Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) combines rubber’s flexibility with plastic’s ease of processing. This makes TPV valuable in automotive, construction, and household applications. This article will explore its properties, manufacturing process, and key uses.
Understanding Thermoplastic Vulcanizate as a Thermoplastic Elastomer

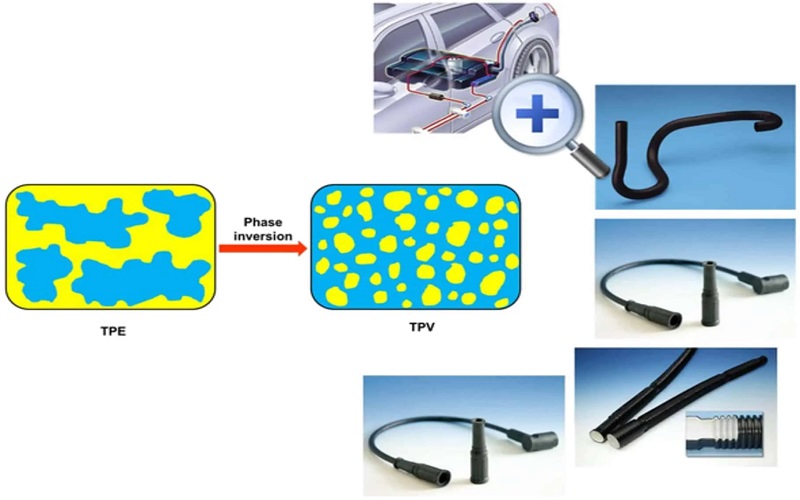
Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) is a remarkable material that merges the properties of rubber and plastic, offering a unique combination of flexibility, durability, and processability. TPV stands for thermoplastic vulcanizate, which is primarily composed of polypropylene and EPDM rubber. This vulcanized composition gives TPV its distinctive elastomeric properties, making it a versatile member of the thermoplastic elastomer family, thermoplastic elastomers, and tpe.
One of the standout features of TPV is its ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures, with a typical service temperature ranging from -40°C to 120°C. Other important characteristics include:
- Excellent aging performance
- Abrasion resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications
- Ability to stretch up to three times its original length, demonstrating significant tensile strength and elongation at break.
Moreover, TPV materials exhibit hardness values typically ranging from 30 to 90 Shore A, providing a range of flexibility and rigidity options for various applications. Whether used in automotive weather seals, pipe seals, or household appliance components, TPV’s combination of elastomeric properties and thermoplastic phase makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking high-performance materials.
The Manufacturing Process of TPV Materials
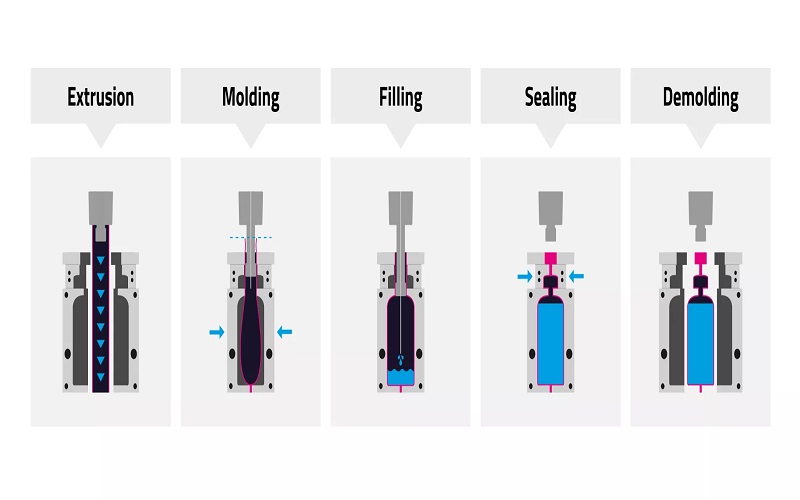
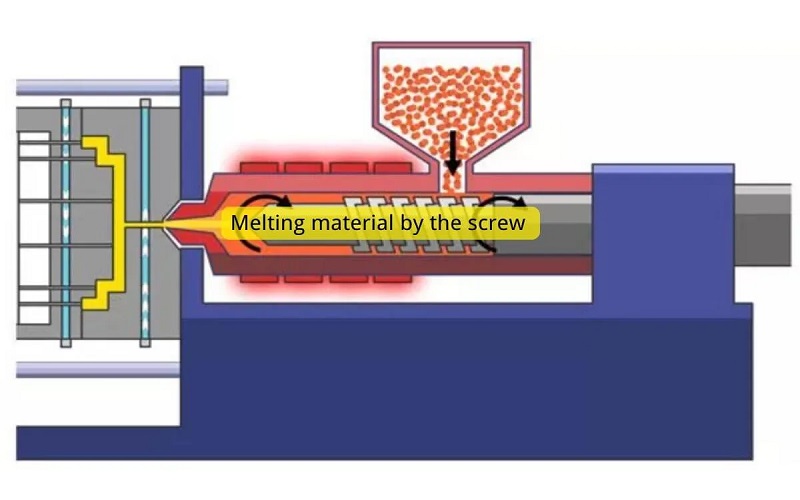
Creating TPV materials involves a sophisticated manufacturing process known as reactive extrusion, which combines polypropylene with EPDM rubber, a type of thermoplastic rubber, under specific shear and mixing conditions. This process ensures a highly dispersed rubber phase within the thermoplastic matrix, resulting in a material that boasts both flexibility and durability.
