Screw bosses are essential in injection molding, serving as attachment points for screws or inserts. This guide details how to design effective screw bosses to enhance the strength and durability of plastic parts. Learn about optimal wall thickness, size, shape, and placement to improve your product’s quality.
Understanding Screw Bosses in Injection Molding
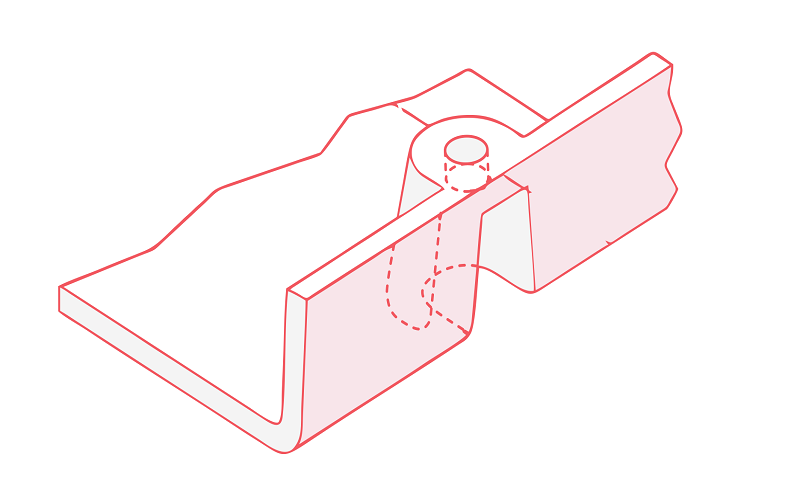
In the realm of injection molding, screw bosses are indispensable features that serve multiple purposes. These cylindrical projections are designed with holes to accommodate screws or inserts, often created using a core pin during the molding process to ensure precise hole formation, making them crucial for attachment and assembly points, positioning aids, and fixation points.
Their significance extends across various industries, from medical devices to automotive parts, electronics, and even toys, improving moldability, mold life, and reducing manufacturing costs. As plastic bosses, they provide a reliable foundation for securing components in these diverse applications.
The design of screw bosses must consider the forces they will encounter during assembly and service, ensuring they can withstand tension, compression, torsion, and flexing. Properly designed screw bosses connect to the nearest side wall for optimal performance, enhancing the overall strength and durability of the injection-molded part.
Understanding the fundamental role of screw bosses allows designers to create parts that are both functional and robust.
Key Design Principles for Effective Screw Bosses
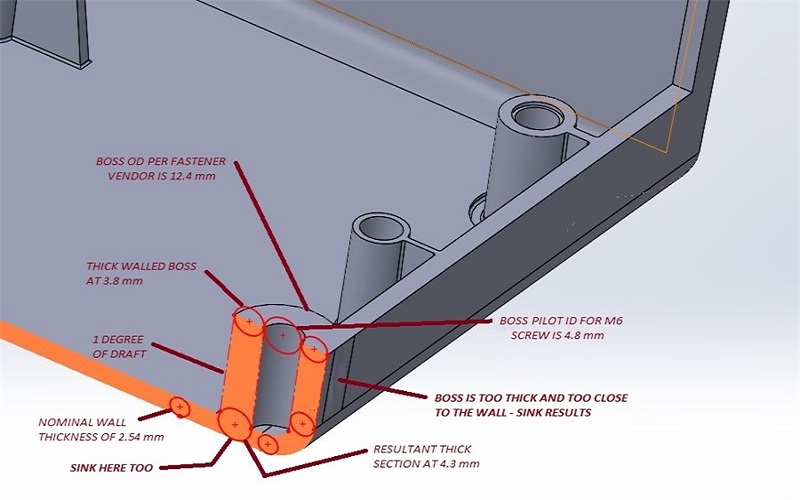
Designing effective screw bosses requires adherence to several key principles that ensure their functionality and durability. These principles encompass aspects such as wall thickness, size and shape, and draft angles, each playing a critical role in the performance of the screw boss.
