Polypropylene, a versatile and widely used thermoplastic polymer, is celebrated for its remarkable balance of strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it a cornerstone in industries ranging from packaging to automotive manufacturing.
Understanding the various types of polypropylene is crucial for selecting the right material for specific applications.
This article delves into the distinct characteristics, properties, and uses of these polypropylene variants, offering insights into their roles in modern industry and their potential for sustainable innovation.
What Is Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer produced through the polymerization process of propylene monomer units (C3H6)n, forming long polypropylene chains with a repeating carbon chain structure.
It is lightweight and exhibits excellent chemical resistance, heat resistance, and dimensional stability, making it an ideal raw material for diverse industrial and consumer applications.
Its molecular structure features a methyl group attached to every other carbon atom in the backbone, which contributes to its semi-crystalline nature and desirable properties such as high tensile strength, good electrical properties, and moisture resistance.
These characteristics make polypropylene suitable for manufacturing products like food containers, storage boxes, protective clothing, automotive components, electrical components, and surgical instruments.
Polypropylene’s versatility is further enhanced by its ability to be processed using various processing methods, including injection molding, blow molding, and cast film extrusion.
Its good resistance to chemical corrosion and mechanical stress, combined with relatively low cost and recyclability through chemical recycling or mechanical means, have made polypropylene a cornerstone material in industrial applications, packaging, medical devices, and the automotive industry.

What Are The Different Types Of Polypropylene?
Polypropylene can be classified according to a number of aspects such as its polymerisation method and molecular structure.
Classification By Aggregation Method
It is primarily divided into two types: homopolymers and copolymers.
Polypropylene Homopolymer
Polypropylene homopolymer is the most common type, made solely of propylene monomer units in a semi-crystalline solid form.
Polypropylene occurs naturally as this semi-crystalline structure, which provides excellent moisture resistant properties and allows it to maintain performance even at high temperatures.
It offers high chemical resistance, strength, and a high melting point, ideal for rigid packaging, automotive door panels, pipe applications, and heat-resistant medical devices like IV bags.
Its low cost and versatility make it a preferred choice in many industrial and consumer products.

Polypropylene Copolymer
Polypropylene copolymers are made by polymerizing propylene with comonomers like ethylene, enhancing impact resistance and flexibility compared to homopolymers.
There are two main types: random copolymers, known for clarity and used in food and flexible packaging, and block copolymers (impact copolymers) that include ethylene propylene rubber for superior toughness, ideal for automotive parts, medical devices, and sports equipment.
Produced in gas phase reactors, these copolymers offer good dimensional stability and heat resistance. Additives like flame retardants and glass fibers can further improve mechanical properties, broadening their industrial applications.
| Property | Polypropylene Homopolymer | Polypropylene Copolymer (Random/Block) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Uniform propylene monomer units | Propylene with ethylene or other comonomers |
| Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, less stiff than homopolymer |
| Flexibility | Lower flexibility | Higher flexibility |
| Impact Resistance | Lower impact resistance | Higher impact resistance |
| Clarity | Less transparent, opaque | Random copolymer: High clarity; Block: Less transparent |
| Heat Resistance | Higher melting point (~160-170°C) | Lower melting point (~130-150°C) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Excellent, slightly less than homopolymer in some cases |
Classified According To Molecular Structure
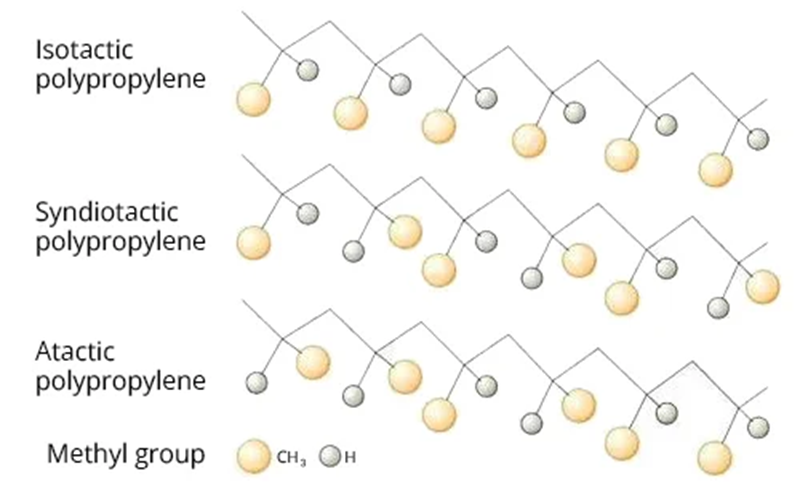
Polypropylene is categorized by its molecular structure, which includes three distinct stereoregular forms: isotactic, syndiotactic, and atactic.
