TPE and TPU are two kinds of thermoplastics that work a bit like rubber. They’ve been around since the 1950s and are used in lots of different stuff. TPE is really flexible, making it a go-to for things like phone cases, covers, and shoe soles.
TPU is a tougher version of TPE. It’s built to handle more wear and tear, so you’ll find it in places where durability is crucial, like shoe soles, wheels, and car parts. Even though they’re similar, TPU is better for items that see a lot of use.
This article covers what sets TPE and TPU apart and what each is good for, helping you figure out which one’s right for your project.
What is TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)?
TPE, or thermoplastic elastomer, is a super useful material that brings together the best of plastic and rubber. When heated, it becomes soft and can be shaped like plastic, but it’s also stretchy and flexible like rubber. The best part? TPE doesn’t need any fancy processing—just standard techniques like injection molding or extrusion do the trick. This makes it quick and affordable to make. It’s like having the strengths of both rubber and plastic in one material.

You’ll see TPE in a bunch of products where you need both softness and durability—think car parts, medical equipment, seals, cable protectors, toys, and household items. It’s eco-friendly, recyclable, and you can tweak how hard or soft it is by adjusting its mix. Plus, it’s really easy to handle. TPE gives you the flexibility of rubber and the practicality of plastic, which is why it’s especially great for medical and food-related uses.

What is TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)?
TPU, or thermoplastic polyurethane, is a material that’s pretty handy because it’s as easy to shape as plastic but as flexible as rubber. It’s super tough, handling wear, oils, chemicals, and cold temperatures without breaking a sweat, and it’s hard to tear.
You can make TPU using different methods like injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and even 3D printing. This means TPU pops up in all sorts of products, from car parts and shoe soles to phone cases, cable covers, sports gear, medical tools, and some industrial films. It’s also clear and resists UV light, so it’s great for stuff that needs to be both durable and good-looking.
When you stack TPU up against TPE, TPU is the stronger, more durable choice. It’s perfect for situations where you need something extra tough and precise. Think of TPU as TPE’s more rugged cousin. It’s newer to 3D printing but already making waves. TPU works well as filament or powder in 3D printers and comes in various colors and hardness levels. You’ll find it in cool things like aerospace parts, car interiors, medical devices, and industrial belts.
In general, if you need a particularly wear-resistant, chemical-resistant and transparent material, TPU is a good choice, especially for outdoor and medical products.

TPE VS TPU: Attribute
| Attribute | TPE | TPU |
| Density | 0.89 – 1.30 g/cm³ | 1.05 – 1.25 g/cm³ |
| Elongation at Break | 300% – 600% | 300% – 700% |
| Melting Temperature | 160 – 230 °C | 170 – 220 °C |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 20 – 90 Shore A | 60 – 95 Shore A |
| Tensile Strength | 5 – 25 MPa | 25 – 70 MPa |
| Abrasion Resistance (mm³ ) | 200 – 400 mm³ | 30 – 80 mm³ |
| Tear Resistance (kN/m) | 10 – 50 kN/m | 80 – 200 kN/m |
| Compression Set (%) | 5% – 50% | 10% – 30% |
| Water Absorption (%) | 0.1% – 0.3% | 0.2% – 1.2% |
| Glass Transition Temperature | -50 to -60°C | -35 to -45 °C |
TPE vs TPU Material: Applications
The diagram below shows the differences between TPE and TPU in terms of application areas:
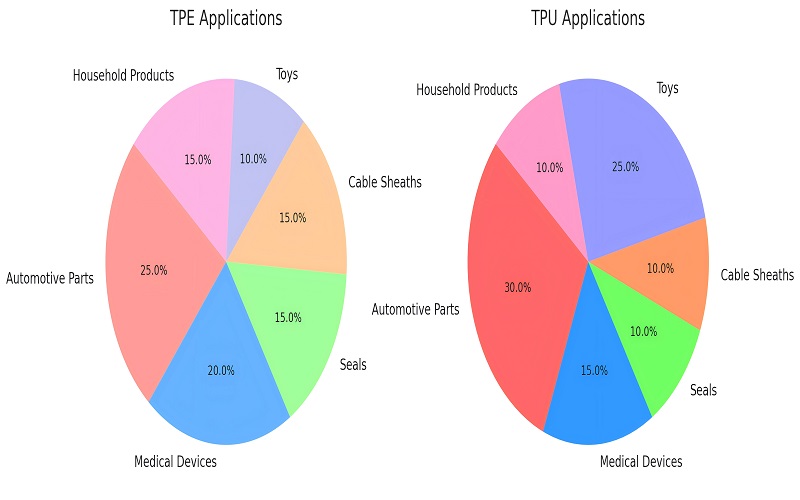
It can be seen that both materials, TPE and TPU, have the largest share in the automotive industry. This is because these two materials are easy to process, flexible, to meet the automotive industry on the strict requirements of high-performance materials.
TPE vs TPU: How to Choose?
Step 1: Understand the Application
First, determine what the material will be used for. TPU is ideal for items that need high wear and pressure resistance, like heavy-duty industrial parts, and has a longer service life. TPE is better suited for everyday consumer products, including medical devices such as syringes and IV systems.
Step 2: Cost-Benefit Analysis
Next, consider the cost. TPU and TPE are usually pricier than other plastics, so it’s important to choose wisely if you’re on a budget.
Step 3: Testing and Evaluation
After selecting a material, perform thorough testing. Check physical properties like hardness, strength, and durability, and assess chemical resistance to things like solvents and UV light. Ensure all tests meet standards like ISO and RoHS to confirm the material’s suitability.
Difference between TPE and TPU in 3D Printing
Before TPE and TPU became available for 3D printing, people frequently used flexible or soft PLAs to achieve rubber-like properties.. However, these alternatives are not as durable or elastic as TPE and TPU. For industrial uses, 3D printing with TPE or TPU delivers far superior results compared to PLA.
When to choose for 3D printing with TPU over TPE and vice versa?Since TPU is a type of TPE, it follows that TPE is more commonly used in 3D printing because it is more widely available..
The key difference lies in the hardness grades available for each material. Your choice between TPU and TPE should be based on the hardness requirements of your 3D printed part.
3D Printing With TPE
TPE materials are available in both filament form for FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers and powder form for SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) printers. Companies like EOS, CRP Technology, Roboze, and Sintirit offer TPE materials for 3D printing through the Beamler platform.
EOS introduced their TPE SLS material, PrimePart ST (PEBA 2301), back in 2013.
CRP Technology provides TPE SLS powder under the name Windform® RL.
Sintirit also offers TPE powder in their product lineup.
For those seeking TPE filament, Roboze offers a TPE filament called FLEX, designed for use with their Roboze FDM printers.
These options are highly recommended for engineers interested in 3D printing with TPE due to the excellent quality of the printed parts.

