In plastic manufacturing, Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) are both very common materials, widely used in packaging, containers, pipes, and electrical insulation, among other fields.
So, which material is better, PP or PET? This article will compare and analyze them from multiple aspects, including performance, applications, and recyclability.
What Is Polypropylene ?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic resin made from the polymerization of propylene and ethylene.
It is one of the five major general-purpose thermoplastic resins and is typically colorless, semi-transparent, and lightweight, with excellent heat and chemical resistance.
However, it has poor weather resistance and low-temperature impact strength, often requiring plastic additives for improved performance.
In recent years, PP has seen extensive use in the automotive, electronics, packaging, construction, and furniture industries, driving rapid growth in production.
Among the five major general-purpose plastics, polypropylene ranks third in production volume, after polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride.

What Is PET Plastic?
PET plastic, or Polyethylene Terephthalate, is formed by the polycondensation of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol.
It is a crystalline saturated polyester and, along with PBT, is classified as a thermoplastic polyester.
Known for its high transparency, excellent toughness, and heat resistance, PET also boasts outstanding chemical resistance and superior barrier properties.
As Plastic #1, PET can be used for bottles, films, sheets, and fibers, making it widely applicable in the packaging industry, electronics, medical and healthcare, construction, and automotive fields.

PP vs PET:Properties
Performance is the most important factor in determining the quality of materials, so it is necessary to understand the characteristics of PP and PET.
Physical Properties
PP: It is the lightest of the commonly used resins, with a density of 0.890.91g/cm³, a melting point of 164170℃, and a usable temperature range of -30~140℃.
PET: It is a milky white or pale yellow, highly crystalline polymer with the greatest toughness among thermoplastics, high transparency, and can be used long-term within a temperature range of 55-60℃.
Chemical Properties
PP: It has good chemical stability and does not react with most chemicals except strong oxidizers.
PET: Due to the presence of ester bonds, it decomposes under the action of strong acids, strong bases, and steam. However, it is resistant to oil, fats, dilute acids, dilute alkalis, and most solvents.
Thermal Properties
PP: It has good heat resistance, with a continuous use temperature of 110-120℃.
