Deciding between PETG and ABS for 3D printing? PETG is stronger and UV-resistant, while ABS is more impact-resistant and cheaper.
In this article, we will explore the properties, printability, and applications of both materials, including a comparison of PETG vs ABS, to help you choose the best filament for your needs.
Strength and Durability

Strength and durability are key factors in choosing a 3D printing filament. PETG and ABS offer strong mechanical properties, making them versatile for various applications. Their distinct strengths and weaknesses can determine the best choice for your project.
PETG usually has higher tensile strength than ABS, making it a stronger material. In contrast, ABS is known for its high impact resistance, reducing the likelihood of cracking or breaking under stress.
Both materials are durable and can endure significant wear and tear, but their unique properties suit different applications.
Tensile Strength
PETG has an edge in tensile strength, reaching up to 50 MPa compared to ABS’s 42 MPa. This makes PETG preferable for applications requiring strong, long-lasting components, such as functional prototypes that need to endure rigorous testing.
Although ABS has slightly lower tensile strength, it still offers robust mechanical properties for many uses.
The choice between PETG and ABS depends on your project’s specific demands and the importance of tensile strength.
Impact Resistance
ABS excels in impact resistance, making it ideal for applications involving mechanical stress or potential impacts. Its high impact strength reinforces its durability and suitability for robust applications.
PETG offers good impact resistance but doesn’t match ABS.
For projects needing materials that can withstand high impacts without cracking, ABS is a more cost-effective and reliable option.
Longevity and Outdoor Use
For longevity and outdoor use, PETG outperforms ABS in UV light resistance, making it better for applications exposed to sunlight and outdoor conditions. However, both materials have limited longevity under constant UV exposure, which can degrade their properties over time.
PETG’s enhanced durability in outdoor environments is a key advantage, especially for prolonged exposure to the elements. Where UV exposure is minimal, ABS remains a viable and cost-effective alternative.
Printability

