Polyamide is a synthetic polymer known for its durability and strength.
Used widely in automotive, textiles, and food packaging, it is essential for products requiring wear resistance and flexibility.
In this article, we will explore the properties, types, and applications of polyamides.
Key Takeaways
- Polyamides, including nylon, are versatile synthetic materials known for their durability, strength, and resistance to wear, making them suitable for various industries such as automotive, textiles, and food packaging.
- Different types of polyamides, such as PA 6-6 and high-performance variants like Kevlar, exhibit distinct chemical structures and properties that cater to specific application requirements, including extreme conditions and high-impact resistance.
- The sustainability of polyamides can be enhanced through the development of bio-based alternatives and recyclable methods, addressing environmental concerns associated with their petroleum-derived counterparts.
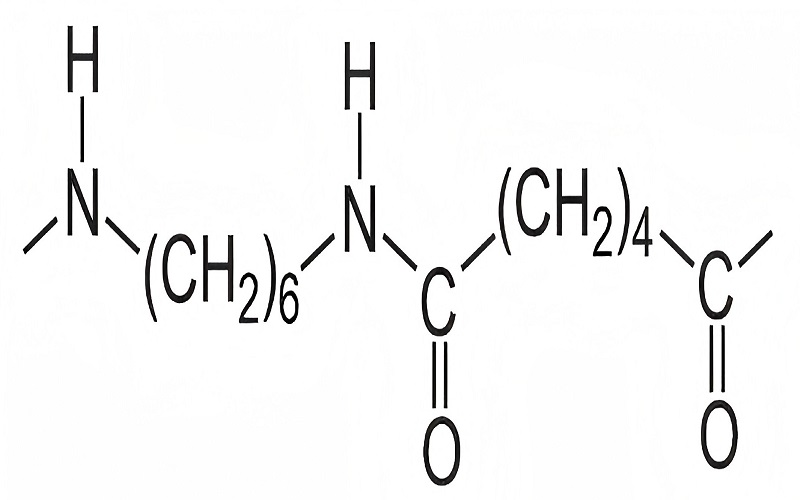
Understanding Polyamide

Polyamides, developed by DuPont in the mid-1930s, are synthetic polyamides characterized by their durability, strength, and stretchable structure. They are formed through the bonding of organic compounds containing carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen, resulting in materials that can withstand significant wear and tear. This unique composition is what makes polyamide polymer so resilient and versatile.
Polyamides stand out among synthetic materials for their exceptional cleanliness standards, making them ideal for the food and beverage industry. Their capacity to uphold stringent hygiene while offering robustness highlights their superior engineering.
Polyamides find extensive use across various industries, from automotive parts to textiles. Their versatility and strength make them indispensable for products needing both durability and flexibility, securing their place in manufacturing and industrial applications.
Types of Polyamides
Polyamides come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and performance requirements. The most common types are PA 6-6 and PA 6, which are widely used in everyday products due to their excellent balance of properties.
These polyamides offer a combination of strength, flexibility, and durability that make them suitable for a broad range of uses.
For more demanding applications, high-performance polyamides like PPA and PA 4-6 are preferred. These materials can withstand extreme conditions, making them ideal for use in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
Specialized polyamides like Nomex and Kevlar are renowned for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, showcasing the diversity and adaptability of these materials.
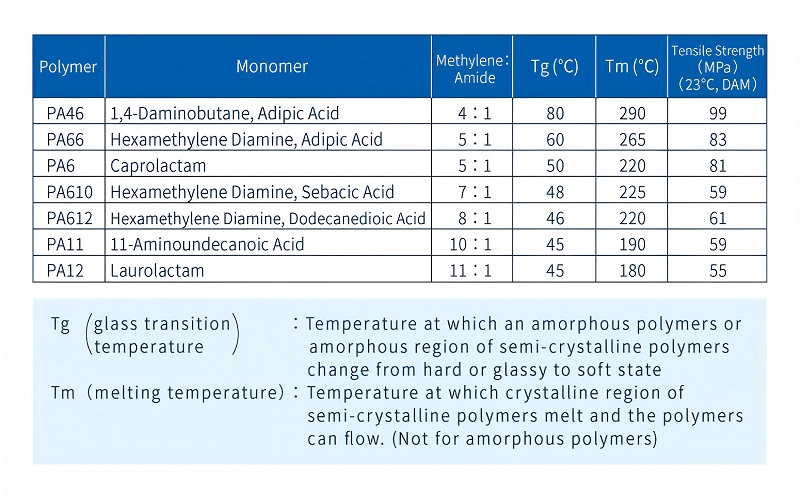
Chemical Structure of Polyamides
The chemical structure of polyamides and their molecular structure is defined by repeating units connected through amide links, characterized by the -CONH2 structure. This unique bonding is crucial for the material’s mechanical strength and thermal resistance.
