ABS plastic material is a strong, versatile material used in many industries, including automotive and electronics. This article discusses the properties of plastic material ABS, manufacturing processes, and common applications.
What is ABS Plastic?
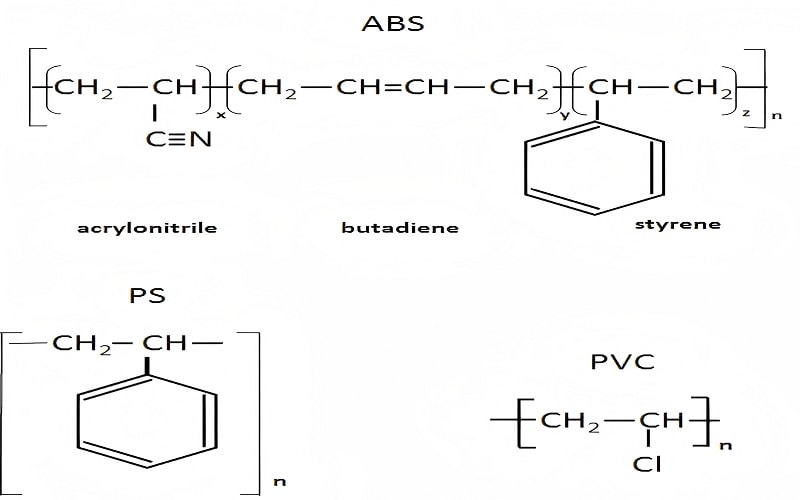
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a popular thermoplastic material known for its exceptional versatility and strength. The chemical composition of ABS consists of three primary monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.
Each component contributes unique properties to the final material: acrylonitrile provides chemical resistance, butadiene adds toughness, and styrene offers rigidity.
ABS plastic stands out for:
- Its affordability and robust nature, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Being an impact-resistant engineering thermoplastic polymer, meaning it can withstand significant forces without breaking.
- Being classified as an amorphous polymer, which means it does not have a crystalline structure, lending it excellent dimensional stability. Additionally, it is often referred to as popular plastic abs material properties in various industries.
The history of ABS plastic dates back to its patent in 1948, marking the beginning of its widespread use across various industries. Today, ABS remains a staple in manufacturing due to its advantageous properties and cost-effective nature. abs plastic sheet, machine grade abs, and abs plastic parts are commonly utilized forms of this material in production processes.
How ABS Plastic is Manufactured
Producing ABS plastic involves sophisticated manufacturing processes aimed at maximizing its unique properties, with the emulsion technique being the most common method. It can also be created using the continuous mass technique. These methods involve mixing styrene and acrylonitrile with polybutadiene under carefully controlled conditions to form the ABS polymer, including polymerizing styrene.
One of the most prevalent techniques for producing abs parts, such as lego bricks and protective headgear, is injection molded molding. This process involves the high-pressure injection of molten ABS into molds, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape.
The benefits of injection molding include the rapid production of complex shapes and a significant reduction in waste. Additionally, techniques like overmolding can be employed to layer different materials, enhancing product functionality.
The adaptability of ABS plastic in manufacturing allows for easy molding and shaping, making it versatile for various applications. However, managing temperature carefully during molding is crucial, as ABS’s viscosity increases at higher temperatures. Solvent resistance further contributes to its durability in diverse environments.