Printability is crucial when choosing a 3D printing filament. PETG offers better print adhesion than ABS, reducing warping and improving print quality. Good bed adhesion is critical for both materials, but PETG generally performs better.
ABS can be more challenging to print due to its tendency to warp during cooling. Knowing the specific print settings and techniques for each material can help you achieve optimal results in your abs print 3D printing projects.
Print Temperature and Settings
Both PETG and ABS generally require print temperatures between 220°C and 260°C.
ABS typically prints best between 220°C and 250°C, while PETG falls within a similar range but with less risk of warping. Adjusting print settings for these temperatures is crucial for high-quality prints.
Proper temperature management is crucial to ensure that PETG or ABS prints meet your expectations. Understanding the necessary adjustments for each material can significantly impact the final print quality.
Bed Adhesion Techniques
Good bed adhesion is vital for successful 3D printing. Using a heated bed is crucial for both PETG and ABS. Techniques like applying a glue stick or using a suitable build plate surface can enhance adhesion and prevent print failures.
Good bed adhesion not only improves print quality but also reduces warping and other defects. Excellent layer adhesion can significantly impact the success of your 3D printing projects, especially when addressing issues like poor layer adhesion.
Warping and Layer Adhesion
ABS is more prone to warping due to higher cooling shrinkage compared to PETG. PETG’s lower shrinkage reduces warping risk, making reliable prints easier. Proper layer adhesion is critical for both materials to avoid print failures.
A heated bed and an enclosed environment can minimize warping with ABS. For PETG, managing print temperatures and cooling times can enhance print stability and prevent warping.
Post-Processing Techniques
Post-processing techniques like sanding, painting, and vapor smoothing can improve the aesthetic and functional qualities of 3D printed parts through additive manufacturing. PETG and ABS respond differently to these techniques, so understanding these differences is essential for achieving the desired finish.
Sanding PETG and ABS can be done effectively using various grits of sandpaper, starting coarse and progressing to finer grits for a smooth finish. When painting, clean the surface first and use compatible paints for good adhesion.
Vapor smoothing is popular for ABS, creating a glossy finish. PETG may require other smoothing methods like sanding or heat gun processing.
Sanding and Smoothing
Sanding PETG minimizes surface imperfections. Due to its higher melting point, PETG requires specialized tools or techniques for post-processing, making standard methods challenging. However, PETG is generally easier to sand and polish compared to ABS.
Achieving a smooth finish on ABS often requires chemical smoothing. Sanding ABS is more effort-intensive than sanding PETG, but proper techniques can result in a high-quality finish.
Painting and Coloring
Sanding or priming is essential for painting ABS to ensure better paint adhesion. PETG is less receptive to conventional paint but can be effectively colored using acrylic spray paints after proper surface preparation. Chemical smoothing of ABS also reduces visible layer lines, creating a glossy finish.
Proper preparation and using compatible paints are critical for achieving a good finish on both PETG and ABS prints. Understanding these techniques can enhance the appearance of your 3D printed parts.
Vapor Smoothing
Vapor smoothing, designed for ABS, enhances its finish by softening the outer layer with acetone vapors. This technique creates a glossy, smooth surface, reducing the visibility of layer lines.
PETG can achieve a polished finish through sanding but requires more effort than ABS, which benefits from chemical smoothing. Proper ventilation is essential when performing vapor smoothing to ensure safety and prevent warping.
Chemical and Temperature Resistance
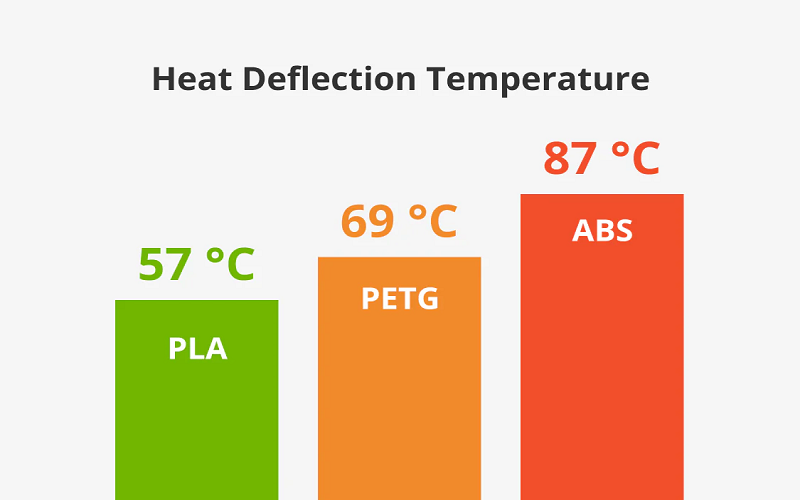
The chemical and temperature resistance of a filament greatly influences its suitability for various applications. PETG exhibits superior resistance to various acids and bases compared to ABS. Both materials provide heat and chemical resistance, but their distinct characteristics suit different uses.
ABS’s heat resistance makes it suitable for applications involving higher temperatures. Understanding the chemical and temperature resistance properties of PETG and ABS helps in selecting the right material for demanding environments.
Chemical Resistance
PETG is generally more resistant to chemicals than ABS, making it better for environments with potential chemical exposure. For solvent exposure, PETG is less likely to break down compared to ABS, ensuring greater durability in harsh environments. On the other hand, ABS can be more susceptible to solvents, especially when used with solutions like ABS juice, a mixture often used to smooth or bond ABS prints, which can inadvertently weaken its structure if not handled carefully.
Chemical resistance is crucial when choosing materials for 3D printing, especially in applications exposed to solvents and chemicals. PETG outperforms ABS in this regard, making it the preferred choice for applications that may encounter aggressive solvents or chemicals.
Temperature Resistance
ABS has a glass transition temperature of 105 °C, compared to PETG’s 80 °C. This higher glass transition temperature allows ABS to maintain structural integrity at higher temperatures, making it a better choice for applications involving high-temperature exposure.
In high-temperature environments, ABS’s ability to withstand higher temperatures enhances its suitability for demanding applications.
Environmental Impact

The environmental impact of 3D printing materials is an important consideration. PETG is considered more environmentally friendly compared to ABS due to differences in their material properties. While PETG can be recycled, it is derived from oil-based materials, unlike some other renewable plastics.
Understanding the environmental implications of using PETG and ABS can help you make more sustainable choices for your 3D printing projects. Consider their recyclability and emissions when making your choice.
Recyclability
Both PETG and ABS are recyclable but not in normal collections. Specialized services are available to recycle 3D prints made of both materials, though recycling ABS is more complex and requires specialized facilities.
Recycling PETG and ABS can be challenging due to the need for specialized facilities. Understanding these challenges and opportunities can help you make more informed decisions about the sustainability of your 3D printing projects.
Emissions and Safety
During printing, ABS releases significantly more nanoparticles than PETG, raising greater health concerns.
Using well-ventilated spaces when printing with PETG can help minimize health risks associated with emissions.
Understanding the emissions and safety considerations of PETG and ABS is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment. Proper ventilation and safety measures can mitigate the risks associated with these materials during the printing process.
Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor when choosing a 3D printing filament. ABS filaments typically range from $15 to $30 per kilogram, while PETG generally costs between $20 and $40 per kilogram. ABS is known for its cost-effectiveness, usually being cheaper compared to PETG, which is priced higher due to its advanced properties.
When considering long-term value, factors such as durability and maintenance frequency play critical roles in evaluating cost-effectiveness. While PETG comes with a higher initial investment, it may prove more worthwhile depending on specific application needs.