A well-engineered screw boss enhances the strength of molded parts, providing proper alignment during assembly and accommodating self-tapping screws with ease.
Reinforcing screw bosses with gussets or ribs significantly boosts their strength and resilience. This guide will delve into the specifics of these design principles, offering practical tips and guidelines to achieve optimal results.From avoiding placing screw bosses too close to external walls to connecting them with ribs for added support, these strategies are vital for creating robust and reliable screw bosses.
Correct Wall Thickness
A critical aspect of screw boss design is ensuring the correct wall thickness. Adequate wall thickness is essential to prevent sink marks and maintain surface quality, which are common issues in injection-molded parts.
The ideal wall thickness for a screw boss should be around 60 percent of the nominal wall thickness, striking a balance that mitigates the risk of sink marks while maintaining the structural integrity of the part.
Furthermore, avoiding excessively thick sections is crucial, as they can lead to defects like sink marks and voids, ultimately increasing cycle time and production costs. Maintaining sufficient wall thickness ensures that screw bosses remain robust and free from aesthetic and structural flaws. This attention to detail is a cornerstone of high-quality plastic part design.
Optimal Boss Size and Shape
The size and shape of screw bosses are pivotal factors that influence their effectiveness and durability. Calculating the appropriate screw boss size involves considering elements such as length, pitch, and thread diameter. The diameter of a screw boss should correspond to the wall thickness of the injection-molded part, ensuring adequate strength and stability. Additionally, the load type plays a significant role, with longer screws or larger diameters providing a higher carrying capacity.
Key geometric factors that enhance screw boss design include maintaining appropriate draft angles, wall thickness, and fillet radii. To avoid thread failure and ensure the overall strength of the part, the height-to-OD ratio for screw bosses should be less than three times the screw boss’s outer diameter. This balance helps in achieving uniform shrinkage and maintaining the structural integrity of the molded part.
Strategies to improve screw boss strength without thickening the walls include surrounding the boss with gussets. These design enhancements ensure that the screw boss can withstand the stresses it will encounter, providing a reliable and robust attachment point in the final product. By optimizing the size and shape, designers can create screw bosses that are both functional and durable.
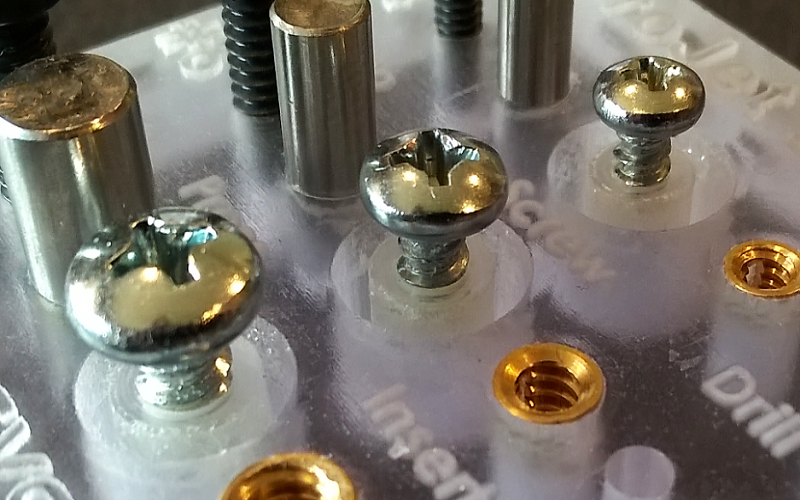

Ideal Draft Angles
Incorporating appropriate draft angles is essential in screw boss design to facilitate easier removal from the mold. A minimum draft angle of 0.5 degrees is recommended to ensure the smooth ejection of the boss, preventing damage during the molding process.
This small but critical detail can significantly enhance the manufacturability and quality of the injection-molded part, ensuring that the screw bosses maintain their intended shape and function.
