Choosing the right materials is very important to make the right products in our industry and everyday life. Today we will compare two common types of plastic: thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
TPE is known for its resistance and environmental protection, while PVC is widely used in construction and industry due to its strength and low cost. For many manufacturers and investors, there are many factors to consider when choosing between these two materials, including performance, cost, and environmental protection.
This article provides a detailed introduction to the characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of TPE and PVC and their uses. Our goal is to help you understand the differences between these two materials so you can make better choices.
Next, let’s compare various aspects of these two materials. I hope you find this information helpful.
Definition of TPE
What is TPE?
TPE, also called thermoplastic elastomer, is a special plastic that combines the properties of thermoplastic and elastomeric materials. It is widely used in many fields such as automobiles, electronic equipment, household appliances and medical treatment.
TPE is soft and elastic and can return to its original shape after deformation. These properties make it particularly suitable for use in electronic accessories, toys, medical equipment and other places where flexibility and durability are required. It is also resistant to chemicals, flame and weather, providing superior performance in harsh environments. In addition, TPE is easy to process and recycle, which saves costs and reduces plastic waste.
In general, TPE is a very flexible and durable material, which makes it suitable for a number of applications where flexibility and durability are required.
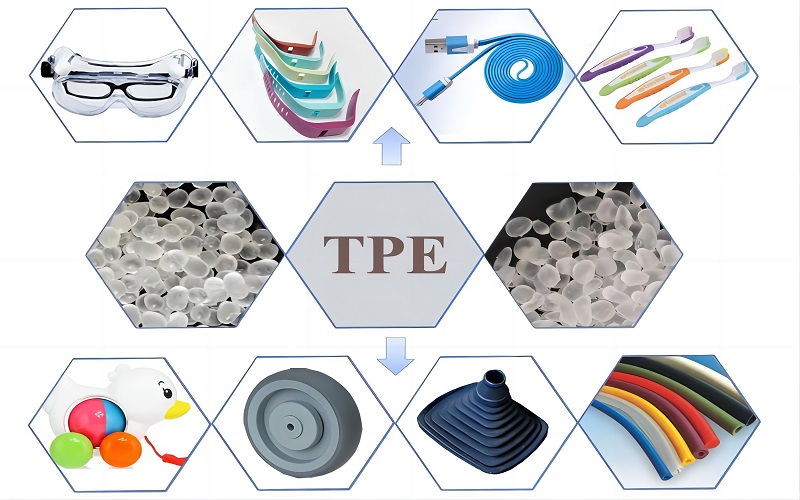

What Are the Types of TPE?
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) is a material that combines the ease of processing plastic with the elasticity of rubber, and is widely used in a variety of industrial and consumer products. TPE can be divided into several main types depending on its chemical structure and properties.
For example, TPO is often used in cars and building materials because it is resistant to wind, rain and UV rays. TPS has the softness of rubber and the workability of plastic, making it suitable for sports equipment, stickers, etc. TPV is resistant to high temperatures and chemicals, so it is widely used in auto parts and industrial equipment. There are other types such as TPE-S, TPE-E and TPE-U, each of which has unique properties and is widely used in medical equipment, household appliances, wear-resistant parts, etc.
These different types of TPE can meet the needs of different industries and products.
Definition of PVC
What is PVC?
PVC, also known as polyvinyl chloride, is a commonly used plastic. It is flexible, waterproof, fireproof and chemical resistant and is used in many places, including construction and industry.
PVC is primarily made from vinyl chloride, which is converted into a durable plastic through a chemical reaction. Different materials can be added to change the properties and make them suitable for different applications.
Because PVC is fireproof and weatherproof, it can be made into a variety of shapes, including water pipes, drain pipes and room dividers. However, during the production and processing of PVC, harmful substances can be formed, just as toxic gases are also released when it is burned. Care must therefore be taken to protect the environment and health when using PVC.
Overall, PVC is a very practical plastic. Environmental issues are numerous and remain important in many industries.

What Are the Types of PVC?
When discussing PVC (polyvinyl chloride), its uses and characteristics are distinguished according to its type. The first type is also called rigid PVC and is widely used in products that require high strength and durability, such as pipes, window frames, and doors. Rigid PVC has excellent chemical resistance and weather resistance, so it is widely used for outdoor and industrial purposes.
Next, soft PVC is made softer and more ductile by adding plasticizers, and is often used in wire and cable insulation, flooring, and inflatable products. Soft PVC has excellent wear resistance and waterproofing, so it is suitable for applications that require softness and visual effects.
Finally, expanded PVC. This is made by adding a foaming agent to create a pore structure, making it easy to manufacture. This type of PVC is commonly found in advertising signs, signs, and decorative materials. It has excellent insulation and soundproofing properties, making it suitable for lightweight structures and decorative needs.
Each of these PVC materials has its own unique uses and advantages, so it is widely used in various fields. It is not only affordable and durable, but also easy to process, so it is a common choice in many industries.