PET: It maintains excellent physical and mechanical properties over a wide temperature range, with a usable temperature up to 120℃.
Electrical Properties
PP: It has excellent electrical properties and maintains good electrical insulation even in humid environments.
PET: It also has good electrical insulation properties, with little impact from temperature changes, but has poor corona resistance.
Processing Properties
PP: It has excellent processing properties, dimensional stability, and is suitable for various molding methods.
PET: It has a slow crystallization rate, long molding cycle, and high molding shrinkage rate.
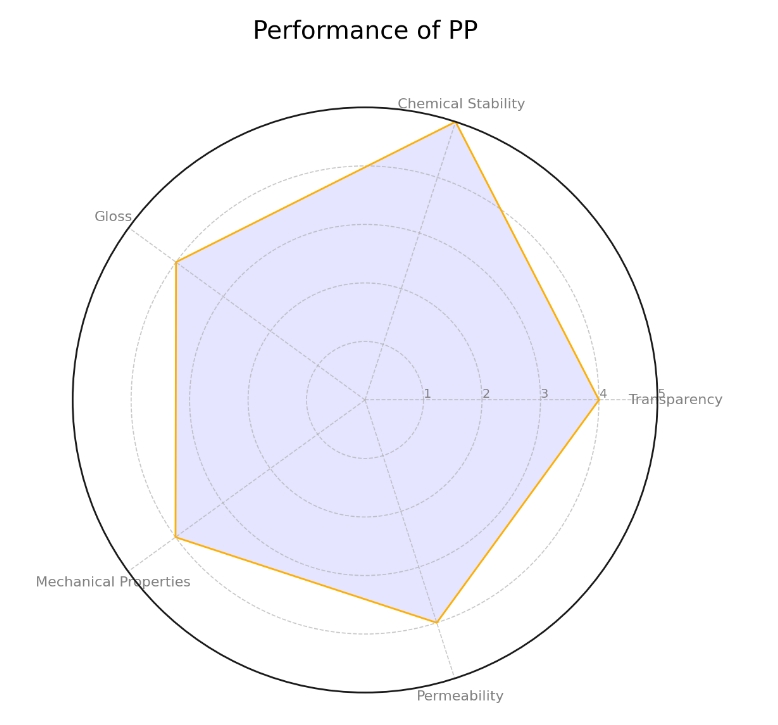
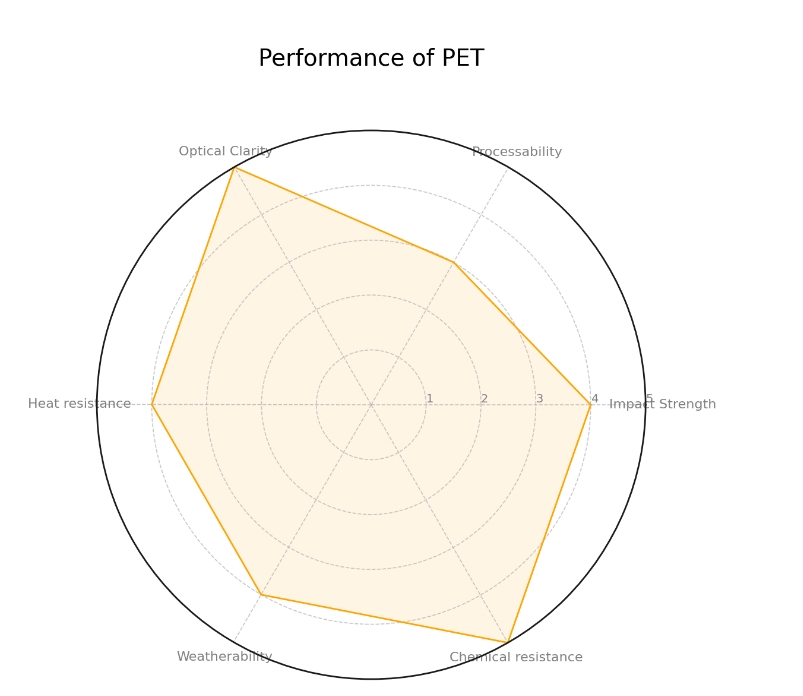
From the above comparison, we can see that PP is lightweight, has high strength, heat resistance, and good electrical insulation; while PET has high transparency, strong toughness, chemical resistance, and good weather resistance.
| Property | PP | PET |
| Density (g/cm³) | 0.89-0.91 | 1.30-1.33 |
| Melting Point (℃) | 164-170 | 250-255 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 21-39 | 53 |
| Bending Strength (MPa) | 42-56 | 200 |
| Impact Strength(KJ/m2) | 2.2-5 | 3-6 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200-400 | 90-150 |
| Water Absorption (%) | <0.03 | 0.06-0.129 |
| Rockwell hardness | R95-105 | R90-95 |
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of PP?
The main advantages of PP material are as follows:
- Lightweight
- Excellent mechanical properties
- High heat resistance
- Chemical stability
- Electrical insulation
Despite the many advantages of PP, its drawbacks cannot be overlooked:
- Poor cold resistance
- Easily ages
- Poor colorability
In summary, PP material excels in corrosion resistance, lightweight, environmental friendliness, processability, and heat resistance.
However, attention should be given to its limitations in dimensional accuracy, low-temperature impact resistance, and weather resistance.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of PET?
The advantages of PET plastic are as follows:
- High transparency
- Strong chemical stability
- Good gloss
- Excellent mechanical properties
- Low permeability to gases and water vapor
The disadvantages of PET plastic include:
- Poor corona resistance
- Not resistant to hot water immersion
- Not resistant to alkalis
In summary, PET plastic has high transparency, strong chemical stability and mechanical properties, and low permeability, making it perform well in various fields.
However, it has certain limitations in terms of corona resistance, resistance to hot water, and resistance to alkalis.
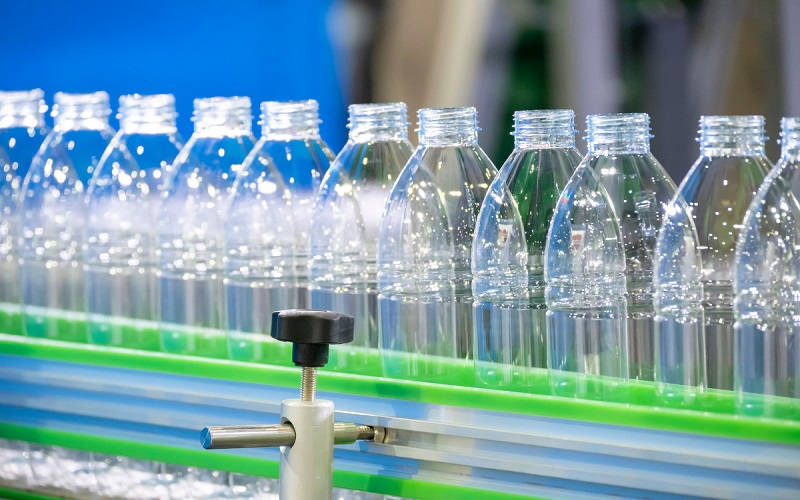