3D Printing With TPU
TPU is available as filament in FDM printers. As a thermoplastic, TPU can be melted, cooled and hardened, making it ideal for extrusion-based processes.
Stratasys offers TPU filament for FDM printers under the FDM TPU 92A brand, launched in November 2018.
Besides filament, TPU powder can also be used in SLS (selective laser sintering) printers.

TPE vs TPU:Injection Molding
TPE Injection Molding
Material Preparation:
- Drying: TPE material has poor water absorption, but it still needs to be dried during injection molding. The drying method is to place TPE in an environment of 60°C to 80°C for 2 to 3 hours.
Machine Settings:
- Temperature Settings: The extrusion temperature for TPE is generally between 180°C and 230°C,
- Mold Temperature: Mold temperature is typically set between 20°C and 50°C

Injection Process:
- Injection Pressure: TPE requires relatively lower injection pressure, sufficient to fill the mold and ensure a smooth surface finish.
- Dwelling Time: The holding time for TPE is shorter to avoid deformation from excessive material flow.
- Cooling: TPE cools more quickly, leading to shorter cooling times and increased production efficiency.
Demolding and Post-processing:
- Demolding: Due to its good elasticity, TPE usually demolds easily without significant issues, and demolding agents are often unnecessary.
- Post-processing: Subsequent processing such as trimming or welding can be performed as needed.
TPU Injection Molding
Material Preparation:
- Drying: TPU is very sensitive to moisture, so it must be dried at 80-100℃ before it starts molding, usually for 2-4 hours.
Machine Settings:
- Temperature setting: Ensure that TPU does not have problems such as material melting and bubbles during injection molding, its extrusion temperature needs to be controlled between 200°C and 250°C.
- Mold Temperature: To ensure the best quality for TPU products, the mold temperature should be set between 30°C and 60°C.
Injection Process:
- Injection Pressure: TPU typically requires medium to high injection pressure to properly fill intricate mold geometries.
- Dwelling Time: Adequate holding time is necessary to prevent sink marks while ensuring a smooth surface finish.
- Cooling: TPU has a prolonged cooling time, so careful control of the cooling process is essential to prevent deformation.
Demolding and Post-processing:
- Demolding: TPU’s high elasticity usually makes demolding smooth, though care must be taken to avoid deformation.
- Post-processing: If required, secondary operations such as cutting or grinding can be performed to refine the final product.

The injection molding of TPU demands careful attention to drying, high-temperature settings, and longer cooling times, making it ideal for complex and durable products.
Conversely, TPE molding is relatively straightforward with lower temperature and pressure requirements, making it suitable for high-efficiency production and applications requiring flexibility. While both processes share similarities, specific molding parameters must be tailored to the material properties and product requirements.
What Are the Mutual Alternatives to TPE and TPU?
Thermoplastic Copolyester (TPC) is another type of thermoplastic elastomer that you might consider if you’re looking at options besides TPE and TPU. It’s more of an engineering-grade material, so it can be harder for hobbyists to get their hands on. TPC is often used for things like bellows and medical stents.
Key characteristics of TPC include:
- Good elasticity
- High tensile strength
- Excellent resistance to high temperatures
- Reliable thermal stability
- Strong chemical resistance
- Outstanding UV resistance
However, TPC is not recommended for applications requiring extreme flexibility.

Summary
TPE and TPU are two popular plastics used in industries like automotive and medical manufacturing. To keep it simple, TPE is soft and flexible, almost like rubber, which makes it great for items that need a comfy feel. TPU, on the other hand, is tough and durable, kind of like steel, making it perfect for high-performance applications. Think of TPE as your cozy sofa at home and TPU as the sturdy sole of your running shoes. Knowing these differences can help you choose the best material for your needs.