For instance, in polyamides such as Nylon-6, polymerization occurs from a single monomer, leading to long chain formations. This results in a highly durable and versatile material.
Different polyamides vary in their molecular structures. Nylon-6,6, for example, is synthesized from two monomers, each containing six carbon atoms.
This specific arrangement contributes to its superior mechanical properties. Polyamides can be categorized into three main groups: aliphatic, semi-aromatic, and aromatic, with nylons being a type of aliphatic polyamide.
Amide bonds in polyamides provide high mechanical strength and thermal stability, making them suitable for numerous applications. These bonds also enhance the material’s wear resistance, ensuring longevity and reliability.
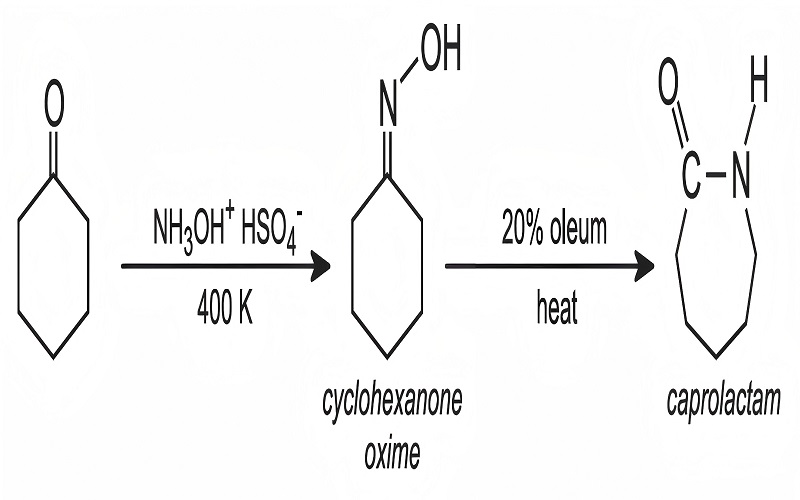
Properties of Polyamides

Polyamides possess a notable range of properties, making them essential in various industries. They exhibit excellent mechanical characteristics such as impact resilience, high stiffness, strength, and abrasion resistance, making them suitable for applications needing robustness.
Incorporating fillers like glass or carbon fiber can further enhance the mechanical properties of polyamides, increasing tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
Aramid polyamides such as Kevlar are particularly famous for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, surpassing standard aliphatic polyamides.
Polyamides exhibit exceptional thermal stability, retaining mechanical strength at temperatures over 200°C. Semi-aromatic polyamides offer even greater thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to standard aliphatic types, making them ideal for more demanding applications.
Applications of Polyamides
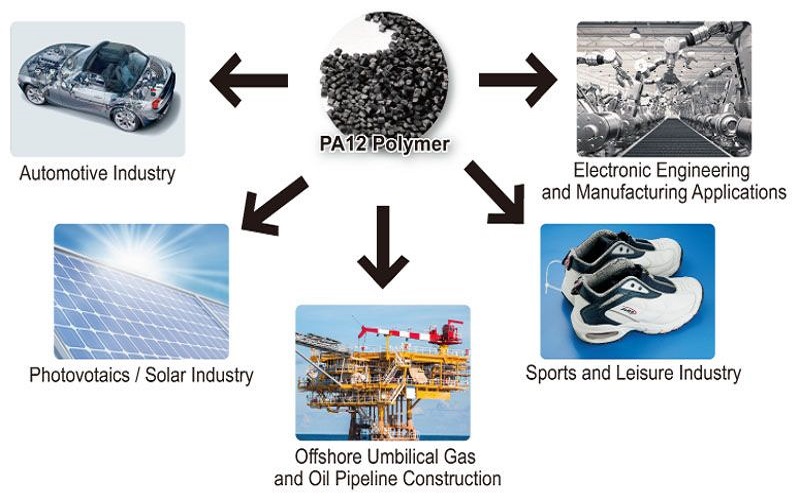
Polyamides are incredibly versatile and find applications across numerous industries. Their use extends beyond textiles to automotive parts, household items, and more.
The production of polyamide fibers, plastics, and engineering materials showcases their adaptability and wide-ranging utility.
Polyamides benefit numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, consumer goods, construction, electronics, medical, packaging, sportswear, and textiles. The following sections explore specific applications in the automotive industry, food packaging, and textile products, emphasizing the unique advantages polyamides offer.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, polyamides are crucial for manufacturing lightweight components that enhance fuel efficiency. By reducing vehicle weight, polyamide parts contribute to better overall fuel efficiency.