Placement and Spacing of Screw Bosses
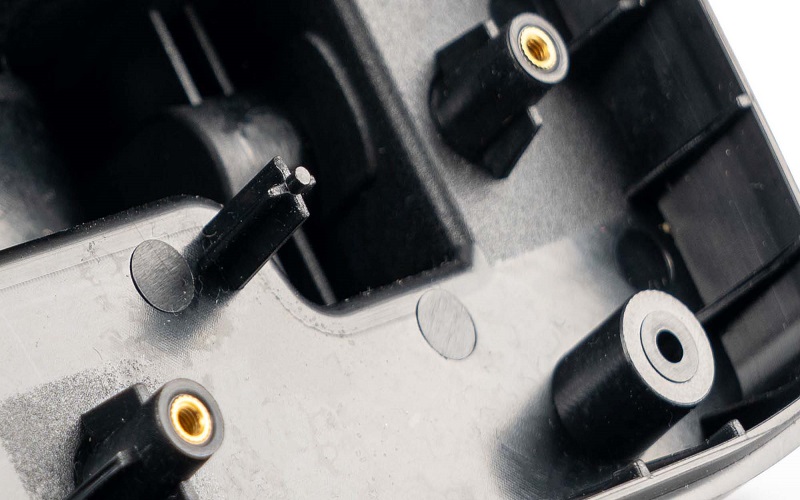

Proper placement and spacing of screw bosses are crucial for evenly distributing stress across plastic parts, which can significantly impact the overall performance and durability of the molded part. The size of the screw boss should match the wall thickness of the injection-molded parts, ensuring that they can withstand the forces they will encounter.
Strategic placement and adequate spacing of screw bosses minimize defects and enhance the stability of the molded part. This section will explore the best practices for achieving optimal placement and spacing, ensuring that the screw bosses contribute to the overall strength and functionality of the plastic part.
Strategic Placement
Strategic placement of screw bosses is essential to avoid deformation and enhance the stability of the fastening points. Placing screw bosses on thicker walls reduces the risk of deformation during the molding process and enhances the strength of the attachment point. It is advisable to avoid placing screw bosses close to external walls to minimize the risk of damage.
Connecting a screw boss to the nearest side wall with a rib provides additional support. Additionally, distributing screw bosses on different sides of the part ensures better stability, preventing concentration of stress in one area.
These guidelines help in creating robust and reliable screw bosses that maintain the structural integrity of the injection-molded parts, following screw boss design guidelines.
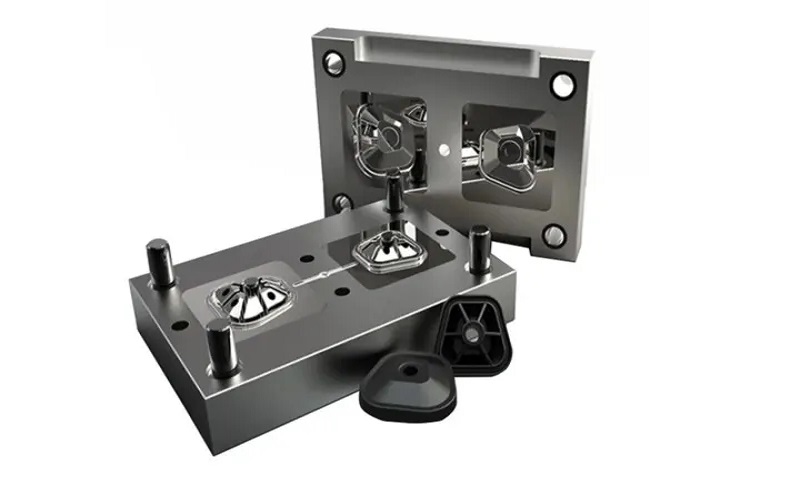

Adequate Spacing
Maintaining adequate spacing between screw bosses is crucial for the overall performance of the injection-molded part. Screw bosses should be spaced at least double the nominal wall thickness apart to prevent cooling issues and ensure dimensional accuracy. This spacing helps in avoiding defects like warpage and sink marks, which can compromise the quality of the molded part.