Detailed Comparison of TPE and PVC Properties
TPE and PVC are two different materials, each with its own characteristics. The following table provides a detailed comparison of several important properties of TPE and PVC.
| Property | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers) | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) |
| Elongation at Break | Over 500% | 20-40% |
| Recyclability | 80-100% | 30-40% |
| Service Temperature | -30°C to 120°C | -10°C to 60°C |
| Tensile Strength | 10-30 MPa | 10-60 MPa |
| Processing Temperature | 160-220°C | 160-210°C |
| Hardness | Shore A 20 to Shore D 85 | Shore A 20 to Shore D 90 |
| Elongation at Break (Repeated) | Over 500% | 20-40% |
What Are the advantages of TPE?
- Flexible: Easy to mold into various complex shapes.
- Soft and Comfortable: Feels like rubber, making it ideal for products that need a comfortable touch.
- Food Safe: Meets FDA standards, suitable for contact with food.
- Medical Safe: Some types meet medical device standards.
- Versatile: Can be used with fatty foods and hot liquids.
- Colorable: Can be made in a wide range of colors.
- Durable: Can withstand repeated bending and stretching.
- Impact Resistant: Can withstand strong impacts.
What Are the advantages of PVC?
- BPA-Free: Does not contain harmful BPA.
- Harder than Rubber: More rigid, suitable for applications that require hardness.
- High Strength: Strong and suitable for applications requiring high strength.
- Non-Conductive: Does not conduct electricity, making it ideal for cable insulation.
- Very Transparent: Allows you to see inside, ideal for packaging and pipes.
- Impact Resistant: Durable and resists deformation.
- Durable: Withstands weather and corrosion, perfect for outdoor use.
- Food Safe: Most PVC meets food safety standards and can be used with food.
TPE vs PVC: Applications
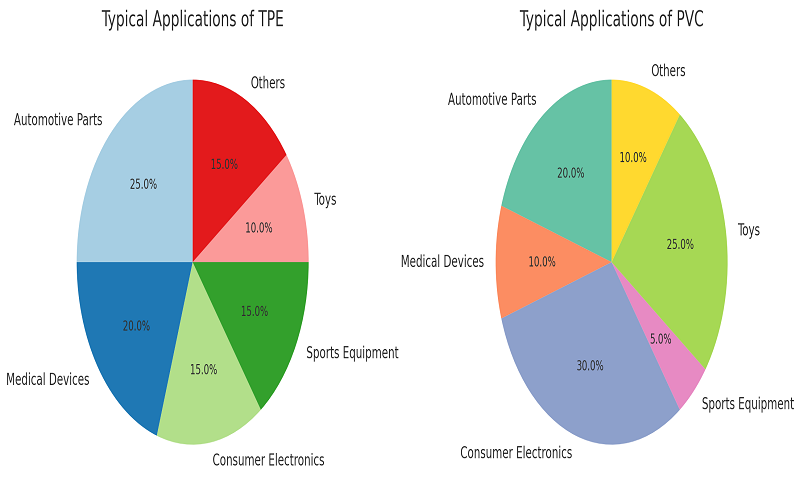
The following two pie charts show the proportion of TPE and PVC materials in different applications. It can be seen from the figures that TPE has a larger share in automotive parts and medical devices. PVC, due to its affordability, is more widely used in home appliances and toys.
TPE vs PVC: Which Offers Better Value?
The value of TPE and PVC largely depends on how they are used. When comparing their value, consider two main aspects:
TPE is often chosen for applications needing high durability and comfort because of its flexibility and reliability in different environments.
Additionally, TPE is generally non-toxic, recyclable, and meets modern environmental standards. This makes it valuable for projects prioritizing environmental protection, comfort, and softness.
Meanwhile, PVC is renowned for its durability, strength, and rigidity. It offers excellent abrasion resistance, impact resistance, flame retardancy, and weather resistance, making it suitable for tough industrial applications like construction, electrical insulation, and plumbing.
Furthermore, PVC maintains stable performance in high temperatures and has strong chemical resistance. Therefore, PVC is valuable in applications requiring material durability, strength, and industrial adaptability.
In summary, TPE and PVC each have distinct advantages. TPE is valuable for projects focused on environmental protection, softness, and recyclability. PVC excels in durability, strength, and adaptability to industrial needs. Before deciding, carefully assess your project’s specific requirements, budget, and environmental impact to choose the material that best fits your needs.

Summary
This article introduces TPE and PVC materials, explains their definitions and discusses the various applications of each. For more information on TPE and PVC, please feel free to contact us.