The strength and durability of polyamides make them ideal for producing functional parts such as airbag containers, engine covers, and fuel systems.
Additionally, nylon 3D printing is favored for creating strong, functional prototypes and end-use components in the automotive sector.
Food Packaging
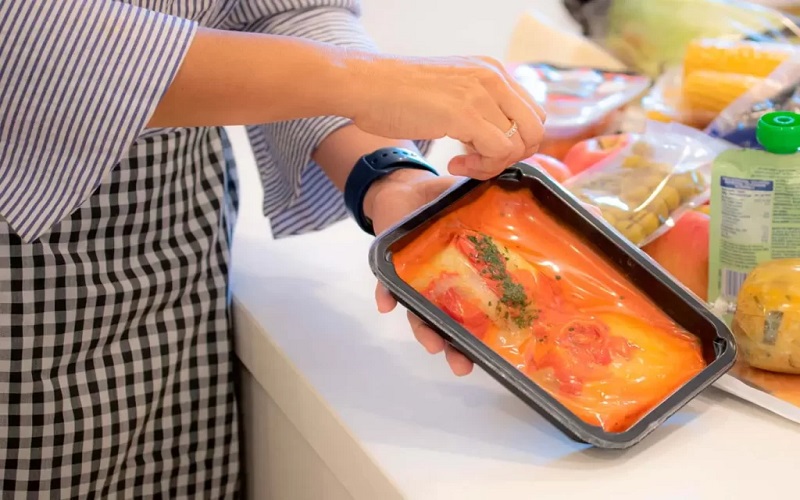
Polyamides are extensively used in food packaging due to their ability to maintain hygiene and safety during food processing. Their exceptional high-barrier properties make them ideal for preserving food safety and extending shelf life.
The chemical resistance, moisture absorption, and abrasion resistant temperature resistance of polyamides ensure that they can withstand the rigors of food packaging applications. These properties, including excellent chemical resistance, make polyamides a reliable choice for ensuring the integrity and safety of packaged food products.

Textile Products
Initially developed as a silk alternative, nylon was introduced in 1939 and quickly gained popularity for its strength and durability. Polyamide fabrics and synthetic fabrics are now commonly used in high-stress applications such as sportswear, swimwear, and activewear due to their excellent durability and elasticity.
Polyamide materials like nylon materials exhibit high elasticity and softness, making them desirable in various textile applications. Their wear resistance and ability to absorb moisture further enhance their suitability for a wide range of textile products, ensuring comfort and longevity. Additionally, polyamide fabric contributes to these qualities.
Polyamides in 3D Printing

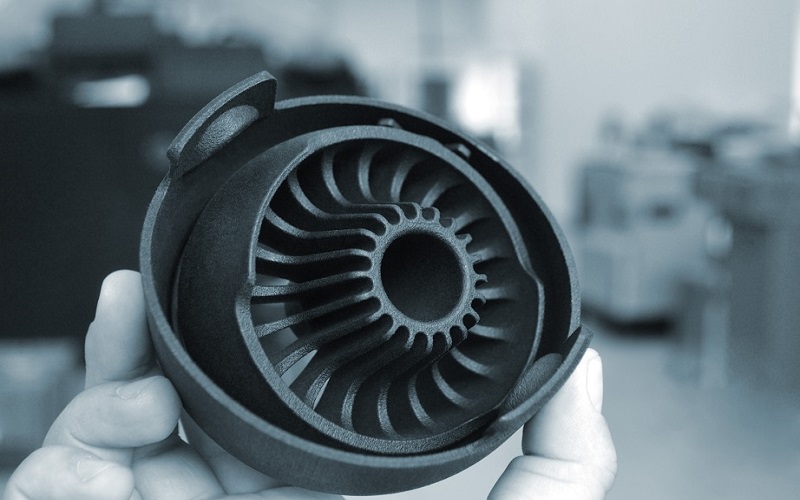
Polyamides are becoming increasingly popular in 3D printing due to their dimensional stability, durability, and high impact strength. Common materials used in 3D printing with polyamides include PA12, Nylon 12, PA6, and Nylon 6.
Technologies such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) enable the creation of complex geometries with polyamides, making them ideal for functional prototypes, automotive components, and aerospace parts.
Manufacturing Processes for Polyamides
The process of forming polyamides often involves condensation polymerization, which results in the loss of small molecules like water.
This method, along with other industrial techniques such as injection molding and selective laser sintering, plays a critical role in determining the properties and applications of polyamide materials.