Adhering to these spacing guidelines prevents the creation of thin areas or prolonged cooling times, enhancing the overall integrity and performance of the plastic part. Proper spacing is a key factor in achieving high-quality screw boss designs that meet the demands of various applications.
Material Selection for Screw Bosses

Choosing the right material for screw bosses is critical for ensuring their mechanical properties, strength, stiffness, and chemical resistance. The material should have low and uniform shrinkage and be soft and less brittle to facilitate screw insertion. Using the same material for both the screw bosses and the main part enhances part integrity and stability.
This section will delve into the recommended materials for screw bosses and the importance of material compatibility. Selecting appropriate materials results in screw bosses that are durable, reliable, and well-suited for their intended applications.
Recommended Materials
ABS is a highly recommended material for screw boss applications due to its strength and durability. Blending ABS with polycarbonate can further enhance the design of screw bosses, providing a balance of strength and flexibility. Materials with low and uniform shrinkage are preferable for ensuring dimensional accuracy and overall integrity of the molded parts.
Using soft and less brittle plastics improves the ease of screw insertion, making them ideal for screw boss applications. Choosing materials with suitable mechanical properties yields high-quality screw bosses that perform effectively in various applications.
Material Compatibility
Ensuring material compatibility is vital for maintaining the structural integrity of the injection-molded part. Using the same material for both the screw boss and the main part prevents structural weaknesses and enhances stability. If the main part is made of a brittle plastic like polycarbonate, blending it with a softer material like ABS can improve the performance and durability of the screw bosses.
This seamless connection between the screw boss and the main part ensures that the entire assembly functions as intended, providing reliable attachment points and enhancing the overall quality of the plastic part. Material compatibility is a key consideration in achieving successful screw boss designs.
Addressing Common Challenges in Screw Boss Design
Designing screw bosses comes with its own set of challenges, such as preventing sink marks and reducing cooling time. These challenges can significantly impact the quality and performance of the injection-molded part if not addressed properly. Maintaining a wall thickness of 40 to 60 percent of the nominal wall thickness is recommended to minimize sink marks and ensure a smooth surface finish.
Proper material selection is also crucial for the effective performance of screw bosses. This section will explore common challenges in screw boss design and provide practical solutions to overcome them, ensuring that the final product meets the desired quality standards.
Preventing Sink Marks
Sink marks are a common issue in screw boss design, often occurring in areas with thick plastic sections where the outer wall meets internal features. To prevent sink marks, it is essential to avoid creating thick sections and instead maintain a wall thickness of 40 to 60 percent of the nominal wall thickness. Including fillets and ribs in the design can also help reduce the occurrence of sink marks.
Following these guidelines minimizes the risk of sink marks and ensures that screw bosses maintain their intended shape and function. Preventing sink marks is crucial for achieving high-quality, aesthetically pleasing plastic parts.
Reducing Cooling Time
Screw bosses can increase the cycle time due to the extra material and thickness, which prolongs cooling time. Differential cooling can lead to defects such as sink marks and warpage, particularly in areas with thicker wall sections. To reduce cooling time and prevent these defects, it is important to maintain a uniform wall thickness and choose materials with low and uniform shrinkage.
Optimizing the design and material selection minimizes cooling time and improves the overall efficiency of the injection molding process. Reducing cooling time is a key factor in achieving high-quality screw boss designs that meet the demands of various applications.
Enhancing Screw Boss Design with Advanced Techniques
Advanced techniques can significantly enhance the strength, durability, and performance of screw boss features. Reinforcing screw bosses with additional features such as gussets or ribs can improve their strength and resilience. Utilizing advanced design software facilitates the creation of precise models and allows for simulations to assess performance under varying conditions.
This section will explore the use of CAD software and 3D printing in screw boss design, highlighting how these advanced techniques can lead to superior design outcomes. Implementing these techniques helps designers overcome common challenges and achieve high-quality screw boss designs.
