In the wide world of plastics, there is a category called thermoplastics, which are characterized by the ability of repeated processing and high production flexibility. This plastic softens when heated and hardens again after cooling. It is often seen being used in various fields. Two examples of these thermoplastics are polypropylene (PP) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). But why are these two types of plastic used so often?
Let’s compare the properties, suitable applications, differences and cost factors of two materials: polypropylene (PP) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). A detailed analysis of PP and ABS will reveal the optimal use cases and potential limitations of these materials in various conditions. Whichever you are, this article will help you make the right choice.
What is Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene, abbreviated as PP, is a common and widely popular thermoplastic polymer in daily life, formed by the polymerization of propylene monomers. It is durable, tough, and flexible. Compared to ABS, it is lightweight, with a density of only 0.90 g/cm3. Additionally, it is resistant to moisture absorption and chemical substances, and it can withstand temperatures up to approximately 100°C.

What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
ABS is one of the most cost-effective thermoplastic plastics. It possesses excellent mechanical properties, such as high impact resistance, and it does not easily deform at high temperatures, being able to withstand temperatures of approximately 110-125°C. ABS is easy to process and manufacture, capable of being molded into various complex shapes, exhibiting outstanding “processability.”

Choosing Between Polypropylene (PP) and ABS
Polypropylene (PP) and ABS are both thermoplastics, so they have many similar properties. However, there is still a large difference in terms of specific performance. For example, the elongation at break of ABS is higher than that of Polypropylene (PP). this means that ABS has a higher toughness than PP and is more suitable for use in scenarios where durability is required.
Regardless of any processing, it is essential to understand all the key factors affecting part design before starting, such as their strength, heat resistance, and flexibility. You can compare these parameters with your own part design project using the table below.
The following table lists the changes in the properties of Polypropylene (PP) and ABS during three different processing processes: injection molding, extrusion and 3D printing.
| Property | ABS Molded | ABS Extrusioned | 3D Printing |
| Heat Distortion Temperature | 85-105°C | 85-100°C | 50-70°C |
| Tensile Strength | 40-50 MPa | 35-45 MPa | 30-40 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 10-30% | 5-25% | 4-10% |
| Density | 1.04-1.06 g/cm³ | 1.04-1.06 g/cm³ | 1.1-1.2 g/cm³ |
| Impact Resistance | 200-300 kJ/m² | 180-250 kJ/m² | 50-100 kJ/m² |
| Hardness, Shore D | 90-100 | 85-95 | 80-85 |
| Water Absorption | 0.2-0.3% | 0.2-0.4% | 0.3-0.5% |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.17 W/(m·K) | 0.16 W/(m·K) | 0.2 W/(m·K) |
| Shrinkage | 0.5-0.8% | 0.4-0.6% | 1.0-2.5% |
| Property | ABS Molded | ABS Extrusioned | 3D Printing |
| Heat Distortion Temperature | 85-105°C | 85-100°C | 50-70°C |
| Tensile Strength | 40-50 MPa | 35-45 MPa | 30-40 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 10-30% | 5-25% | 4-10% |
| Density | 1.04-1.06 g/cm³ | 1.04-1.06 g/cm³ | 1.1-1.2 g/cm³ |
| Impact Resistance | 200-300 kJ/m² | 180-250 kJ/m² | 50-100 kJ/m² |
| Hardness, Shore D | 90-100 | 85-95 | 80-85 |
| Water Absorption | 0.2-0.3% | 0.2-0.4% | 0.3-0.5% |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.17 W/(m·K) | 0.16 W/(m·K) | 0.2 W/(m·K) |
| Shrinkage | 0.5-0.8% | 0.4-0.6% | 1.0-2.5% |
Advantages of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is our main choice for production. It exhibits excellent flexibility during processing and can withstand repeated bending and bending without breaking or breaking. Using Polypropylene (PP) as a cost-effective material also offers the following advantages:
· Cheap plastic with low production costs
· Robust and durable
· The density is only 0.90 g/cm3, which makes it lighter than other plastics.