Initial Filament Cost
Both ABS and PETG typically fall within a similar price range of $20 to $28 per kilogram. PETG filaments are priced higher due to their unique properties, including excellent adhesion and reduced warping compared to ABS. The price of PETG can vary significantly based on brand and quality, often ranging from $23 to $40 per kilogram.
While both PETG and ABS occupy similar price brackets, the specific characteristics and market variations lead to PETG generally being more expensive. This initial cost difference can influence the choice of filament depending on budget constraints and project requirements.
Long-Term Value
ABS generally offers better durability due to its resistance to impact and stress, making it suitable for applications that require long-lasting components.
ABS is often considered a more cost-effective option than PETG because of its widespread availability and efficient manufacturing.
When assessing the long-term value of filaments, it is important to consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and replacement frequency. Overall, ABS tends to be favored for its durability and lower overall costs compared to PETG.
Real-World Applications

PETG and ABS are widely used in various industries due to their unique properties, making them suitable for specific applications. In the automotive industry, ABS is frequently used for parts such as Lego bricks and electronic enclosures, while PETG is favored for its superior impact resistance.
Common consumer products made from ABS include electronic enclosures, while PETG is often used for items like water bottles. Both PETG and ABS offer durability and longevity, making them suitable for high-stress environments and outdoor applications.
Automotive Parts
PETG is utilized for components such as dashboards and light covers in vehicles, thanks to its durability and UV resistance. The durability of PETG allows it to withstand the rigors of automotive environments, making it a reliable choice for various vehicle components.
While ABS has its own set of properties, specific limitations in automotive applications can be further discussed, particularly in terms of suitability compared to PETG.
In summary, the robustness, UV resistance, and general performance of PETG make it a favored choice in the automotive industry over ABS for certain components.
Medical Devices
Medical applications for PETG include syringes and protective equipment, benefiting from its biocompatibility. 3D printing has become increasingly important in the medical field, providing customized solutions and rapid prototyping for various medical devices.
The use of PETG in medical devices highlights its suitability for applications requiring high durability and safety. The biocompatibility and ease of sterilization make PETG an excellent choice for medical applications.
Consumer Products
In the electronics industry, PETG is favored for creating protective covers and housings for devices. PETG’s aesthetic qualities make it ideal for product displays and packaging, where a clear and glossy finish is beneficial.
One notable product made from ABS is Lego bricks. The durability and versatility of ABS make it a popular choice for various consumer products, including electronic enclosures and other high-stress applications.
Summary
In summary, both PETG and ABS offer unique advantages and are suitable for different applications.
PETG is stronger in terms of tensile strength and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor use and applications requiring enhanced durability. ABS, on the other hand, excels in impact resistance and heat resistance, making it suitable for high-stress environments and applications involving higher temperatures.
Choosing between PETG and ABS ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your project. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each material can help you make an informed decision and achieve the best results in your 3D printing endeavors. Remember, the right filament can make all the difference in the success of your next project.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which material has better tensile strength, PETG, or ABS?
PETG exhibits a higher ultimate tensile strength than ABS, making it a superior choice for applications demanding enhanced durability.
Is ABS or PETG better for impact resistance?
ABS is more effective than PETG in terms of impact resistance, reducing the likelihood of cracking or breaking under mechanical stress.
Can I use PETG for outdoor applications?
Indeed, PETG is suitable for outdoor applications due to its superior UV resistance compared to ABS. This quality enhances its durability and performance in outdoor environments.
What are the optimal print temperatures for PETG and ABS?
The optimal print temperatures for PETG and ABS range from 220°C to 260°C, with ABS specifically requiring 220°C to 250°C. Adhering to these temperature ranges will ensure better print quality and adhesion.
Are PETG and ABS recyclable?
Both PETG and ABS are recyclable; however, the recycling process may be complicated due to the requirement for specialized facilities.