Key Properties of ABS Plastic
ABS plastic boasts several key properties that make it an ideal material for a wide range of applications. Among these are its excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and rigidity, which make it suitable for structural purposes. The inclusion of acrylonitrile in its composition contributes to strong chemical resistance, allowing ABS to withstand exposure to diluted acids and alkalis.
One of the standout features of ABS plastic is its impact resistance. The butadiene component provides the toughness required to absorb shocks effectively, making ABS a preferred material for products that must endure physical stress.
Additionally, ABS offers good electrical insulating properties due to its low conductivity, making it suitable for electronic components. High heat resistance and low melting point further enhance its adaptability, ensuring it can perform under varying thermal conditions while remaining easy to process.
The combination of these properties ensures that ABS plastic remains a reliable and durable material, capable of meeting the demands of various industries. Its versatility and robustness make it a go-to choice for manufacturers seeking a balance of strength, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 40-50 |
| Impact Resistance (J/m) | 200-400 |
| Heat Resistance (°C) | 80-100 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.04-1.06 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 200-240 |
| Hardness (Rockwell R) | 100-110 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 15-50 |
Common Applications of ABS Plastic
ABS plastic’s unique properties make it a popular choice in numerous industries. In the automotive industry, ABS is used in automotive components and automotive parts such as dashboards and seat backs, contributing to weight reduction and improved vehicle performance.
It is also used in seat belt components and other dashboard parts and instrument panels that enhance vehicle safety and functionality, particularly in various automotive applications. Fatigue resistance and the ability to perform under low temperatures further enhance its reliability in these conditions.
In electronics, ABS acts as an insulator, perfect for components such as computer keyboards and housings in consumer electronics. Its strength and lightweight nature also make it ideal for vacuum cleaners casings. Additionally, the FDA has approved ABS for kitchen appliances and food packaging, underscoring its safety and versatility.
The medical field also benefits from ABS plastic, using it to create manufacturing nebulizers and drug delivery systems due to its purity and consistency. ABS is considered safe for use in children’s toys and food-related products, underlining its suitability for a wide range of plastic items. Stress cracking resistance adds to its durability in demanding applications.

Advantages of Using ABS Plastic
A major advantage of ABS plastic is its cost-effectiveness, as reasonable production costs make it affordable for manufacturers. Furthermore, ABS’s sturdiness and excellent impact resistance allow it to absorb shocks and withstand physical stress.
Another significant benefit of ABS plastic is its ability to be easily colored with pigments or dyes. This allows for a broad range of color and finish options, making it suitable for products requiring aesthetic appeal. Moreover, ABS can be finished easily, resulting in a smooth and glossy finish surface.
The combination of these advantages makes ABS plastic a versatile and practical material for various applications, ensuring that it remains a popular choice among manufacturers looking for a balance of performance and affordability.

Disadvantages of ABS Plastic
Despite its numerous advantages, ABS plastic has some limitations. One major drawback is its melting point, typically ranging between 200-240°C, restricting its use in high-temperature environments. Additionally, ABS is susceptible to damage from sunlight and UV rays, causing degradation over time.
Another disadvantage is that ABS has relatively low fire resistance and can emit harmful fumes when burned. The material may also undergo dimensional changes with temperature fluctuations due to its higher thermal expansion coefficient, which can affect its performance in certain applications.
While these disadvantages are noteworthy, they do not overshadow the numerous benefits and applications of ABS plastic. However, understanding these limitations is crucial for selecting the right material for specific uses.
Enhancing ABS Properties with Additives
Various additives can enhance ABS plastic’s properties, including:
- Heat stabilizers
- Hydrolysis stabilizers
- Lubricants
- UV stabilizers
- Fire retardants
These improve heat resistance, chemical resistance, and overall durability, making them heat resistant.
Combining ABS with other plastics or incorporating additives can make the material more versatile and functional. For example, adding glass fibers can enhance the material’s strength and rigidity, while heat stabilizers can improve its performance in high-temperature environments.
Utilizing these additives allows manufacturers to customize ABS plastic solutions to meet specific needs, maintaining its reliability and adaptability for various industrial applications.
ABS Plastic in 3D Printing
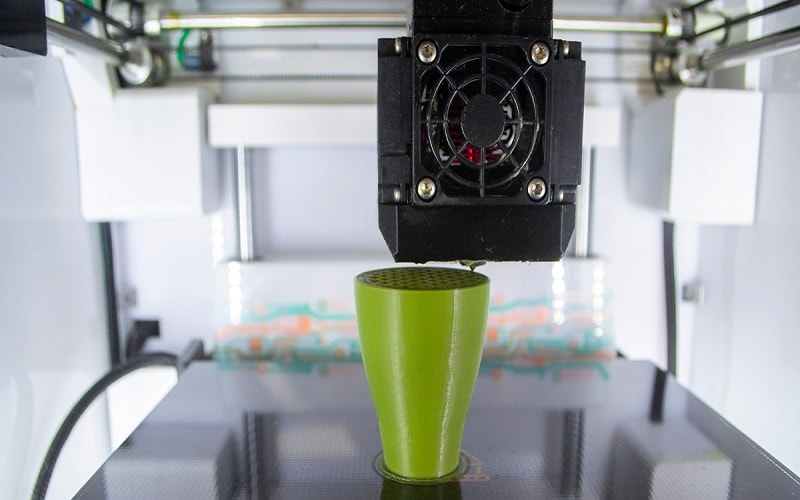