· High flexibility: can be bent repeatedly
· Resistance to different temperatures: high melting point and low temperature impact strength
· Moisture resistance: low water absorption
· Chemical resistance: resistance to acids and bases
· High resistance to the environment: resistance to UV radiation

Advantages of ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is known in thermoplastics for its excellent performance. It is easily processed while maintaining the toughness of the material due to its excellent strength and stiffness in processes such as injection molding, extrusion and 3D printing. ABS is a highly preferred plastic material due to its electrical insulating properties and chemical resistance. It is also a popular choice for injection molding where a cheap, strong and robust plastic is required. Other benefits of ABS include:
· It is a plastic with excellent impact resistance.
· It is very resistant and is not significantly affected by temperature and humidity.
· Electrically insulating properties.
· Chemical resistance – unaffected by acids, bases and other chemical agents.
· It is a stable material with lower shrinkage and better retention of dimensions and shape.
· The surface is smooth and shiny, which makes it suitable for plating and other processes, which greatly improves the aesthetics of the product.

Polypropylene (PP) vs ABS :Applications
Polypropylene (PP) has a wide range of uses, and many products include: materials used for packaging, automotive parts, medical devices, and more.
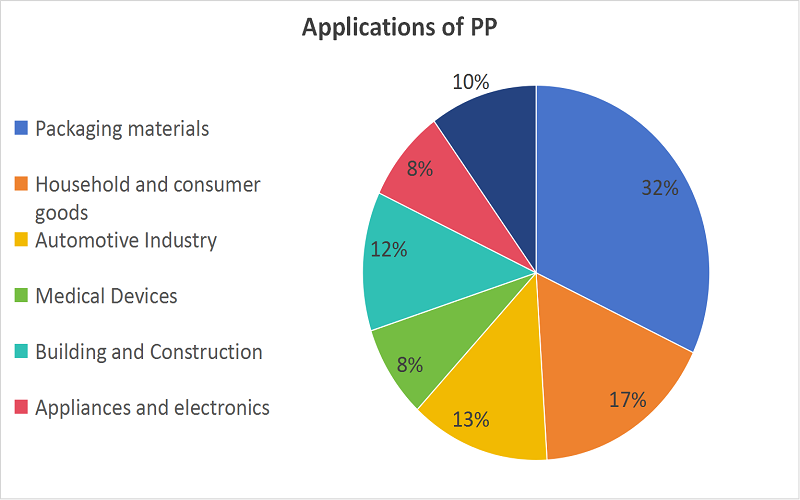
ABS has a wide range of applications. It can be used to manufacture car dashboards and housings; computer housings; phone cases; lawn and garden equipment; and building materials such as pipes and panels.
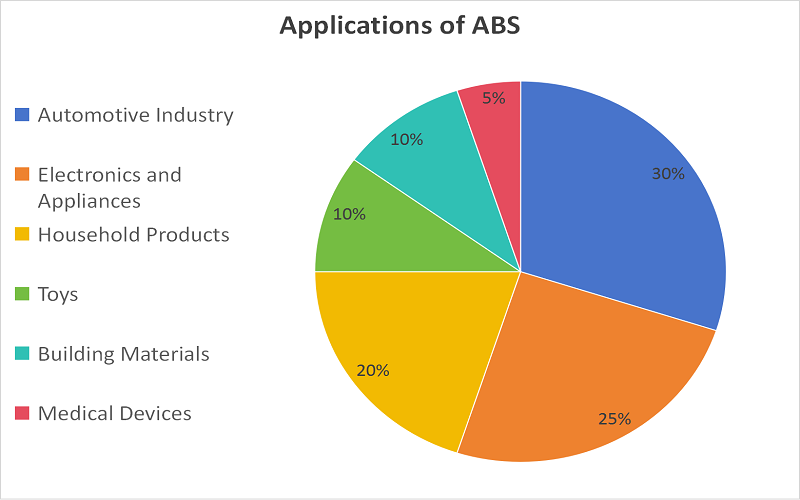
Which is Cheaper, Polypropylene (PP) or ABS?
To compare the cost-effectiveness of Polypropylene (PP) and ABS, we can examine three aspects:
1. Raw material cost: Although the market prices of plastic are not fixed and may fluctuate due to various factors, the raw material cost of ABS is still relatively higher than that of PP. Therefore, Polypropylene (PP) is generally used for large production.
2. Processing cost: Both PP and ABS have good processing and are suitable for injection molding and other similar processes. However, ABS requires higher temperatures during processing, resulting in increased energy costs.