A critical step in the manufacturing process is vulcanization, which enhances the strength, flexibility, and durability of TPV materials through cross linking of the rubber phase. Unlike traditional vulcanization methods that require additional steps and time, TPV’s vulcanization and cross linking occur during the extrusion process, streamlining production and reducing cycle times. This efficient manufacturing process allows for the creation of TPV compounds with tailored properties, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
The engineering of TPV compounds involves blending olefins and EPDM, a versatile thermoplastic rubber, to achieve specific performance characteristics. This customization enables manufacturers to develop TPV materials with enhanced chemical resistance, UV stability, and other desired properties, meeting the unique requirements of various industries. The result is a versatile material that can be easily processed using standard thermoplastic techniques, offering both performance and cost benefits. Polymers play a crucial role in this process.
Processing Techniques for TPV
TPV materials can be processed using standard thermoplastic methods such as injection molding and extrusion, making them a versatile choice for various manufacturing applications, for example, in producing durable tubing for automotive and industrial uses. Injection molding, in particular, requires specific temperature settings, usually between 165-220℃, to ensure smooth melt flow and high-quality surface finishes. The rapid cooling of TPV materials during injection molding necessitates quick injection speeds to maintain the material’s integrity and appearance, especially for intricate components like tubing.
Pre-drying TPV materials before processing, typically at temperatures ranging from 80-110℃, is crucial due to their hygroscopic nature. This step helps in determining moisture-related defects and ensures consistent processing quality, for example, when manufacturing precision parts or tubing. Additionally, multi-component injection molding allows TPV materials to bond with various materials, creating complex and durable components.
Overall, the processing techniques for TPV materials are designed to maximize the material’s benefits while maintaining efficiency and quality. Whether through injection molding or extrusion, manufacturers can leverage TPV’s unique properties to produce high-performance parts, for example, tubing and other components for a wide range of applications, from automotive to household appliances.
