In today’s wide array of industries, material selection is an important aspect of product function and quality. Polycarbonate (PC) and PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol Modified) are two examples of widely used and favored plastic materials.
Their specific physical and chemical properties allow applications in automotive manufacturing, medical devices, and packaging.
As technology is advancing and the continuing demand for high performance materials increases, material choices are more complex than ever. This document independently describes the different performance measures between PC and PETG, with an aim to give professional, substantive material choice by application.
Understanding Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate(or PC for short), is a formidable thermoplastic polymer containing carbonate groups, which characterize above average mechanical resistance, clarity, and resistance to cracking.
Polycarbonate can also be repeatedly softened with heated and reshaped; hence, polycarbonate is often used in processing, which include but are not limited to, injection, extrusion, and thermoforming.

Properties of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional physical properties. Here’s a detailed look at its key characteristics:
- Impact Resistance: Polycarbonate is unique because of its super power to resist impacts. It can tolerate quite a lot of force without bend or breaking, thus, it is best in applications where safety and durability come first.
- Optical Clarity: Polycarbonate is similar to glass in great optical clarity but has more durability than it.
- Thermal Stability: Polycarbonate has high thermal stability and will not lose its strength and rigidity when it is used at high temperatures. For example, polycarbonate can withstand up to 150-degree Celsius (302-degree Fahrenheit) temperatures without being deformed.
- Dimensional Stability: Polycarbonate has great dimensional stability properties, which means it can retain its shape and size in a variety of different environmental and climatic conditions.
| Property | Value Range |
| Density | 1.20 – 1.22 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 55 – 75 MPa |
| Impact Strength | 600 – 900 J/m |
| Flexural Modulus | 2.2 – 2.4 GPa |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) | 120 – 140 ℃ |
| Melting Point | 220 – 230 ℃ |
| Transparency | Transparent to translucent |
| Dielectric Strength | 15 – 35 kV/mm |
| Water Absorption | 0.15 – 0.35 % |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent |
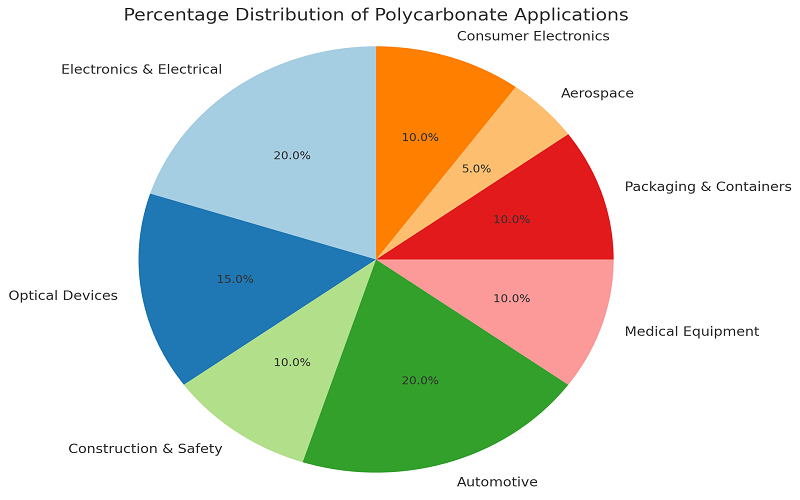
Applications of Polycarbonate
The robust properties of polycarbonate make it applicable to various industries. For example:
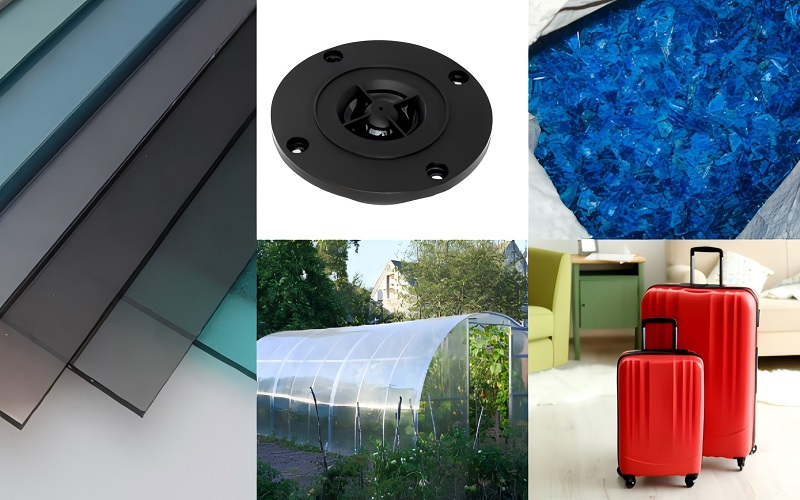
- Automotive Components: Polycarbonate is frequently employed by the automotive industry in components, such as headlamps, dashboards, trim, etc.
- Medical Devices: Polycarbonate plays an important role across medical applications technologically due to its biocompatibility and sterility.
- Eyewear Lenses: Polycarbonate is a popular optical and sports lens choice because of its optical clarity and impact resistance.
- Construction Materials: Polycarbonate sheets are often used in construction including skylights, panels, greenhouses, etc. While providing coverage and protection from the environment, polycarbonate sheets also increase light transmission capability and maximize light transmission.
Advantages of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate’s advantages include:
- Superior Impact Resistance: Its ability to withstand heavy impacts without shattering makes it ideal for high-risk applications.
- High Clarity: Its optical properties ensure clear visibility and minimal distortion.
- Thermal Stability: It maintains its integrity under high temperatures, making it suitable for heat-intensive applications.
- Versatility: Polycarbonate can be used in a wide range of applications due to its adaptable properties.