Understanding these manufacturing processes is essential for optimizing the performance and utility of polyamides in various applications.
By mastering these techniques, manufacturers can produce high-quality polyamide products that meet specific industry requirements.
Polyamide vs Nylon: A Comparison
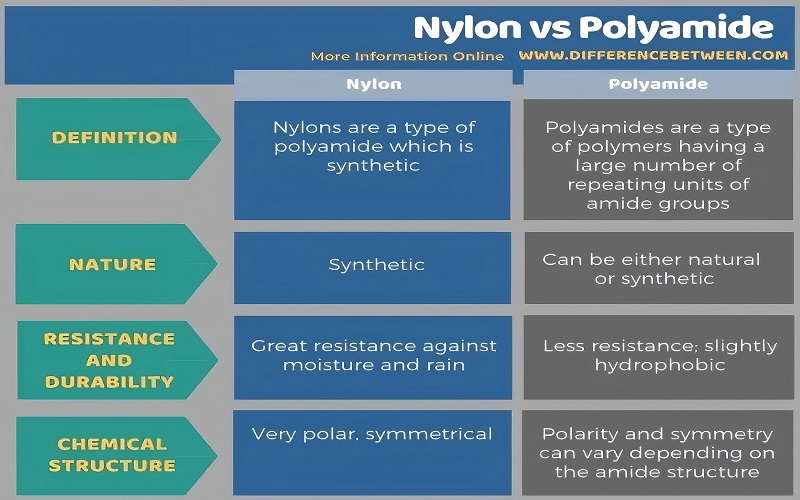
Nylon, an aliphatic polyamide, is synthesized from monomers like caprolactam. Although nylon polymers and polyamides share properties like stretch resistance, chemical resistance, and shape recovery, distinct differences exist between them.
Nylon is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it a popular choice for various applications, including textiles and automotive components. On the other hand, polyamides exhibit a broader range of structures and properties, allowing for greater versatility in their use, including synthetic fibers.
Recognizing the differences between polyamide and nylon is crucial for designers and engineers when selecting materials. This knowledge ensures the appropriate material is chosen for specific applications, optimizing performance and durability.
Recyclability and Sustainability of Polyamides
The production of polyamide materials often involves petroleum oil, making them non-renewable and environmentally challenging.
However, there are sustainable alternatives to traditional polyamides that can significantly reduce environmental impacts, with potential for up to a 75% decrease in global warming potential.
Bio-based polyamides, produced from agricultural waste, promote sustainability while maintaining desirable mechanical properties.
High molecular weight polyamides synthesized from sustainable sources can be efficiently recycled through both mechanical and chemical methods, ensuring their durability and reducing environmental impact.

Safety Considerations with Polyamides
Polyamides can cause skin reactions in some individuals, leading to irritation or allergies. Prolonged contact with polyamide materials may increase the risk of developing skin conditions, such as rashes and itching.
Awareness of potential safety concerns is vital, along with taking measures to minimize exposure. Using protective equipment and ensuring proper handling and processing of polyamide materials can help mitigate adverse effects.
Summary
In summary, polyamides and nylons are versatile, durable, and essential materials in various industries.
Their unique properties, such as mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from automotive components to textiles.
Understanding the differences between polyamides and nylons, their manufacturing processes, and their environmental impact is crucial for making informed decisions about material selection.
By leveraging the benefits of these materials while addressing sustainability and safety concerns, we can continue to innovate and improve our products and processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary uses of polyamides in the automotive industry?
Polyamides are primarily utilized in the automotive industry for creating lightweight components, including airbag containers, engine covers, and fuel systems, which enhance fuel efficiency. This application underscores their significance in advancing automotive performance.
Why are polyamides suitable for food packaging?
Polyamides are suitable for food packaging due to their high-barrier properties that preserve food safety and extend shelf life, while also maintaining hygiene during processing. Their characteristics ensure that food remains safe and fresh for consumers.
How do polyamides contribute to 3D printing?
Polyamides enhance 3D printing by providing dimensional stability, durability, and high impact strength, which are crucial for creating functional prototypes, automotive components, and aerospace parts. Their unique properties make them a preferred material in advanced manufacturing applications.
What is the difference between polyamide and nylon?
The key difference is that nylon is a specific type of polyamide, distinguished by its high tensile strength and durability, while polyamides encompass a wider variety of structures and properties. Thus, all nylons are polyamides, but not all polyamides are nylons.
Can polyamides be recycled?
Yes, polyamides can be recycled using mechanical and chemical methods, providing sustainable options while preserving their desirable mechanical properties.