Key Advantages of TPV Over Traditional Elastomers
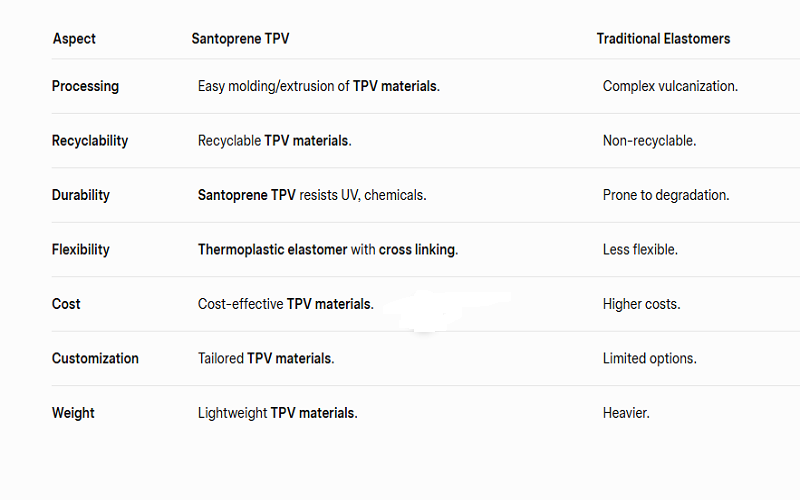
TPV offers several advantages over traditional elastomers, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers. One of the primary benefits is the streamlined processing, which eliminates the need for vulcanization, significantly shortening cycle times and reducing production costs. This efficiency is further enhanced by the absence of costly reworking steps, such as annealing or deburring, which are necessary in traditional elastomer processing.
TPV offers several advantages:
- Superior mechanical anchorage in multi-component injection molding, ensuring secure and durable bonds with other materials.
- Custom solutions that can provide significant cost savings compared to traditional thermoset rubbers while maintaining essential performance characteristics.
- Versatility that allows manufacturers to tailor TPV materials for specific applications, achieving enhanced chemical resistance, UV stability, and other desired properties, including santoprene tpv.
Furthermore, TPV’s resistance to oils, solvents, and various chemicals makes it ideal for demanding applications across different industries. Whether in automotive, construction, or household appliances, TPV’s combination of performance, cost-effectiveness, and customization options make it an exceptional choice for modern manufacturing needs.
Automotive Industry Applications of Santoprene TPV
In the automotive industry, TPV is valued for:
- Its lightweight nature, which contributes to overall vehicle efficiency and fuel savings.
- Durability under high temperatures and exposure to chemicals, making it suitable for under-hood applications where components must withstand harsh conditions.
- The ability to endure extreme temperatures and maintain performance in diverse climatic conditions, ensuring reliability and longevity in automotive parts.
Specific applications of TPV in the automotive sector include weather seals, gaskets, and various under-hood components, as well as other applications. The flexibility and resilience of TPV allow it to withstand repeated cycling, which is critical for parts that face constant movement and stress.
Automotive manufacturers use TPV’s unique properties to create high-performance auto components that enhance vehicle efficiency and durability, addressing the needs of modern transportation technology for the company.
Building and Construction Uses
TPV’s durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions make it an ideal material for building and construction applications. One of the primary uses of TPV in this industry is for seals and gaskets, which require consistent performance over time against varying weather conditions. Whether used in residential glazing seals or industrial gaskets, TPV ensures long-lasting reliability and protection.
The lightweight nature of TPV also contributes to ease of installation, making it a preferred choice for window and door sealing in construction projects. This material’s ability to maintain its properties under different weather conditions ensures that buildings remain well-sealed and energy-efficient.
Incorporating TPV into construction materials enhances the overall performance and longevity of projects, providing long-term value to customers.
Household Appliance Components
TPV is frequently used in household appliances for components like seals, gaskets, and knobs due to its durability and resistance to heat and chemicals. Appliances like washing machines, dryers, and dishwashers benefit from TPV’s excellent mechanical properties, which ensure longevity and reliable performance. The material’s strong tensile properties allow it to withstand repeated use without degrading, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
TPV’s superior aging performance and compression set method also contribute to the continuous longevity of appliance parts, maintaining integrity and functionality even with prolonged exposure to various environmental conditions over a period. If you wish to make a purchase, you can be assured of their quality.
Besides seals and gaskets, TPV is used for knobs and handles, offering a comfortable grip and resistance to wear. This combination of durability, heat resistance, and user-friendly characteristics makes TPV a valuable material for household appliance manufacturers.

