Polyethylene PE foam is a resilient and lightweight material used in packaging, insulation, and healthcare. It offers excellent cushioning and thermal insulation. This guide explores its types, properties, and applications across different industries.

Polyethylene foam, often referred to as PE foam, is a closed-cell material renowned for its durability, lightweight, and resilience. The magic of PE foam lies in its structure, composed of tightly packed cells that prevent the flow of liquids and gases. This unique configuration endows it with properties that make it ideal for a wide range of applications, from cushioning and insulation to packaging and medical uses.
Polyethylene foam is made from polyethylene resins and blowing agents, where the material starts as a molten blend that is expanded into foam. The resulting material is durable, lightweight, and resilient, able to return to its original shape after compression. These properties, along with options for varying thickness to suit specific needs and the availability of fire retardant additives to enhance safety, allow it to serve diverse industries effectively.
Types of Polyethylene Foam
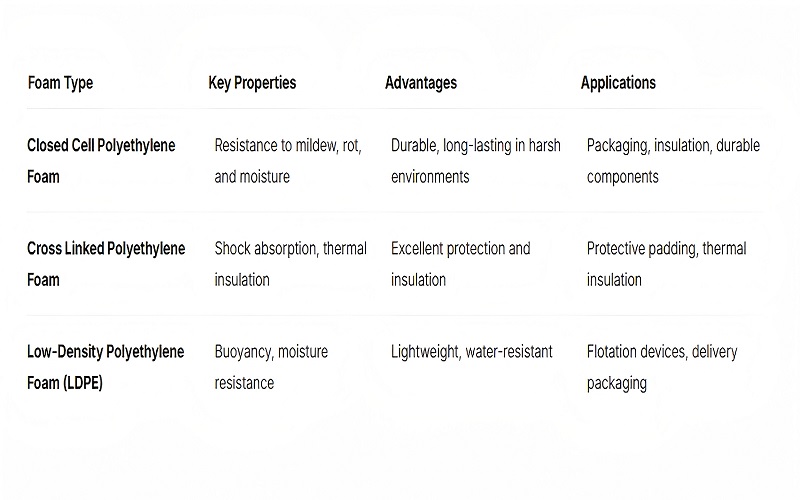
Polyethylene foam is categorized into various types, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
The primary types include closed cell polyethylene foam, cross linked polyethylene foam, and low-density polyethylene foams (LDPE). Each of these types offers distinct advantages, catering to different needs and industries.
Next, we examine the properties and uses of closed cell polyethylene foam, which offers resistance to mildew and rot, making it ideal for durable applications. The shock absorption and thermal insulation of cross linked polyethylene foam ensure reliable performance in protective and insulating roles. Low-density polyethylene foams (LDPE) and their molecules provide excellent buoyancy and moisture resistance, supporting applications like flotation devices and delivery packaging.
Understanding these types showcases the versatility and variety of PE foam in various contexts.
Closed Cell Polyethylene Foam
Closed cell polyethylene foam, with its tightly packed cells that prevent the flow of liquids and gases, is both durable and lightweight. Its versatility makes it suitable for protecting fragile items during shipping or insulating buildings. Closed cell foam is an excellent choice for various applications.
Its properties make it ideal for packaging, insulation, and protective materials. The foam absorbs impacts and returns to its original shape after compression, providing effective cushioning and protection. The closed cell structure also offers excellent thermal insulation, making it a preferred choice for construction projects.
Cross Linked Polyethylene Foam
Known for its strong cushioning properties, cross linked polyethylene foam offers excellent shock absorption, ensuring reliable protection for items in packaging, automotive, or construction industries.
Beyond shock absorption, cross linked polyethylene foam also provides effective thermal insulation, contributing to energy efficiency and temperature protection. Its versatility and durability make it valuable in sectors like automotive, construction, insulation, and sports equipment.
Low-Density Polyethylene Foams (LDPE)
Low-density polyethylene foams (LDPE), noted for their buoyancy and moisture resistance, are ideal for marine applications and packaging delicate items. Their softness and compressive nature ensure effective cushioning and protection against water.
Valued in the packaging industry for their lightweight nature, LDPE foams reduce shipping costs while providing high-level protection. They reliably protect electronics, medical equipment, and other sensitive products, thanks to their buoyancy, moisture resistance, and compressive properties.
Extrusion Process of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is produced using methods like batch foaming and foam extrusion. In extrusion, polyethylene is melted and formed into foam using an extruder.
In extrusion, gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide are injected to expand the foam. As the foam exits the extruder, the gas expands, forming the foamed structure. This method results in extruded polyethylene foams known for high insulation properties, lightweight, and durability.
Extruded polyethylene foam provides excellent thermal insulation, impact resistance, and buoyancy, making it suitable for various applications, including:
- Packaging
- Construction
- Marine
- Medical uses
The extrusion process ensures structural integrity and reliable performance in various environments.
Applications of Polyethylene Foam