Application Of PET And PP Products
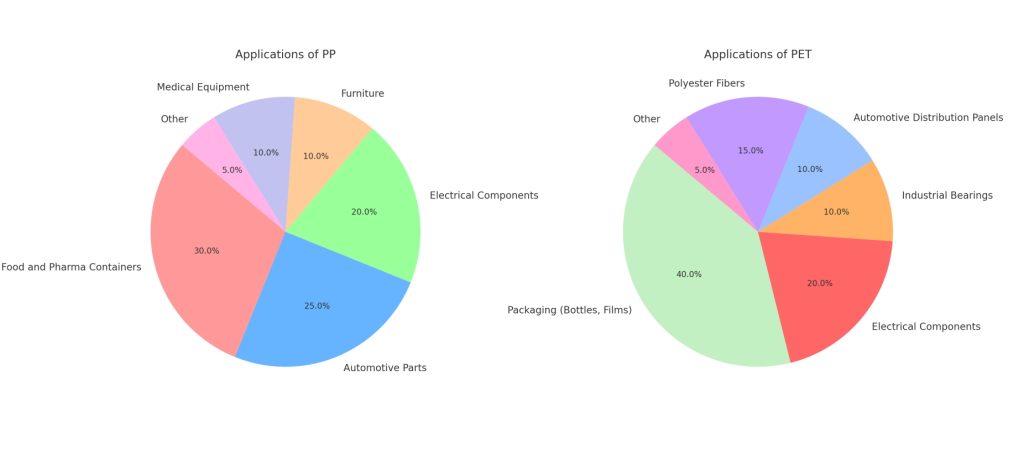
Polypropylene (PP) is commonly used to produce food and pharmaceutical containers and packaging.
PP injection-molded products dominate the consumer market, typically used in automotive parts, electrical components, furniture, and medical equipment.
For PET plastics, the packaging sector is the largest application market, including bottles, films, and more.
PET is also used for electrical components, industrial bearings, and automotive distribution panels.
Additionally, PET is used to manufacture polyester staple fibers and filament yarns, serving as raw material for polyester fiber companies to process fibers and related products.
PP And PET: Which Plastic Is Safer?
From a safety perspective, both PP and PET have undergone rigorous monitoring and testing to meet food safety standards. Neither material contains substances harmful to human health, thus posing no direct threat.
Additionally, their production processes adhere to environmental principles, minimizing their impact on the environment.
Therefore, in terms of safety and non-toxicity, both PP and PET are reliable choices.
PP is non-toxic, odorless, stable, and highly recyclable, making it a relatively environmentally friendly material.
Under normal temperature and pressure, PP remains stable and does not easily decompose into harmful substances.
It boasts good thermal stability, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance, making it commonly used for food containers, medical supplies, and household items.
PET plastic has excellent transparency, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, effectively protecting food from external influences.
In conclusion, both PP and PET are safe and non-toxic plastic materials.
They each have their own advantages in practical applications and show no significant differences in terms of safety.

The Recyclability of PET and PP
Amid the growing global concern over plastic pollution, plastic recycling has become a focal point. Both PP and PET are recyclable plastic materials.
PP plastic is highly recyclable due to its stable chemical properties and high heat resistance.
This allows it to maintain its physical and chemical stability through multiple recycling processes.
PP products, such as packaging materials and turnover boxes, can be repeatedly recycled by heating, melting, and reshaping, without losing their original physical properties.

PET plastic, especially food-grade PET (such as food packaging bottles), is also recyclable.
During the recycling process, PET can be reused through cleaning, crushing, and melting, to produce new packaging materials or other products.

In summary, PP and PET plastics are common types of recyclable materials. Through proper recycling processes, these plastics can effectively reduce environmental pollution and promote resource reuse.
Is PP Or PET More Expensive?
Generally, the cost of PET may be slightly higher than that of PP, primarily due to differences in material costs, production processes, and market demand for the two materials.
PP is priced at approximately $10-30 per kilogram. Its production process is relatively simple and low-cost, making it relatively inexpensive.
On the other hand, PET typically costs $15-40 per kilogram. It has a higher recycling efficiency and, when producing food-grade packaging materials, requires stringent cleaning and processing, which increases production costs.

Which Is Better,PP or PET ?
In summary, PP and PET each have their advantages, and there is no absolute “better” choice. The selection should be based on specific application scenarios and requirements.
For example, if the product needs to be used in high-temperature environments or requires excellent transparency and barrier properties, PET may be the better choice.
If the product needs to be used in corrosive media or requires lightweight materials, PP might be more suitable.
Cost is also an important factor to consider. Since PET is relatively more expensive, if the performance requirements of the product are not particularly high, the lower-cost PP material can be chosen.
If you are unsure whether to choose PP or PET for your project, please contact Octivi, and we will provide you with professional advice and technical support!