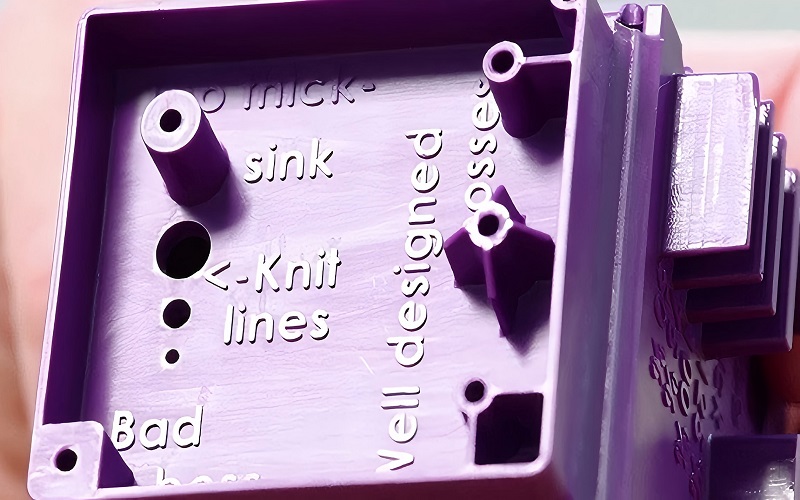
Utilizing CAD Software
CAD software plays a crucial role in enhancing screw boss design by allowing designers to create more accurate and reliable components. These tools streamline the design process, improving efficiency by enabling quick modifications and simulations before physical production.
Integrating CAD software with 3D printing technology enables rapid prototyping, facilitating faster testing and iterations for screw boss designs. The combination of CAD design and advanced prototyping methods results in better design outcomes, ultimately enhancing product quality.
Prototyping with 3D Printing
3D printing allows for rapid prototyping, enabling quick testing of screw boss designs for fit and functionality before mass production. This rapid prototyping phase is crucial in the product design process, allowing designers to test new concepts quickly and identify potential issues early on.
Integrating 3D printing in the prototyping phase enhances the efficiency of designing high-quality screw bosses. This approach saves time and resources, ensuring that the final product meets the desired quality standards.
Summary
In conclusion, designing effective screw bosses for high-quality plastic parts involves a comprehensive understanding of various design principles and techniques. From ensuring correct wall thickness and optimal boss size and shape to strategic placement and spacing, each aspect plays a crucial role in the overall performance and durability of the molded part. Material selection is equally important, with recommended materials like ABS and considerations for material compatibility enhancing the integrity and reliability of screw bosses.
Addressing common challenges such as preventing sink marks and reducing cooling time is essential for achieving high-quality designs. Advanced techniques like using CAD software and 3D printing for rapid prototyping further refine the design process, enabling designers to create precise, robust, and efficient screw bosses. By following the guidelines and strategies outlined in this guide, you can elevate your plastic part designs and ensure they meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the optimal wall thickness for screw bosses?
The optimal wall thickness for screw bosses should be about 60 percent of the nominal wall thickness to effectively prevent sink marks and ensure high surface quality.
Why is it important to avoid placing screw bosses close to external walls?
It is crucial to avoid placing screw bosses near external walls as this can compromise the integrity of the fastening point and heighten the risk of damage. Providing additional support by connecting bosses to the nearest side wall with ribs is advisable for enhanced strength.
What materials are recommended for screw boss applications?
For screw boss applications, ABS is highly recommended due to its strength and durability; blending it with polycarbonate can further enhance the design’s performance.
How can I prevent sink marks in screw boss design?
To effectively prevent sink marks in screw boss design, ensure that the wall thickness is maintained at 40 to 60 percent of the nominal thickness, and incorporate fillets and ribs into the design. This approach enhances structural integrity and minimizes deformation.
What are the benefits of using CAD software in screw boss design?
Utilizing CAD software in screw boss design significantly enhances precision and allows for quick modifications, leading to improved efficiency in the overall design process. Additionally, it facilitates rapid prototyping when paired with 3D printing technology.

