Medical injection molding is a critical manufacturing process that plays a pivotal role in producing high-precision, reliable, and safe medical devices and components.
This specialized form of injection molding involves the creation of intricate parts used in medical applications, such as syringes, IV connectors, surgical tools, and implantable devices.
This article explores the key aspects of medical injection molding, including its processes, materials, applications, and the importance of adhering to regulatory requirements to deliver safe and effective medical solutions.
What Is Medical Injection Molding?
Medical injection molding is a highly specialized manufacturing process used to produce precise, reliable, and biocompatible plastic components for medical devices.
This process involves injecting molten medical-grade plastics into custom-designed steel molds within a strictly controlled cleanroom environment, ensuring contamination-free production and adherence to rigorous regulatory standards.
Advanced methods such as insert molding and two shot molding enable the integration of multiple materials and components into a single part, enhancing device functionality and reducing assembly time.
The medical injection molding process supports scalable production, from rapid prototyping and low-volume runs to full scale production and assembly, making it a cornerstone of modern medical device manufacturing and medical molding in the healthcare industry.
Key Materials Used In Medical Injection Molding
Medical injection molding requires the use of specialized materials that meet stringent safety, durability, and biocompatibility standards to ensure patient safety and optimal device performance.
Careful material selection is critical in the medical device manufacturing process to achieve the necessary chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and sterilization compatibility.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Known for its exceptional impact resistance, transparency, and dimensional stability, polycarbonate is widely used for medical device components such as surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and housings.
Its strength and clarity make it ideal for parts requiring repeated sterilization and visual inspection in hospitals and clinical environments.
Polyethylene (PE)
This versatile plastic, available in HDPE and LDPE forms, is commonly used for disposable medical products like syringes, tubing, and containers.
PE is highly valued for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it a preferred choice in medical molding applications.
Polypropylene (PP)
Frequently selected for its durability, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand repeated sterilization cycles, polypropylene is used to manufacture syringes, connectors, and other medical components that require robustness and reliability. Its lightweight nature also contributes to ease of use in medical devices.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
TPE combine flexibility, toughness, and biocompatibility, making them suitable for soft-touch grips, seals, flexible tubing, and other components that require rubber-like properties.
Their adaptability and safety profile make them essential materials in the healthcare industry.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS offers a strong balance of strength, rigidity, and ease of processing, making it suitable for non-implantable medical devices such as equipment housings and casings.
Its cost-effectiveness and ability to be sterilized effectively contribute to its widespread use in medical device injection molding.
All in all, by utilizing these medical-grade plastics and elastomers, medical professionals can rely on plastic injection molding to produce high-quality plastic parts that meet the rigorous demands of the healthcare industry.
Advantages Of Medical Injection Molding
Medical injection molding is a widely adopted manufacturing process for producing precise and reliable medical components. Its numerous advantages make it the preferred choice for creating high-quality medical devices used across the healthcare industry.
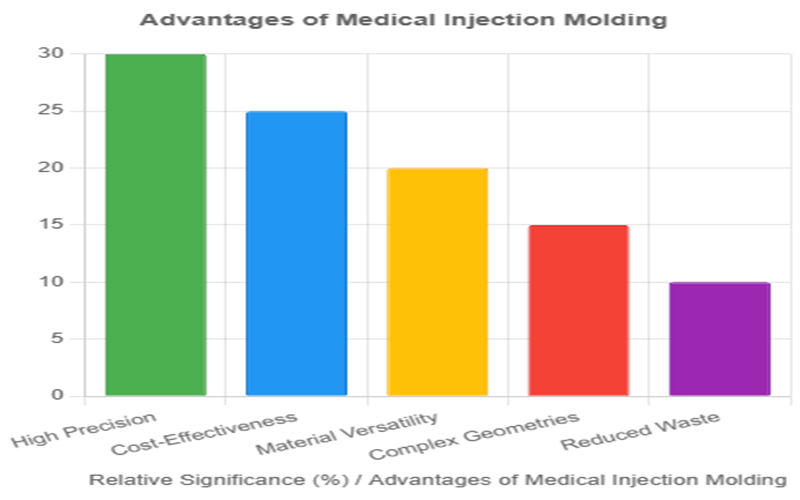
High Precision
Injection molding allows for the production of intricate, high-precision parts with tight tolerances, ensuring uniformity and consistency across high volume production runs.
This level of precision is critical for medical devices such as syringes, implants, and complex medical devices that demand flawless functionality.
Cost Effectiveness
Once molds are created, the process enables rapid and cost-effective production of large quantities of parts, significantly reducing per-unit costs.
This makes medical injection molding especially economical for mass-producing disposable items like catheters, vials, and other plastic parts essential in healthcare.
Reduced Material Waste
The process is highly efficient, with minimal material waste due to precise mold filling and the ability to recycle excess material.
This aligns well with sustainable manufacturing practices, reducing environmental impact while maintaining high-quality production standards.
Disadvantages Of Medical Injection Molding
While medical injection molding is a highly effective manufacturing process for producing precise medical components, it also has certain limitations that can affect its suitability for specific applications and project requirements.
High Initial Costs
The design, engineering, and production of precision molds demand significant upfront investment.
This high initial cost can be a barrier for low-volume production runs, startups, or smaller manufacturers entering the competitive medical device market.
Extended Lead Times
The creation and rigorous testing of molds to comply with stringent medical standards, such as ISO 10993 and FDA regulations, often require several weeks or even months.
These extended lead times can delay project timelines, particularly for custom or complex components with tight tolerances.
Complexity In Manufacturing Process
Medical injection molding involves complex processes requiring specialized knowledge, strict quality control, and cleanroom environments.
This complexity can increase the risk of defects if not managed properly, necessitating skilled operators and advanced equipment.