Polyethylene foam’s versatility and effective cushioning properties make it widely used across industries, including packaging, insulation, healthcare, and marine applications.
Next, we’ll explore specific applications in detail, highlighting how PE foam meets the needs of different sectors.
Packaging Solutions
Known for impressive impact resistance and durability, polyethylene foam is ideal for cushioning applications. It absorbs impacts and returns to its original shape after compression, protecting fragile items during shipping. This reliability makes it popular for e-commerce and other industries.
Lightweight polyethylene foam is valued for ease of handling and transport, reducing shipping costs while providing high protection. Used in foam pouches, sheets, or die cuts, it offers effective packaging solutions for various needs. The light weight of this material enhances its usability.
Thermal Insulation
With low thermal conductivity, polyethylene foam is an excellent insulator, suitable for both residential and industrial applications. In construction, it’s used for soundproofing and insulation, providing effective thermal barriers.
The closed cell structure of the foam maintains its insulating properties over time, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort. In building projects or industrial settings, polyethylene foam provides reliable thermal insulation, maintaining optimal temperatures and reducing energy costs.
Medical Uses
In medical settings, polyethylene foam’s non-abrasive nature ensures patient comfort. Its closed cell structure prevents bacteria and mold development, enhancing hygiene.
Furthermore, PE foam’s antimicrobial properties make it suitable for medical applications where cleanliness and comfort are crucial.
Advantages of Using Polyethylene Foam
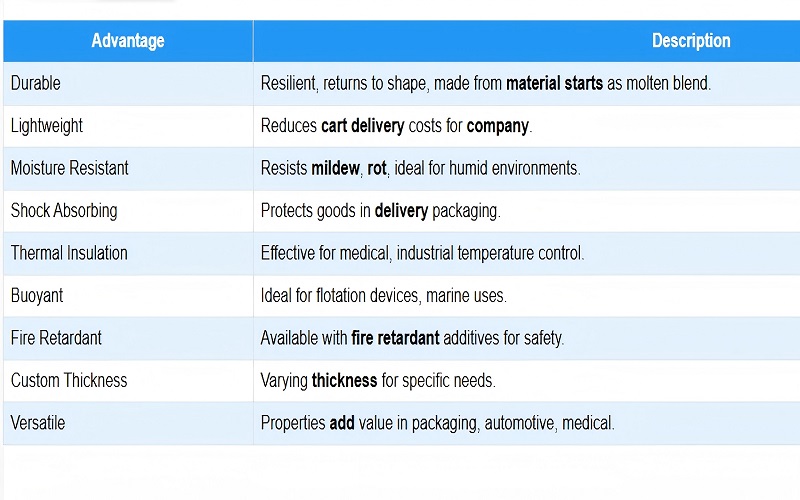
Polyethylene foam offers excellent vibration dampening, insulation, and high resistance to chemicals and moisture, making it versatile for various applications. EPE foams are also lightweight, non-abrasive, and recyclable, enhancing their appeal.
Extruded polyethylene foam’s closed cell structure provides effective mechanical protection. Additionally, PE foam is fully recyclable, allowing it to be remolded for new applications.
Cross-linked polyethylene foam withstands weather, resists chemical reactions, and is a durable insulating material. These benefits make it an environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution for diverse industries, particularly when using cross linked foam.
Customization Options for Polyethylene Foam
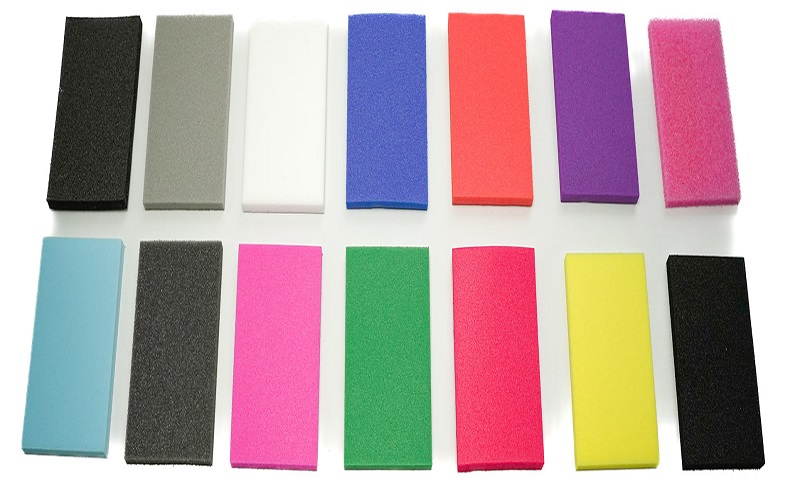