3. Product life and maintenance costs: ABS heat resistance and chemical resistance allow it to be used in harsh environments. However, compared to PP, it is less resistant to chemicals and moisture, which often leads to higher maintenance costs than Polypropylene (PP).
Therefore, if you compare who is more profitable, PP clearly has an advantage over ABS. It is more suitable for large-scale production and has lower costs. Of course, cost is only one factor in choosing materials; we should also consider facts and requirements.
Is Polypropylene (PP) Compatible With ABS?
In layman’s terms, compatibility is like the ability of friends to get along. We can understand that if there are two different colors of erasers, if they can be mixed together to produce a new color all the time, then it shows that the two erasers are compatible, and vice versa. So the analogy to PP and ABS, if the two can get better and more durable products after mixing, it shows that the two are compatible.
To understand whether PP and ABS are compatible, we first need to compare their molecular structures; PP is a non-polar polymer while ABS is a polar polymer because some of them have “polar” groups in their molecular structures, such as hydroxyl (-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), amino (-NH2), etc., while others do not.
This is because some of them have “polar” groups in their molecular structure, such as hydroxyl (-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), amino (-NH2), etc., while others do not. The difference in chemical structure causes PP and ABS to become incompatible when mixed at high temperatures, resulting in lower strength and toughness of the materials.
Although PP and ABS are not directly compatible, the use of compatibilizers during the addition step can be considered. For PP and ABS, polyolefin graft copolymer or maleic anhydride graft polypropylene can be selected as compatibilizer and then melted and mixed at high temperature.
Alternatively, physical bonding can be considered, which combines PP and ABS through mechanical bonding. For example, in the automotive industry, ABS is commonly used to create elaborate shells, while PP is required for internal structural parts. This combination allows them to maximize their profits.
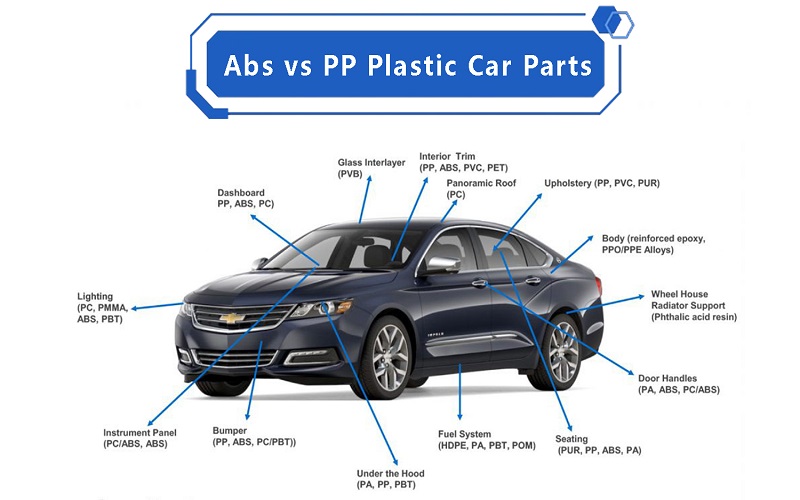
Does ABS Plastic Break Easily?
To answer this question, let’s first look at the basic characteristics of ABS. It is known to be impact resistant and has high strength. Because of its impact resistance, it can withstand large physical impacts without breaking easily, so it is commonly used in auto parts and electronic enclosures, and is sometimes used as a material for toys.
Chemical and heat resistance ensures that it is not easily changed or damaged, even in different temperatures and environments.
Therefore, you don’t have to worry about the ABS being damaged in daily life, and you can use it with confidence.
Conclusion
How do you choose between Polypropylene (PP) and ABS? If you want to use it in a product that requires absorbency and elasticity, PP may be more suitable. But if the product requires a certain strength, hardness, impact resistance and stability, ABS is clearly better than PP.PP has a greater selection of raw materials and requires less energy for injection and blow molding.
In contrast, ABS raw materials are strongly influenced by the market, have unstable price fluctuations, and have high requirements for processing technology. Considering only cost, PP is more economical than ABS and can be mass produced.
We hope this information will help you choose materials.Consider the above information in conjunction with your basic needs. For more information about plastics, please visit our company website.

