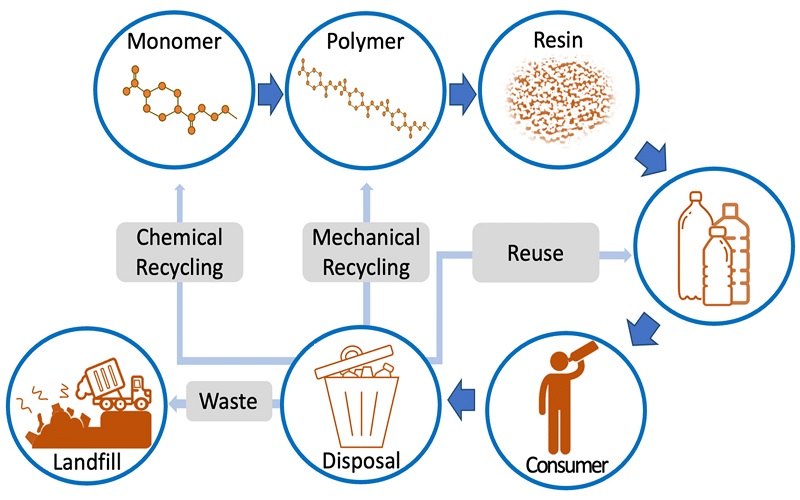
PET vs HDPE: Recyclability Comparison
PET and HDPE are common recyclable plastics used in everyday life, but they are recycled differently.
Let’s start with PET. This plastic is often recycled to make lower quality textile products. Imagine the sportswear you are wearing. It can be made from recycled PET bottles. The recycling process for PET is relatively complex. First, discarded PET bottles are sent to a recycling station, where they are cleaned, crushed and melted into new material, which ultimately becomes new bottles and packaging. However, due to the cumbersome process, PET can usually only be reused one to three times. Often these bottles end up being discarded or incinerated.
HDPE is more durable and can be reused 5 to 10 times. Despite this, much of the HDPE plastic is discarded or used for energy production, and only a small amount is actually recycled. The recycling process for HDPE includes cleaning, drying, crushing and heating. The processed pellets can be used to make a number of new products, such as baking trays, outdoor furniture and even plastic pipes.
As technology advances, so does the recycling process for PET, making it possible to use recycled PET in higher quality products. Overall, HDPE and PET each have their advantages and disadvantages. While HDPE is suitable for the manufacture of a number of new products, PET is particularly suitable for food and beverage packaging, improved recycling technology can reduce resource waste and better protect the environment.

PET Plastic vs HDPE: Cost
HDPE (high-density polyethylene) and PET (polyethylene terephthalate) are two common types of plastic with very different costs and recycling methods. HDPE costs approximately $8.50 per cubic meters to produce, but recycling costs are very low at only $2.50. Therefore, HDPE is not only environmentally friendly, but also economical.
PET raw material costs are typically $0.80 to $2 per ton, but high-grade PET can be even more expensive at $2 to $3 per tonne. kilograms. PET is often used in food and beverage packaging due to its high transparency and corrosion resistance.
In general, the cost difference between HDPE and PET is very large. If we can better recycle these materials or find other alternatives, we can reduce the cost of using these materials.
PET vs HDPE: Alternative Materials
Considering the cost and environmental factors in the manufacturing process, the use of alternative materials is a valid approach. Choosing the right alternative materials not only reduces costs, but also reduces pollution. Both PET and HDPE have some good alternatives. Here are two common examples.
Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene has high heat resistance, and special processing can make PP material transparent, can also replace PET materials to meet packaging needs It also has excellent chemical resistance, so it can be used as an alternative to HDPE.

Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA): EVA is highly transparent, making it very suitable for packaging materials. It has excellent chemical resistance and flexibility and maintains its performance even at low temperatures. Therefore, EVA can be produced and used instead of HDPE in situations where flexibility is required.

By using PP or EVA instead of PET or HDPE, manufacturers can not only maintain or improve the performance of their products, but also better protect the environment and improve economic returns. This approach is advantageous for producers.
Conclusion
PET and HDPE are common types of plastic that we all know. They are cheap and have many uses. PET is often used for food and beverage packaging because it is transparent and strong. HDPE is particularly resistant to high temperatures and chemicals, so it is often used to make industrial products such as barrels and pipes.
Recently, with the progress of science and technology, new materials such as polypropylene (PP) and vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) are very popular. Companies choose these new materials not only because of their good performance, but also because they are more environmentally friendly.
It is important for companies to understand the properties of PET and HDPE in order to choose the most suitable materials. If you want to know more about these materials, you can always contact me.