Electrical Component Applications
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates (TPVs) play a crucial role in electrical applications, particularly in creating watertight seals and gaskets. These components are essential for preventing moisture ingress and ensuring the longevity of electrical devices. TPV’s flexibility and durability make it an excellent choice for these applications, providing reliable performance under various conditions.
In addition to electrical applications, TPV gaskets are commonly used in plumbing to prevent the passage of moisture, ensuring a secure and watertight seal. The material’s versatility and effectiveness in creating durable seals make it a valuable resource for both electrical and plumbing applications.
Environmental Benefits and Recyclability of TPV

One of the most significant advantages of TPV is its environmental benefits, particularly its recyclability:
- Unlike traditional rubber, TPVs can be reprocessed and recycled multiple times, including sprues and start-up material, significantly reducing waste.
- This re-meltable property allows for efficient shaping and rework.
- It minimizes production costs and waste during manufacturing.
TPV’s recyclability contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices, as production scrap can be reclaimed and recycled entirely. This capability not only prevents waste from ending up in landfills but also reduces the need for virgin materials, conserving natural resources.
Additionally, processing TPV requires less energy compared to the traditional vulcanization process used for rubber materials, further enhancing its environmental profile. Maintaining its properties over time and offering recyclability, TPV supports sustainable manufacturing, helping companies achieve their environmental goals.
This makes TPV an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainability in modern industries.
Custom Solutions with TPV Compounds
The ability to create custom solutions with TPV compounds is one of its most appealing features. TPV can be tailored using different formulation to meet specific performance requirements across diverse applications, offering significant advantages over traditional elastomers. For instance, the automotive industry leverages TPV for its lightweight and heat-resistant properties, enabling the creation of tailored components that enhance vehicle performance and form.
Household appliances benefit from customized TPV components that provide durability and excellent aging performance, ensuring long-term reliability. In electrical applications, tailored TPV compounds offer watertight seals and can withstand high temperatures, enhancing the longevity and safety of devices.
The construction industry also takes advantage of custom TPV solutions, using them for weather-resistant and durable building materials. Moreover, the recyclability of TPV compounds contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices, making them an environmentally favorable choice. Offering custom solutions that meet specific needs while promoting sustainability, TPV compounds provide a versatile and eco-friendly option for various industries.

Summary
In summary, Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) offers a unique combination of properties that make it an invaluable material for modern manufacturing.
From its versatile applications in the automotive, construction, and household appliance industries to its environmental benefits and customizability, TPV stands out as a high-performance, sustainable alternative to traditional materials.
As industries continue to evolve and prioritize efficiency, durability, and sustainability, TPV provides the solutions needed to meet these demands. Embracing TPV in manufacturing processes not only enhances product performance but also contributes to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TPV made of?
TPV is made primarily of polypropylene and EPDM rubber, which together offer a versatile thermoplastic elastomer. This combination enhances its durability and elasticity for various applications.
What are the environmental benefits of using TPV?
The use of TPV provides significant environmental benefits, as it is recyclable and can be reprocessed multiple times, thereby reducing waste and conserving natural resources. Additionally, its processing requires less energy than traditional rubber materials, further contributing to environmental sustainability.
How is TPV used in the automotive industry?
TPV is utilized in the automotive industry for components like weather seals, gaskets, and under-hood parts, offering benefits such as lightweight construction, heat resistance, and enhanced durability. This makes TPV a valuable material in the manufacturing of efficient and reliable automotive parts.
Can TPV be customized for specific applications?
Yes, TPV can be customized through various formulations to fulfill specific performance needs, making it versatile for multiple applications across different industries.
What makes TPV a better choice compared to traditional elastomers?
TPV is a superior choice over traditional elastomers due to its streamlined processing, cost-effectiveness, enhanced mechanical properties, and environmental advantages. These qualities make TPV a more efficient and sustainable option.