Medical Applications Of Injection Molded Components
Medical injection molding is widely used across various medical applications due to its precision, reliability, and efficiency.
Surgical Instruments
Production of complex, durable surgical tools that require high precision, strict sterilization compatibility, and exceptional reliability.
These molded components must meet rigorous medical industry standards to ensure optimal performance during critical medical procedures.
The medical injection molding process enables the manufacture of surgical instruments with tight tolerances and chemical resistance, essential for maintaining safety and functionality in demanding healthcare environments.
Diagnostic Equipment
Manufacturing of high-precision components for diagnostic devices such as blood analyzers, imaging equipment, and laboratory instruments, where accuracy, material quality, and reliability are critical to ensure accurate patient diagnosis and optimal device performance.
These components must meet stringent medical industry standards and withstand repeated sterilization processes to maintain safety and functionality in clinical environments.
Implantable Devices
The creation of biocompatible parts used in implantable medical devices is a highly specialized aspect of medical injection molding.
These components must ensure safety, long-term durability, and compatibility within the human body, meeting stringent regulatory and quality standards.
Medical device injection molding enables the production of complex, precise parts that withstand the physiological environment, supporting critical applications such as orthopedic implants, cardiovascular devices, and dental prosthetics.
Disposable Medical Products
Medical injection molding enables the mass production of disposable medical products such as syringes, catheters, and IV connectors.
This process ensures cost-effective manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality, biocompatibility, and strict adherence to regulatory standards.
The ability to produce high volumes of reliable, sterile plastic parts is essential for meeting the demands of hospitals and healthcare providers worldwide, supporting patient safety and efficient medical care delivery.

Innovations In Medical Injection Molding
The field of medical injection molding has experienced significant advancements that are reshaping the manufacturing landscape.
Cutting-edge technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced robotics are increasingly integrated into the medical injection molding process to enhance precision, reduce cycle times, and boost overall efficiency.
The ongoing development of novel biocompatible and high-performance materials expands the range of applications, enabling the production of medical components with superior durability, chemical resistance, and patient safety.
Innovative techniques like gas-assisted injection molding and two shot molding improve part quality by minimizing defects, optimizing material distribution, and allowing for the combination of multiple materials in a single molded component.
These technological breakthroughs not only facilitate the manufacturing of increasingly complex medical devices but also support scalable high volume production while ensuring strict regulatory compliance and adherence to cleanroom environment standards.

Conclusion
In summary, medical injection molding is a critical process in the production of high-quality medical devices.
Its ability to produce complex parts with high precision, consistency, and biocompatibility makes it invaluable in the healthcare industry.
As technology continues to advance, so too will the capabilities of medical injection molding, driving further innovation in medical device manufacturing.
Manufacturers must stay updated on the latest technologies and regulations to maintain optimal performance and ensure the highest quality standards.
Embracing these advancements helps them deliver support for the project to develop life-saving medical devices for clients and contribute to the knowledge advancement of the medical industry healthcare expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Medical Device Injection Molding?
Medical device injection molding is a precise manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into molds to create complex, high-quality components used in medical devices.
What Materials Are Commonly Used In Medical Injection Molding?
Medical-grade plastics such as polyethylene (PE) and polystyrene (PS) are commonly used in injection molding due to their biocompatibility and durability. Additionally, silicone is favored for its versatility and biocompatibility in medical applications.
What Are The Advantages Of Medical Injection Molding?
Medical injection molding offers the benefits of high precision in complex designs, cost-effectiveness for large-scale production, and the ability to create strong, durable devices with excellent surface finishes. These advantages make it a preferred manufacturing method in the medical industry.
What Are The Challenges Associated With Medical Injection Molding?
Medical injection molding faces challenges such as high initial tooling and setup costs, which can be prohibitive, alongside limited suitability for low-volume production and stringent regulatory and quality control demands. These factors contribute to increased material waste and complexity in the manufacturing process.
How Has Medical Injection Molding Evolved With Recent Innovations?
Medical injection molding has evolved significantly with the integration of automation and AI, enhancing production efficiency and accuracy, alongside advanced materials that improve biocompatibility and durability. These innovations are crucial for meeting the growing demands in the healthcare sector.