Exploring PETG
PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified polyethylene terephthalate) is a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) derived thermoplastic modified by ethylene glycol.
It is a clear, strong thermoplastic material that incorporates the positive qualities of PET and PC (polycarbonate).

Properties of PETG
PETG, a polymeric derivative of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), some of its component traits yield their own unique set of attributes for application. This is reviewed in detail below:
- Chemical Stability: PETG has excellent resistance to a variety of chemicals; it is resistant to acids, bases, and a numerous organic solvents, because of this unique resistance it is suitable for conditions that encountered exposure to robust materials, like food packaging and chemical processing.
- Impact Resistance: PETG does not have the same capacity for impact resistance as Polycarbonate, but it can still perforom adequately and handle moderate impacts as an alternative if extreme conditions are not necessary.
- Clarity Under Stress: PETG maintains clarity under pressure or stress, which is important when applications involve transparency or visual appearance factor, such as in display cases and packaging.
- Processability: PETG is readily processed. It can be extruded, thermoformed, and/or injection molded producing a plethora of designs in the manufacturing processes.
| Property | Value Range |
| Density | 1.27 – 1.29 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 48 – 55 MPa |
| Impact Strength (Izod Notched) | 60 – 90 J/m |
| Flexural Modulus | 2.0 – 2.3 GPa |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) | 65 – 75 ℃ |
| Melting Point | 210 – 230 ℃ |
| Transparency | High transparency |
| Dielectric Strength | 16 – 20 kV/mm |
| Water Absorption | 0.13 – 0.20 % |
| Weather Resistance | Good |
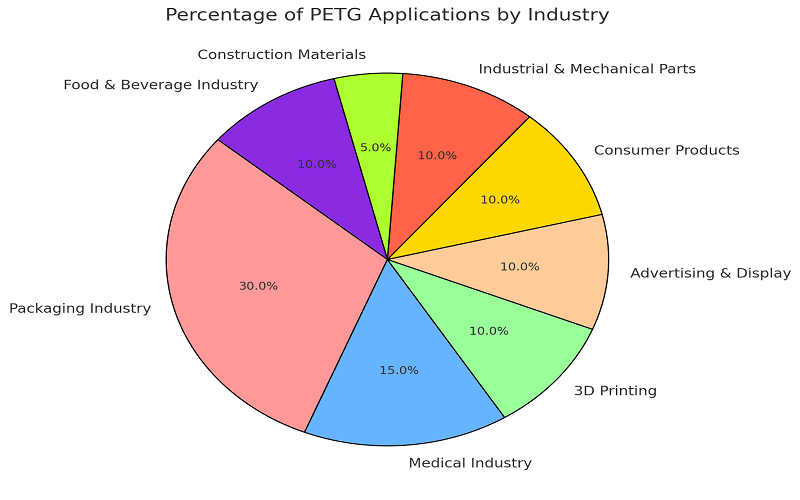
Applications of PETG
The versatility of PETG’s characteristics contributes to its use across multiple applications such as:
- Food Packaging: PETG’s chemical resistance and optical clarity is often used for food and beverage packaging to keep contents visible while protecting against contamination and extending shelf life.
- Medical Implants: PETG has biocompatability and can be sterilized easily. Its properties allow it to be used for medical implants and devices, as it can safely interact with the human body while also withstanding sterilization practices.
- Outdoor Signage: PETG’s weather resistance and optical clarity make it suitable for outdoor signage as well as outdoor displays. It can withstand continuous exposure to sunlight, rain and other elements without excessive degradation.
Advantages of PETG
PETG offers several advantages:
- High transparency: With PETG being as transparent as glass, many items made with it are used in display items.
- Impact resistance: very resistant to falling, not easy to break, suitable for use in places where durability is required.
- Good chemical resistance: PETG has good chemical resistance, as it can resist chemicals such as acids and alkalis.
- Easy to process: can be easily processed by injection mold, 3D printing, etc.
- Safety: One more advantage is that because of its good safety aspects, it meets the safety standards for food contact and is used extensively for food and/or beverages packaging material.
Comparative Analysis: Polycarbonate vs PETG
Physical Properties
When making comparisons between polycarbonate (PC) and PETG there are differences that are worth noting:
Impact Resistance: polycarbonate (PC) is more durable than PETG and is suitable for applications that have high strength requirements such as shields and automotive applications. Although PETG is a simple way to get good impact resistance, it is not up to the level of polycarbonate (PC) when it comes to durability.
Heat Resistance: Because of its structure, polycarbonate can withstand higher temperatures, which means it could be used in high-temperature environments or in processes that generate heat. PETG on the other hand, does have low thermal resistance, but it can be processed through manufacturing processes at lower temperatures which simplifies the manufacturing process.
Optical Clarity: Both polycarbonate and PETG are clear materials, but polycarbonate is generally superior when it comes to clarity for the material to be used in applications that have optics and require high visible optical precision, such as lenses and high-definition displays. In contrast, PETG works great as a transparent application when it does not have to be as visually precise.
Costs of Different Formats
The pricing of these materials will depend on the form and application, specifically about:
Within extrusions, PC sheet material is costlier than PETG sheet material due to superior impact resistance, high temperature resistance, and transparency, which will influence which material you would use with applications that seems included architectural materials needing high protection. PETG is cheaper, and can be utilized where there aren’t high performance characteristics, like display racks.
In filaments, this will generally be true too, with PC filament being more expensive in 3D printing applications than PETG filament is due to heat resistance and high strength, so if you need a part that particularly needs high strength then PC filament is better suited while PETG filament is subjective to some price point for regular printing.