Polyethylene foam is available in various densities, ranging from 1.2LB to 9.0LB. This allows for tailored solutions based on specific needs, ensuring the foam meets different application demands. Whether for lightweight packaging or dense insulation, PE foam can be customized to fit your requirements.
Polyethylene foam sheets come in colors like:
- blue
- white
- green
- pink
These colors enhance aesthetic appeal for applications where appearance matters in a search for great visual color options details excellence commonly easy and interested. You can use these plain colors effectively.
Customization options in densities and colors enhance the versatility and applicability of polyethylene foam across industries.
Pricing Factors for Polyethylene Foam
The quality of polyethylene foam, influenced by its density and processing methods, affects its market pricing. Higher quality foams with greater density and advanced processing command higher prices. Market demand in industries like packaging, automotive, and medical also plays a crucial role in pricing.
Increased market demand, driven by company needs in sectors like e-commerce for protective packaging in cart shipments, often raises polyethylene foam prices due to limited supply. Government regulations can also impact production costs, influencing the final price of polyethylene foam products. An increase in demand can further complicate the pricing structure.
Material quality, market demand, shipping costs, and regulations all add to the overall pricing of PE foam.

Processing Techniques for Polyethylene Foam
Lamination techniques for polyethylene foam include pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) lamination, which bonds foam with a sticky backing, and heat lamination, which creates durable composite materials. These techniques enhance PE foam’s functionality for various applications.
Thermoforming heats thermoplastic polyethylene foam until pliable, allowing it to be molded into specific shapes, making it suitable for cushioning applications. Die cutting, another widely used method, allows for consistent production of identical shapes using a custom steel rule die.
These processing techniques, along with CNC cut and hot wire foam cutting, enable the customization of PE foam into specific shapes and sizes to meet project requirements.
Maintenance and Care of Polyethylene Foam Products
Maintaining polyethylene foam products ensures their longevity and optimal performance. Regular inspections can find wear or damage early, allowing for timely repairs or replacements.
Clean polyethylene foam gently using mild soaps and soft cloths to prevent damage. Store PE foam products in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight to prevent degradation and extend their lifespan.

Summary
Polyethylene PE Foam is a versatile and indispensable material used across various industries. Its unique properties, including durability, lightweight, and resilience, make it suitable for a wide range of applications. From packaging and thermal insulation to medical uses, PE foam meets the demands of diverse sectors with efficiency and reliability.
The benefits of using polyethylene foam are numerous, including excellent vibration dampening, high resistance to chemicals and moisture, and recyclability. The customization options in densities and colors further enhance its versatility, making it a preferred choice for many applications.
As we have explored in this guide, understanding the types, applications, processing techniques, and maintenance of PE foam can help you make informed decisions and leverage its advantages for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is polyethylene foam commonly used for?
Polyethylene foam is primarily utilized for packaging, thermal insulation, and medical applications because of its durability, lightweight nature, and effective cushioning properties.
How is polyethylene foam produced?
Polyethylene foam is produced by melting polyethylene and injecting gases such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide during the extrusion process to create expansion. This method effectively yields the desired foam structure.
What are the benefits of cross linked polyethylene foam?
Cross linked polyethylene foam provides superior shock absorption, thermal insulation, and exceptional durability, making it highly suitable for both protective and insulating applications.
Can polyethylene foam be customized?
Yes, polyethylene foam can be customized in different densities and colors to suit specific application requirements.
How should polyethylene foam products be maintained?
To ensure the longevity of polyethylene foam products, they should be regularly inspected, cleaned with mild soaps and soft cloths, and stored in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight.