Isotactic polypropylene
Isotactic polypropylene is the most common form of polypropylene, characterized by its regular molecular structure where all methyl groups are aligned on the same side of the polymer chain.
This arrangement results in a highly crystalline material with excellent mechanical properties, high melting point, and superior chemical resistance.
Due to these features, isotactic polypropylene is widely used in applications requiring rigidity, dimensional stability, and heat resistance, such as automotive parts, food containers, and medical devices.
Syndiotactic polypropylene
Syndiotactic polypropylene is a less common type of polypropylene characterized by an alternating arrangement of methyl groups along the polymer chain.
This unique molecular structure results in a material with lower crystallinity compared to isotactic polypropylene, offering enhanced flexibility and transparency.
Syndiotactic polypropylene is valued for its toughness and elasticity, making it suitable for specialized applications that require a balance between rigidity and flexibility.
Its distinctive properties expand the versatility of polypropylene in industries such as packaging, textiles, and automotive components, especially where improved clarity and impact resistance at varying temperatures are desired.
Atactic polypropylene
Atactic polypropylene is an amorphous form of polypropylene where the methyl groups are arranged randomly along the polymer chain.
Unlike isotactic and syndiotactic polypropylene, it lacks crystallinity, resulting in a soft, rubber-like material with low melting point and limited mechanical strength.
Due to these properties, atactic polypropylene is mainly used as a tackifier, adhesive component, or in modifying other polymers, rather than for structural applications.
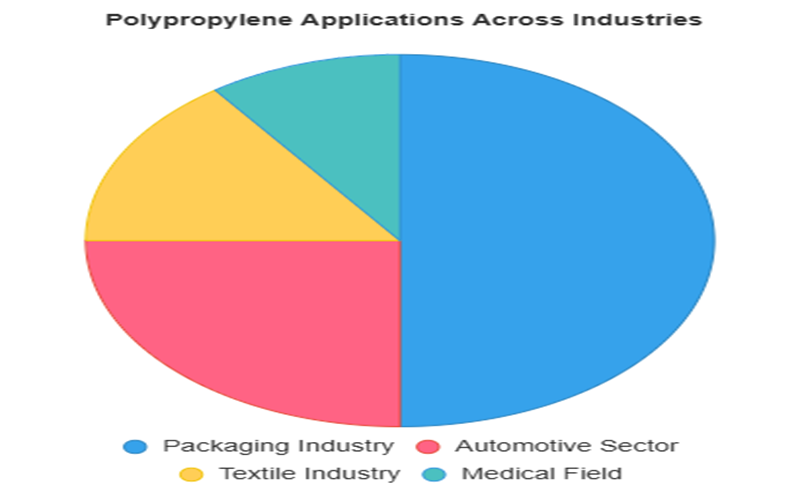
Polypropylene Applications Across Industries
Polypropylene’s versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness make it a vital material across multiple sectors. Its diverse types, including homopolymers and copolymers, cater to specific needs in various industries.
Packaging Industry
Polypropylene is widely used in packaging for its light weight, chemical resistance, and flexibility.
Homopolymers suit rigid packaging like storage boxes and bottles, offering strength and durability.
Random copolymers are preferred for flexible packaging such as films and pouches, providing clarity, moisture resistance, and protection.
These properties ensure product safety, longer shelf life, and support cost-effective, recyclable industrial packaging.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, polypropylene is prized for its high strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, and chemical resistance.
Homopolymers are used in rigid parts like interior panels, dashboards, and battery cases for their stiffness and stability.
Impact copolymers, containing ethylene propylene rubber, offer toughness for bumpers, fender liners, and door trims.
These materials enhance vehicle durability, reduce weight for better fuel efficiency, and resist corrosion. Their thermal stability and compatibility with injection and blow molding make them versatile for automotive applications and electrical components.

Medical Field
Polypropylene’s biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and sterilizability make it vital in medical applications.
Random copolymers, valued for clarity and flexibility, are used in syringes and IV bags. Homopolymers, known for rigidity and heat resistance, serve in sterile packaging and durable devices.
Impact copolymers provide toughness for flexible yet strong medical tools. These properties ensure safety and reliability across various healthcare uses while meeting strict regulatory standards.
Textile Industry
Polypropylene is essential in textiles due to its durability, moisture, and chemical resistance. Homopolymers are used in carpets, upholstery, and industrial fabrics for strength and stability.