In addition, there is an additional processing cost- conservation, PC material would require a higher temperature and a more complicated processing process- and processing the PC material would be more expensive than PETG.
PETG is more time efficient and convenient, so PETG is generally the more affordable material overall, taking specifications of large scale production into consideration, if you are producing products continuously.
Performance Metrics
- Impact Strength: Polycarbonate outperforms PETG in terms of impact strength, making it more suitable for high-impact applications.
- Thermal Processing: Polycarbonate’s higher thermal stability allows it to withstand greater temperatures, while PETG’s processing flexibility makes it easier to use in various manufacturing techniques.
Safety Performance
- Flame Retardancy: Polycarbonate generally has better flame retardancy, which is important for applications involving fire safety. It meets higher fire safety standards compared to PETG.
- Chemical Stability and Biocompatibility: PETG’s chemical stability and biocompatibility make it a preferred choice for medical and food-related applications. It is less likely to react with substances it comes into contact with, ensuring safety in sensitive environments.

Environmental Impact and Recycling Options
Recycling Procedures: The processes for recycling PETG are less complicated than polycarbonate. The processes for recycling polycarbonate are usually complicated and less frequently utilized, hindering environmental sustainability.
Environmental Impacts: Both plastics exhibit some environmental development aspects reminiscent of their production and later decline when disposed. Polycarbonate has the added worry of bisphenal A (BPA). On the other hand, PETG is going to have a more benign environmental impact.
It is commonly accepted to have lower toxicity, not complicated recycling processes, impacting the strength of performance of the material, compared to polycarbonate in healthcare and food applications.
Polycarbonate is ideal when you need a material with high heat resistance, excellent strength, rigidity, and clarity. In contrast, PETG is more suited for applications requiring medium strength and clarity, offering the advantage of lower production costs, easier processing, and moderate impact resistance.
Alternative Materials to Consider in Material Selection Process
When selecting materials, it’s also important to consider alternatives to Polycarbonate and PETG:
Acrylic (PMMA): This polymer gives best light transparency which makes it very good for the display boxes and lenses. However, it is not as strong than polycarbonate.
Figure 1: injection molding PMMA products

Trivex: This one is very light and therefore provides good clarity as well as impact resistance. However, this one is mainly found in glasses and masks.
Figure 2: Trivex eyeglasses

Polystyrene (PS): This is a material which is very low price but has short durability so it is suitable for using in disposable products and packaging.
Figure 3: disposable polystyrene (PS) boxes

ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): is commonly used for parts that need to be impact-resistant and have good mechanical properties, such as car interiors and home appliance housings. However, it is not transparent.
Figure 4: ABS blocks
Conclusion
In summary, polycarbonate and PETG each have distinct advantages, meaning they are suited to specific applications due to their properties.
Polycarbonate has a reputation for great impact resistance, optical clarity, and thermal stability making it particularly good for stressing applications.
PETG is known for superior chemical stability, good processing ease, and high transparency, making it suitable for packaging and some medical applications.
Overall, understanding the properties of these materials will allow you to make a better choice for your intended application.