ABS plastic has become a staple in the world of 3D printing, particularly with the fused-deposition modeling (FDM) technique. This method involves extruding ABS filament layer by layer to create detailed and durable objects. ABS is available in various forms, including filament and pellets, making it suitable for different 3D printing setups.
Objects printed with ABS plastic offer higher strength, flexibility, and durability, making them ideal for a range of applications from prototyping to functional plastic parts. The material’s impact resistance and ability to be easily machined or post-processed further enhance its appeal in 3D printing, particularly when considering various plastic materials.
The versatility and performance of ABS plastic make it an excellent choice for both hobbyists and professionals in the 3D printing community, as it is a versatile thermoplastic.
Recycling ABS Plastic

Recycling ABS plastic is a crucial aspect of its sustainability. ABS is 100% recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option for manufacturers and consumers. Mechanical recycling involves breaking down ABS into smaller pieces, which can then be reprocessed into new products.
Chemical recycling techniques, on the other hand, decompose ABS into its basic monomers, allowing for the creation of new polymer chains. Recycled ABS can be combined with virgin material. This process produces high-quality products at a lower cost while preserving the material’s desirable qualities. The recycling number associated with ABS plastic is 9, indicating its recyclability and encouraging proper disposal and recycling practices.
By promoting the recycling of ABS plastic, we can reduce waste and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Is ABS Plastic Safe?
Safety is a paramount concern when it comes to any material, and ABS plastic is no exception. ABS is non-toxic and harmless, with no known carcinogens associated with its use. There are no known adverse health effects related to exposure to ABS plastic, making it a safe choice for various applications.
ABS plastic is also biocompatible, meaning it can be used in medical applications without adverse effects. It can be sterilized using gamma radiation or ethylene oxide, further enhancing its suitability for medical use. Additionally, ABS is stable and does not leach harmful substances, ensuring that it remains safe for consumer products.
These safety features make ABS plastic a reliable material for a wide range of industries, from medical to consumer goods.
Summary
ABS plastic’s unique combination of affordability, versatility, and strength makes it an invaluable material across numerous industries. From automotive components to consumer electronics and medical devices, ABS continues to prove its worth as a reliable and adaptable material.
The various manufacturing processes, key properties, and applications of ABS plastic demonstrate its widespread utility. Despite some limitations, such as sensitivity to UV light and lower fire resistance, the advantages of using ABS far outweigh these drawbacks.
As we look to the future, the potential for ABS plastic remains vast. Whether through advancements in additive technology or increased recycling efforts, ABS will continue to be a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ABS plastic made of?
ABS plastic is made of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, which combine to give it its distinctive characteristics.
How is ABS plastic manufactured?
ABS plastic is manufactured using emulsion or continuous mass techniques and is commonly shaped through injection molding. This ensures a versatile and efficient production process.
What are some common applications of ABS plastic?
ABS plastic is widely utilized in automotive components, electronic housings, medical devices, and consumer products such as toys and kitchen appliances. Its versatility makes it an ideal choice across various industries.
Can ABS plastic be recycled?
Yes, ABS plastic can be recycled using both mechanical and chemical recycling methods, making it a fully recyclable material.
Is ABS plastic safe for use in consumer products?
ABS plastic is considered safe for use in consumer products as it is non-toxic and biocompatible, suitable for items like children’s toys and food-related applications.