Both homopolymers and random copolymers are utilized in ropes, geotextiles, and protective clothing, offering resistance to environmental damage, UV exposure (with additives), and microbes.
These features ensure long-lasting performance in outdoor textiles, agricultural covers, and filters, making polypropylene vital in consumer and industrial textiles.
The Impact Of Different Types Of Polypropylene On Processing Methods
Different types of polypropylene affect processing methods due to their unique molecular structures and properties.
Polypropylene homopolymer, known for its high melting point, rigidity, and low thermal expansion, is ideal for injection molding and blow molding, providing excellent dimensional stability and heat resistance.
Its Processing Methods typically involves gas phase or bulk polymerization, resulting in a semi-crystalline solid with consistent properties.
Random copolymer polypropylene, with improved flexibility and clarity thanks to ethylene comonomer units, is better suited for film extrusion and applications requiring transparency, such as flexible packaging and medical devices.
Impact copolymers, which incorporate ethylene propylene rubber phases, offer superior toughness and impact resistance, making them preferred in automotive parts manufacturing and other applications demanding durability.
By selecting the appropriate polypropylene type, manufacturers can optimize processing techniques, enhance mechanical properties, and improve product performance while maintaining good chemical resistance and corrosion resistance.
How To Choose The Right PP Type?
Selecting the appropriate type of polypropylene (PP) is crucial to ensure optimal performance and durability in your application.
Factors to consider include the required mechanical properties, chemical resistance, processing methods, and end-use environment.
For applications demanding high stiffness and heat resistance, polypropylene homopolymer is the ideal choice due to its semi-crystalline structure and high melting point.
If flexibility, clarity, and moisture resistance are priorities, especially in food packaging or medical devices, random copolymer polypropylene offers enhanced performance.
For products needing superior impact strength and toughness, such as automotive components and protective equipment, impact copolymer (block copolymer) polypropylene with ethylene propylene rubber phases is recommended.
Additionally, consider the processing techniques like injection molding or blow molding, as different PP types respond uniquely to these methods.
Understanding these distinctions helps in selecting the right polypropylene type, optimizing product quality, and minimizing plastic waste through efficient material use and recyclability.
Summary
To recap, polypropylene is a highly versatile material with various types, each uniquely suited for specific applications and industries.
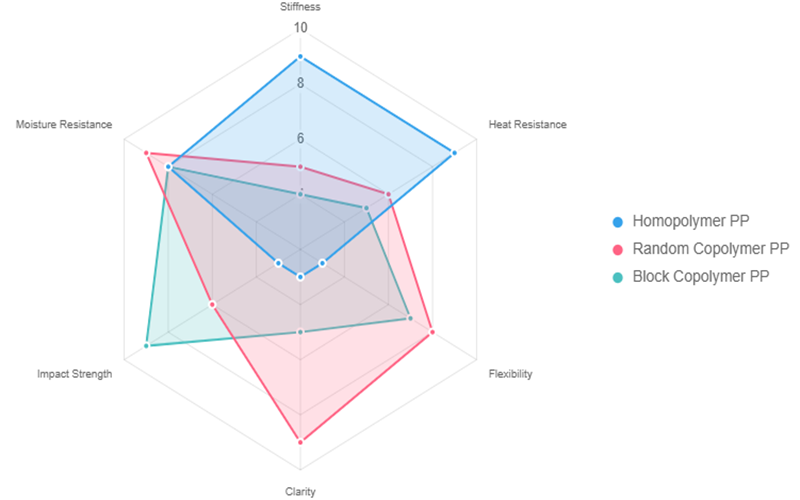
Polypropylene homopolymer offers high strength, rigidity, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for rigid packaging, automotive parts, and medical devices.
Random copolymer polypropylene provides enhanced flexibility, clarity, and moisture resistance, which are essential for food packaging, flexible packaging, and medical applications requiring transparency.
Block copolymer polypropylene, also known as impact copolymer, delivers exceptional toughness, superior impact resistance, and improved low-temperature performance, making it indispensable in automotive components, protective clothing, and sports equipment.
Additionally, advances in polypropylene production, including the development of syndiotactic polypropylene and atactic polypropylene variants, as well as the incorporation of fine powder additives, flame retardants, glass fibers, and other materials, further expand its range of desirable properties.
These diverse types and modifications enable polypropylene to meet the demanding requirements of the automotive and electrical segments, industrial packaging, and medical devices, all while maintaining its characteristic high chemical resistance, heat resistance, and dimensional stability.
By understanding the different types of polypropylene and their tailored applications, industries can make informed choices that reduce plastic waste and promote environmental responsibility.

